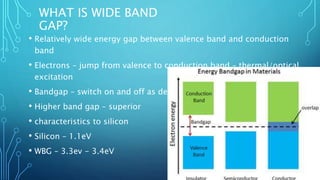
The document discusses wide band gap semiconductors like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN). These semiconductors have band gaps that are roughly 3-4 times wider than traditional silicon semiconductors. Wide band gap semiconductors can operate at much higher temperatures, voltages, and frequencies than silicon, making them well-suited for applications in power electronics, electric vehicles, energy storage, and military systems. They allow for more compact, efficient, and durable electronic components.