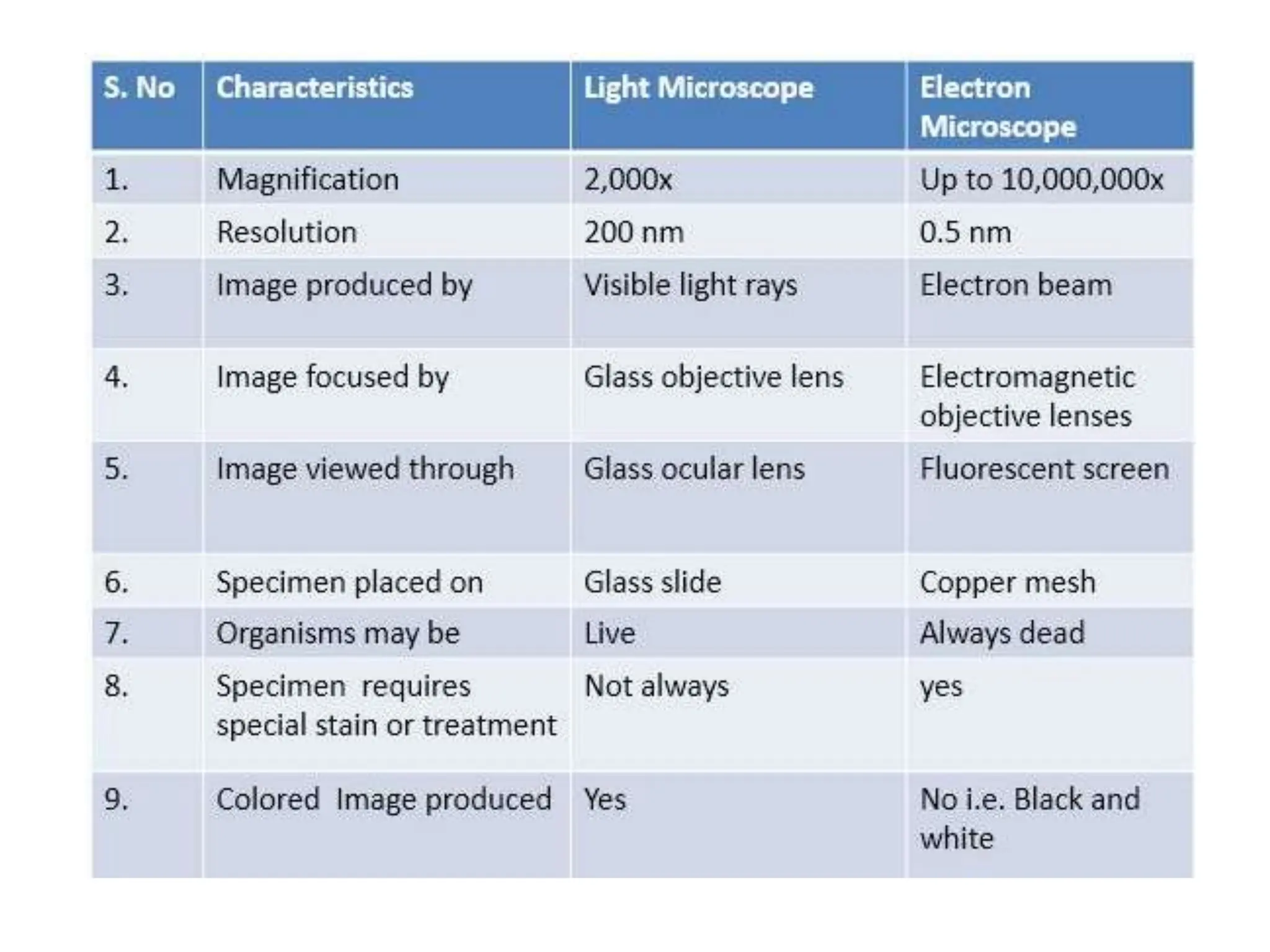
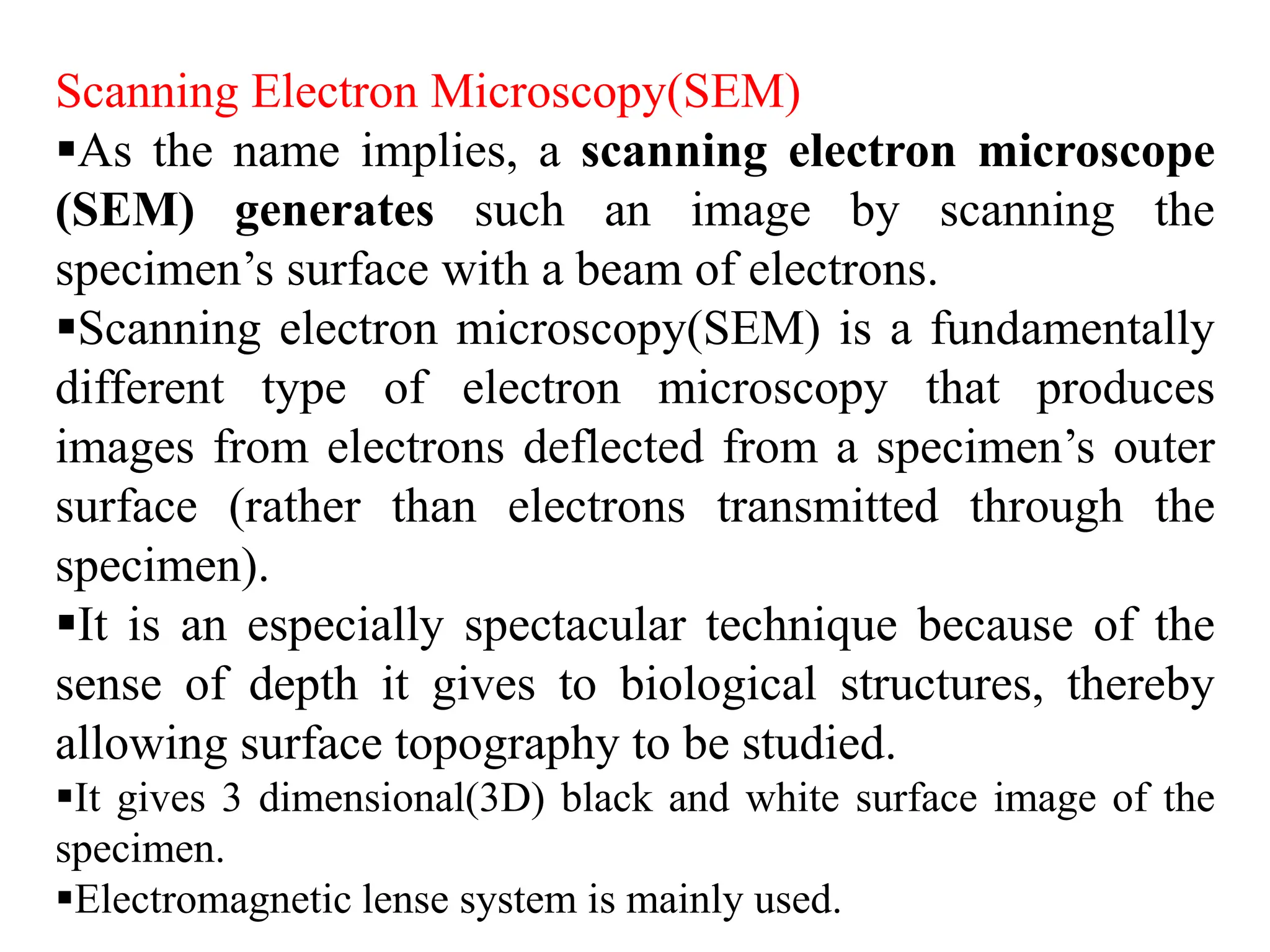
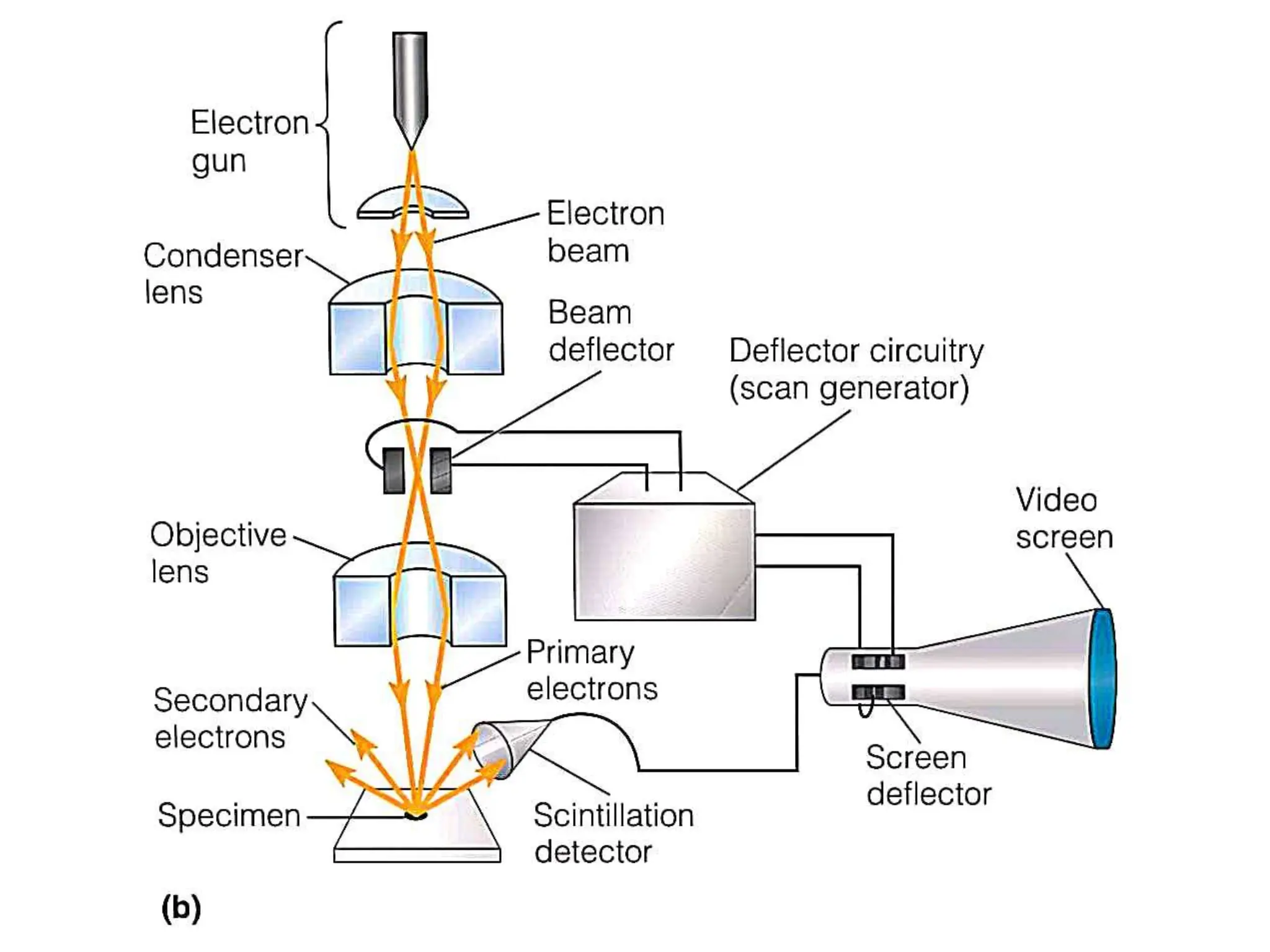
Electron microscopes use a beam of accelerated electrons rather than light to generate magnified images. There are two main types: scanning electron microscopes (SEM) and transmission electron microscopes (TEM). SEMs scan the surface of a specimen with electrons and produce 3D images, while TEMs transmit electrons through very thin specimens to form 2D sectional images. Both use electromagnetic lenses and detectors to focus and detect electrons and form magnified images of nanoscale structures.