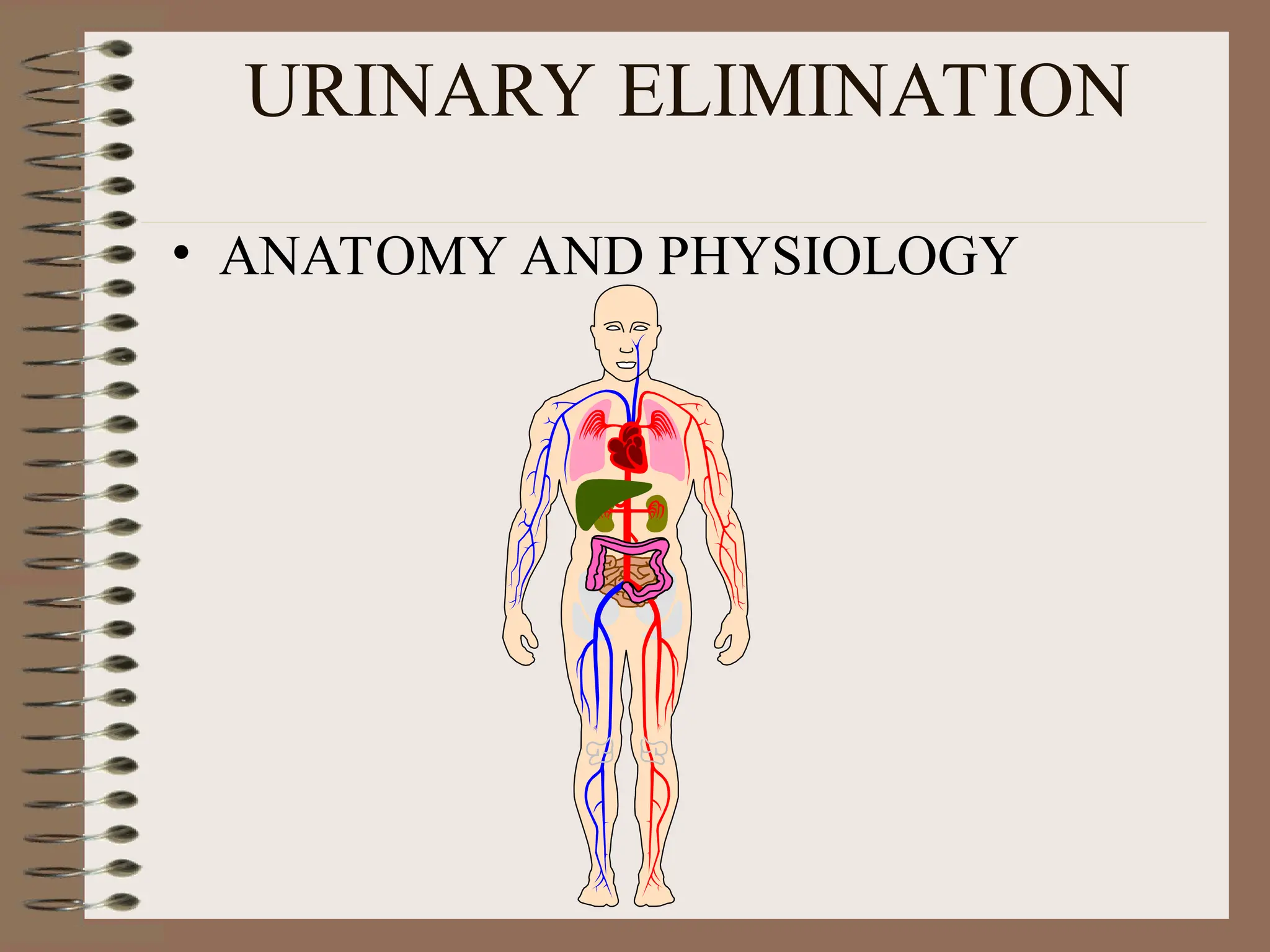
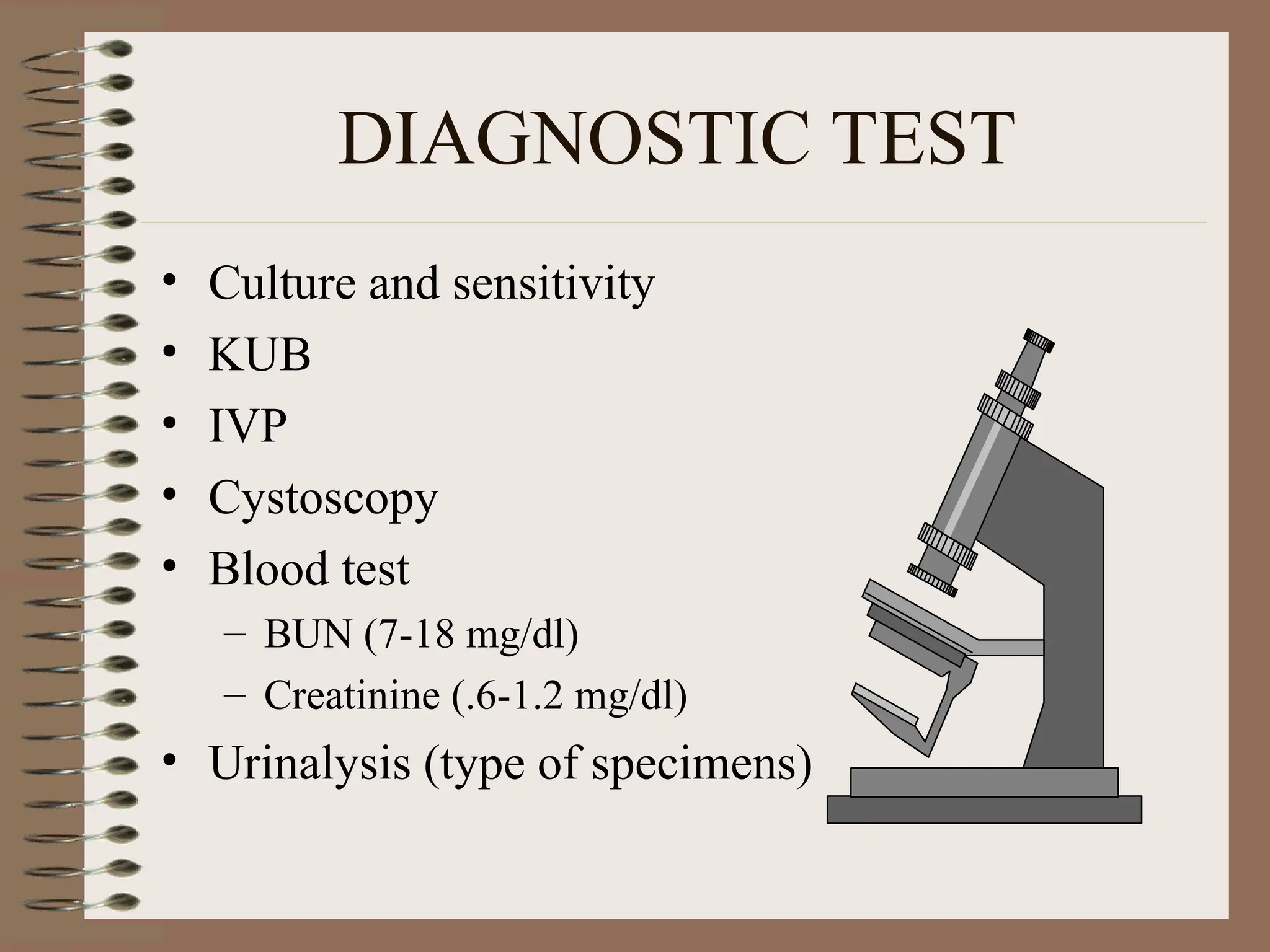
