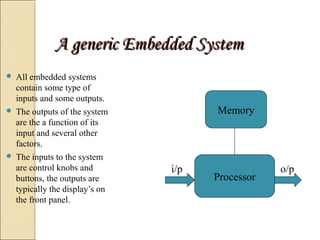
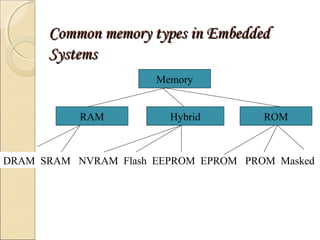
This document discusses embedded systems and their role in everyday devices. It provides details on embedded system design, hardware, memory types, programming languages and applications. Embedded systems combine computer hardware and software to perform specific tasks, and are found in watches, phones, vehicles and more. They differ from general computers in being dedicated to a single purpose. The document concludes that embedded systems are essential technologies that will continue growing significantly.