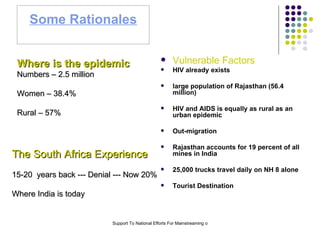
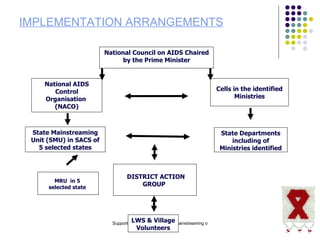
The document discusses mainstreaming HIV/AIDS interventions across various sectors in India. It notes that HIV/AIDS has spread widely in India, especially in rural areas, necessitating a multi-sectoral response. Mainstreaming involves addressing HIV/AIDS internally and externally across all sectors. Examples are given of mainstreaming HIV/AIDS awareness and services within government departments like rural development, tourism, panchayati raj, and urban development as well as private sectors. The roles and potential activities of these sectors for effective mainstreaming are outlined.