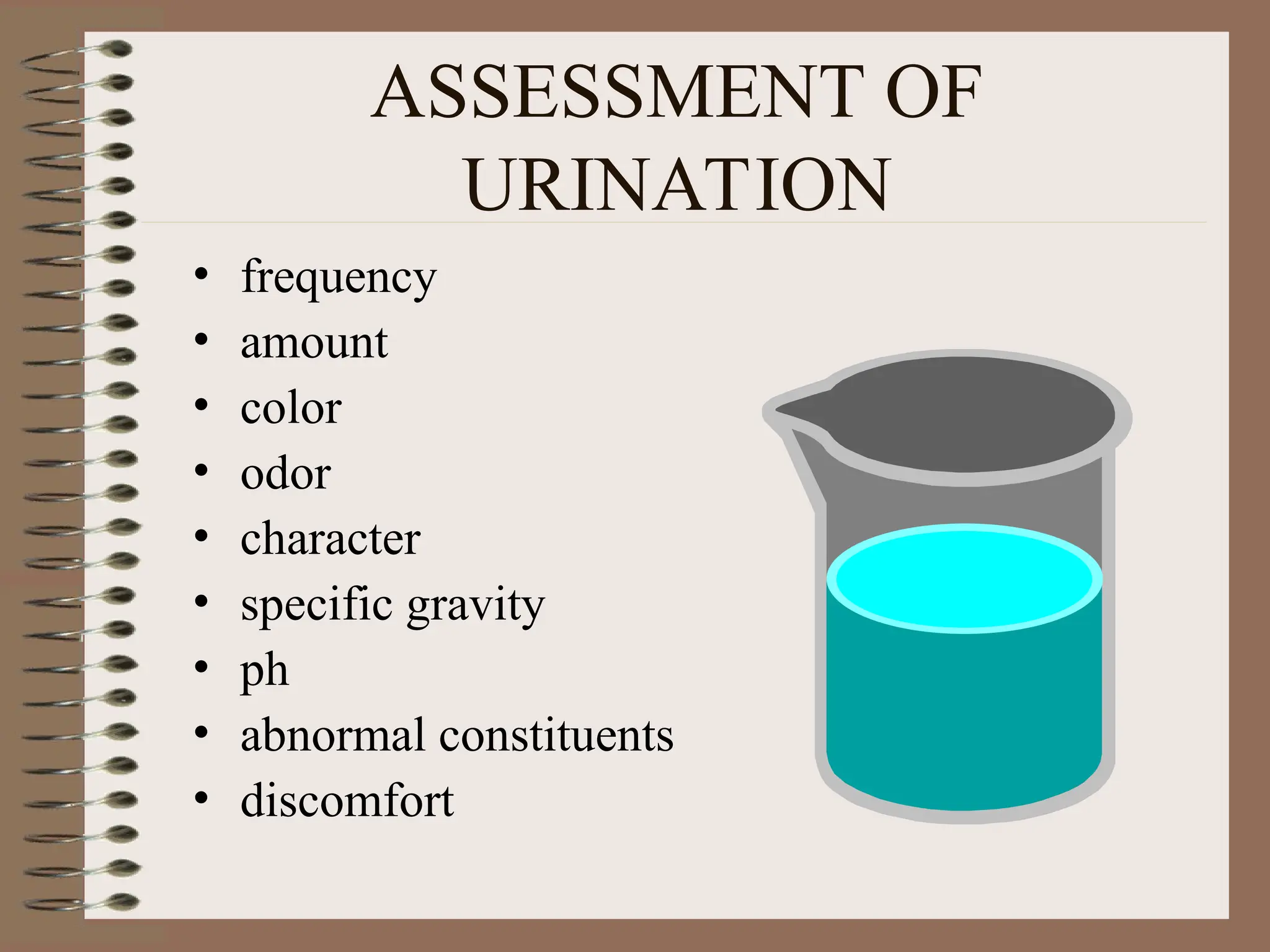
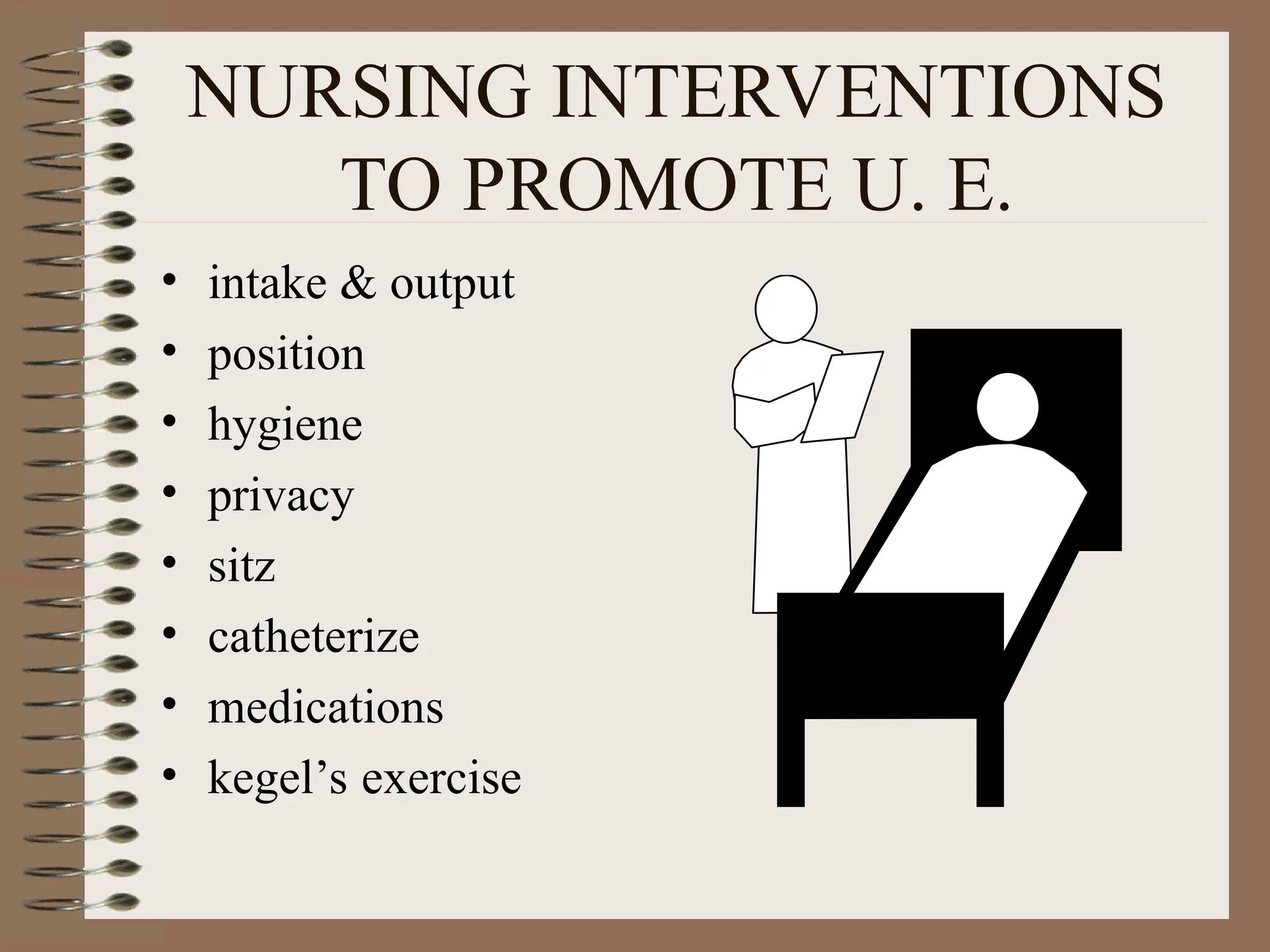
