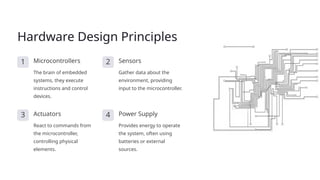
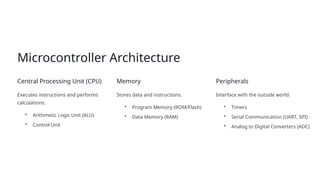
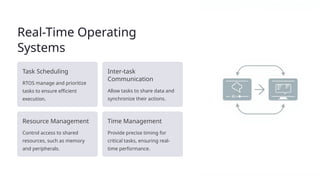
Embedded engineering integrates hardware and software to create intelligent devices, utilizing microcontrollers, sensors, actuators, and power supplies. The development process includes defining requirements, designing software, coding, and deployment, with real-time operating systems for task management and debugging techniques for testing. Trends in the field include the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence integration, cloud computing, and a focus on cybersecurity.