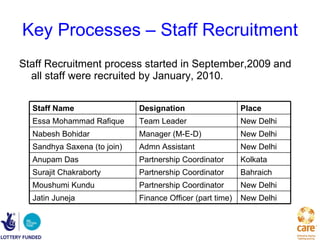
The document summarizes the EMPHASIS (Enhancing Mobile Populations’ Access to HIV & AIDS Services, Information, and Support) program, which aims to reduce vulnerability to HIV/AIDS among mobile populations crossing borders between Bangladesh, India, and Nepal. It discusses the high mobility between the countries, related vulnerabilities like unsafe sex and lack of access to healthcare, prevalence of HIV, and gaps in government responses. It outlines the program's goals, approach working with NGOs in source, transit and destination areas, activities undertaken so far like mapping and stakeholder meetings, and plans to demonstrate effective models and influence policies to support mobile populations.










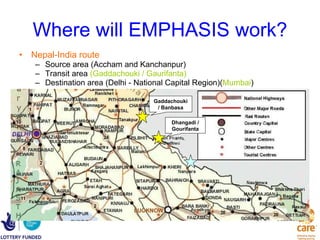
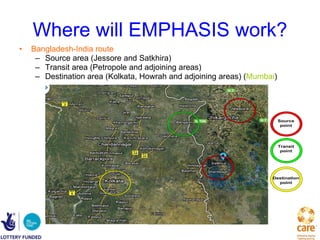











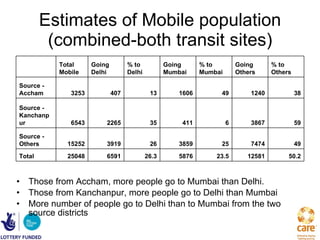
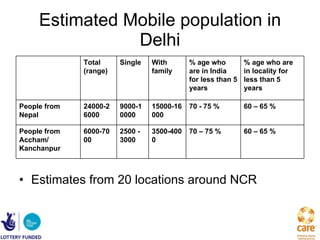
![Projection Analysis at Transit Points - Nepal Approximately, 100,000 Nepali Mobile population cross over into India in a year through the two transit points [1] Out of that, approximately 11000 come to Delhi as destination and 8500 come to Mumbai.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emphasis-pres-sep1-2010-12-111222034419-phpapp01/85/Emphasis-pres-sep-1-2010-12-26-320.jpg)