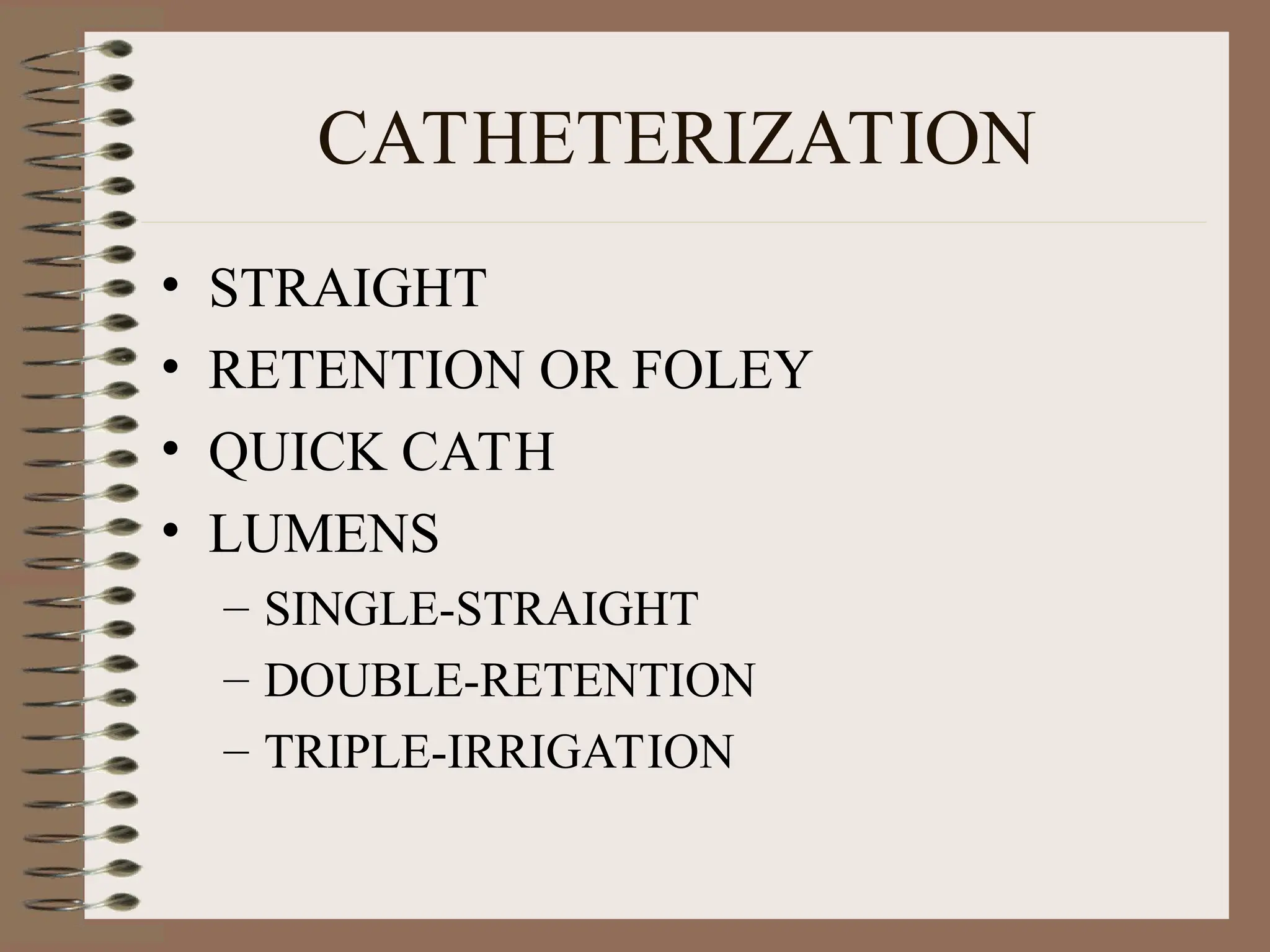
