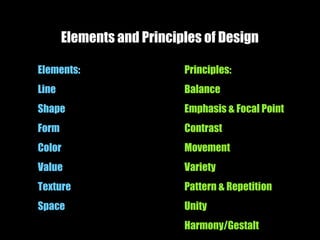
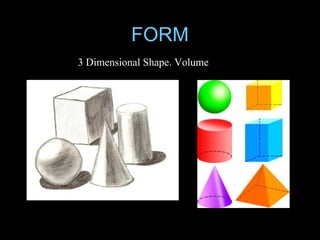
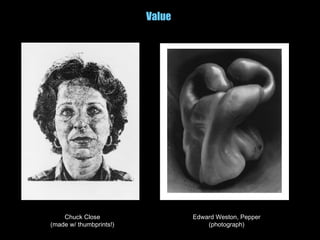
The document discusses the artistic process and the elements and principles of design. It explains that the artistic process involves imagining ideas, planning works, making and refining art, and presenting completed works. It then defines the key elements of line, shape, form, color, value, texture, and space. Finally, it explores principles of design like balance, emphasis, contrast, movement, variety, pattern and repetition, and unity that can be applied through the elements.