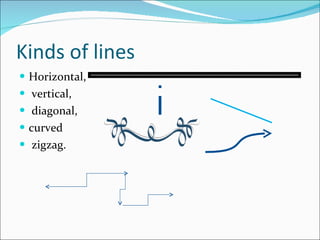
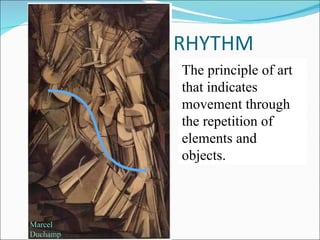
The document defines key terms related to visual art, including art, artist, fine art, applied art, and visual culture. It then explains the basic visual elements or "vocabulary" used by artists to create works, including line, color, value, shape, form, space, and texture. Each element is defined and examples are provided. The document also discusses principles of design such as balance, emphasis, contrast, movement, pattern, repetition, unity, harmony, variety, and scale/proportion.