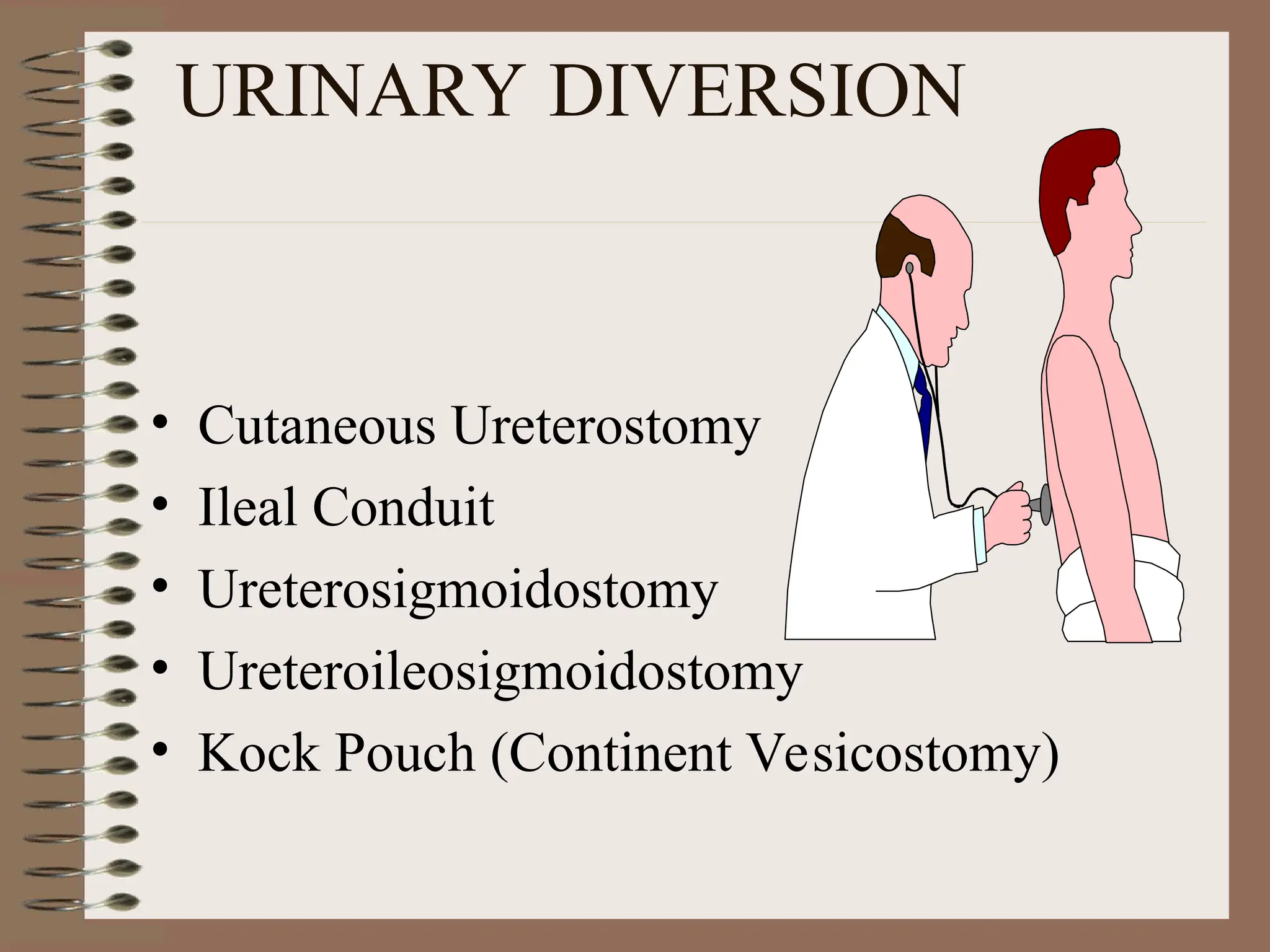
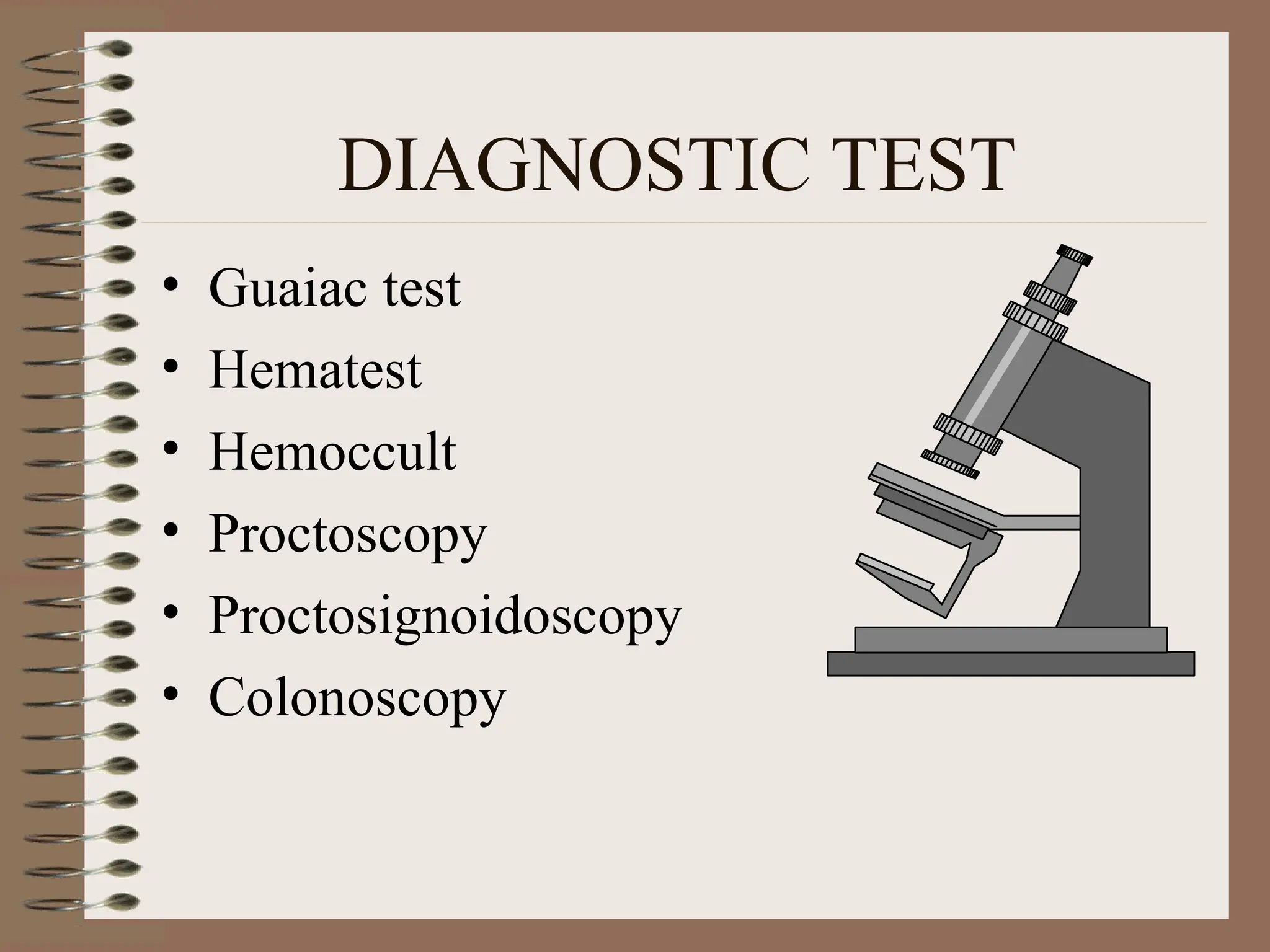
