This document provides an overview of embedded systems including:
- Defining embedded systems as hardware and software components that form part of a larger system and are designed to run without human intervention.
- Examples of application areas for embedded systems like consumer electronics, medical devices, automobiles, and more.
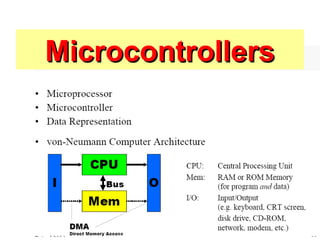
- Microcontrollers being commonly used for embedded systems as they integrate a CPU with timers, I/O, RAM and sometimes ROM on a single chip.
- Input and output for embedded systems requiring communication with external devices through sensors, actuators, and various I/O methods.







![• TV Application Areas
• stereo
• remote control
• phone / mobile phone
• refrigerator
• microwave
• washing machine
• electric tooth brush
• oven / rice or bread cooker
• watch
• alarm clock
• electronic musical instruments
• electronic toys (stuffed animals,handheld toys, pinballs, etc.)
• medical home equipment (e.g. blood
pressure, thermometer)
•…
• [PDAs?? More like standard computer system]
Consumer Products](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2007-0001week1-embeddedsystems-130305104503-phpapp01/85/2007-0001-week1-embeddedsystems-8-320.jpg)
![Application Areas
• Medical Systems
– pace maker, patient monitoring systems, injection systems,
intensive care units, …
• Office Equipment
– printer, copier, fax, …
• Tools
– multimeter, oscilloscope, line tester, GPS, …
• Banking
– ATMs, statement printers, …
• Transportation
– (Planes/Trains/[Automobiles] and Boats)
• radar, traffic lights, signalling systems, …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2007-0001week1-embeddedsystems-130305104503-phpapp01/85/2007-0001-week1-embeddedsystems-9-320.jpg)