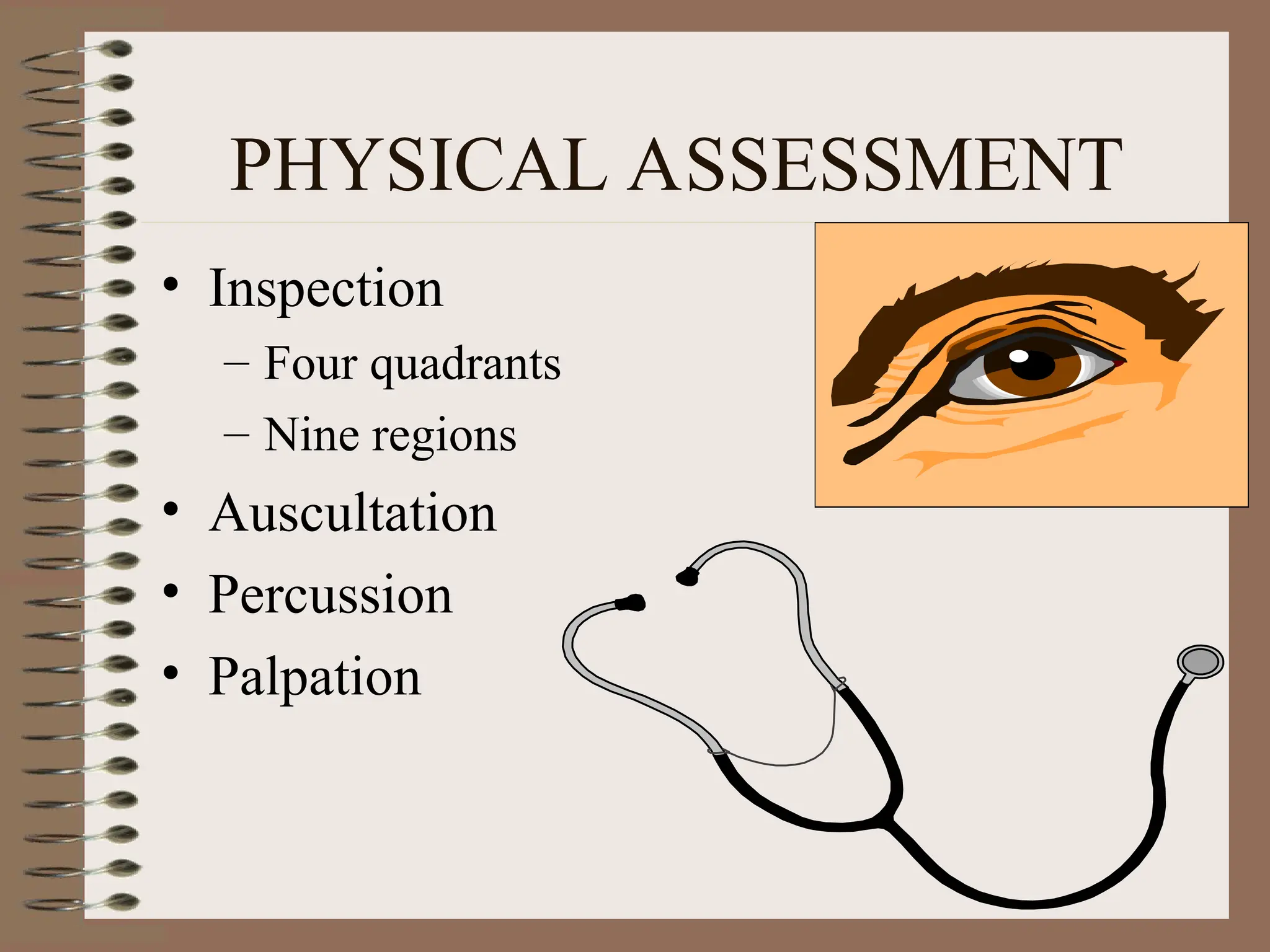
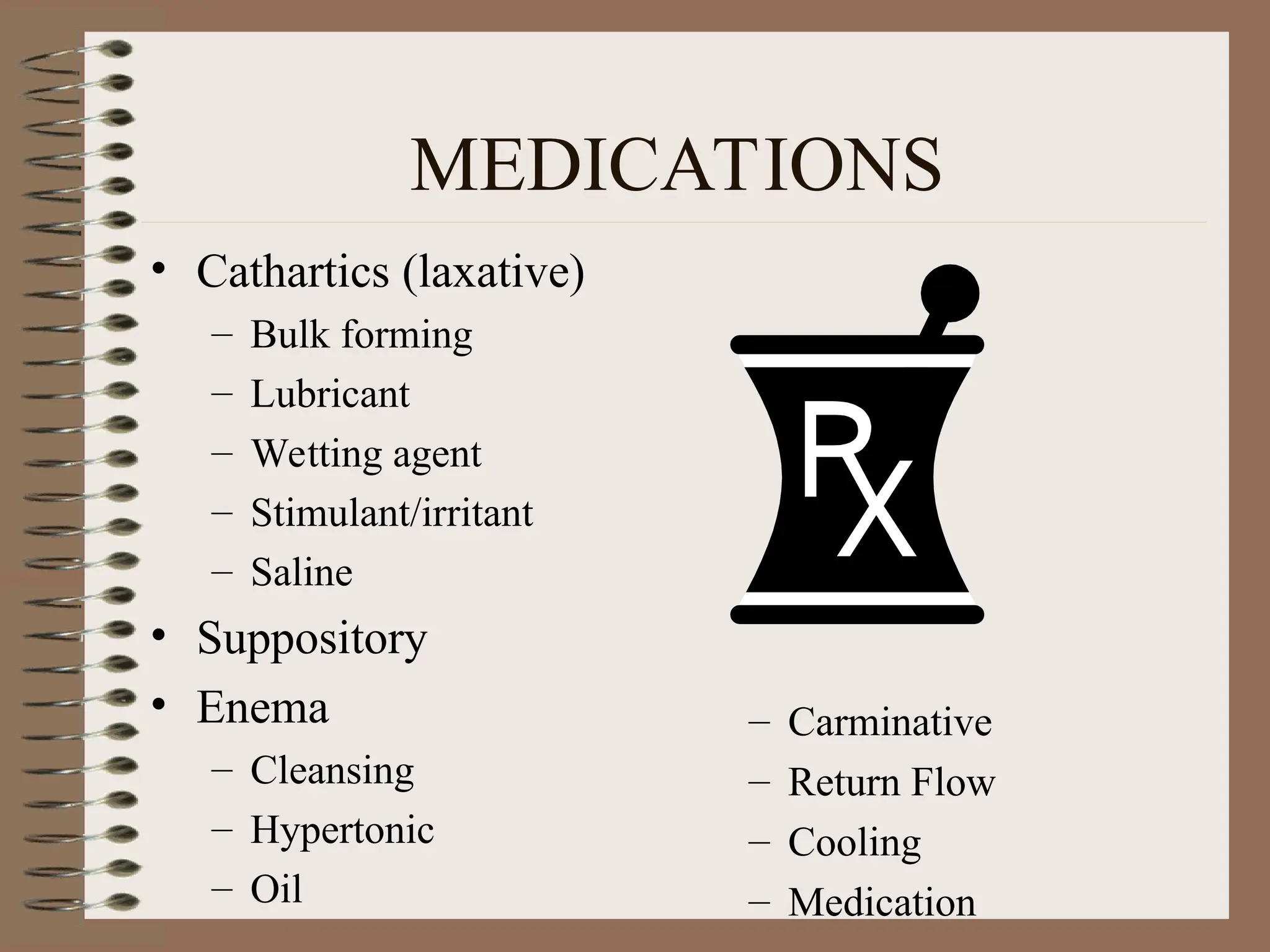
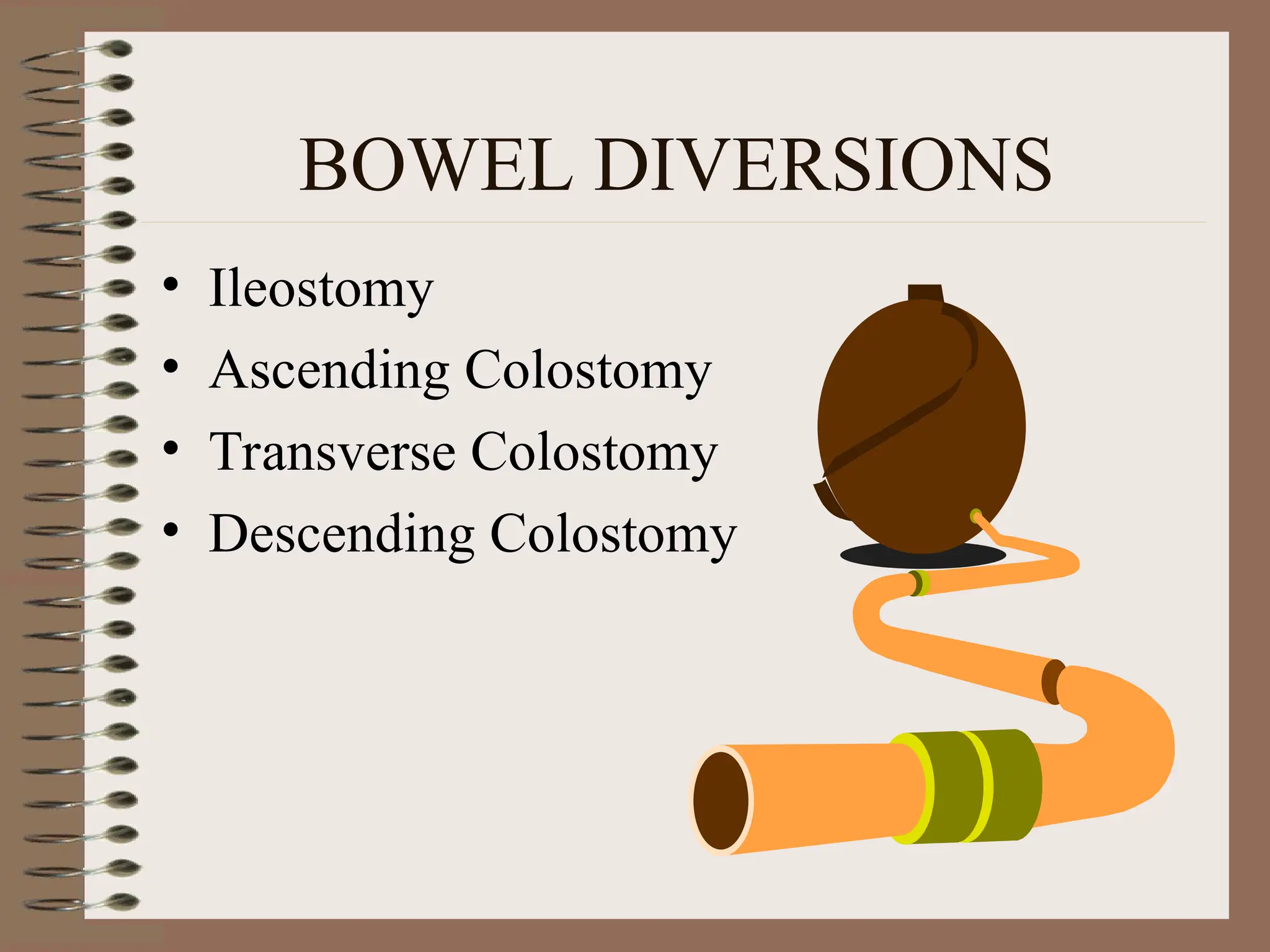
DetailBusiness reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion about business Business reserach are very essential to make presentation and final conclusion a