Embed presentation
Download to read offline


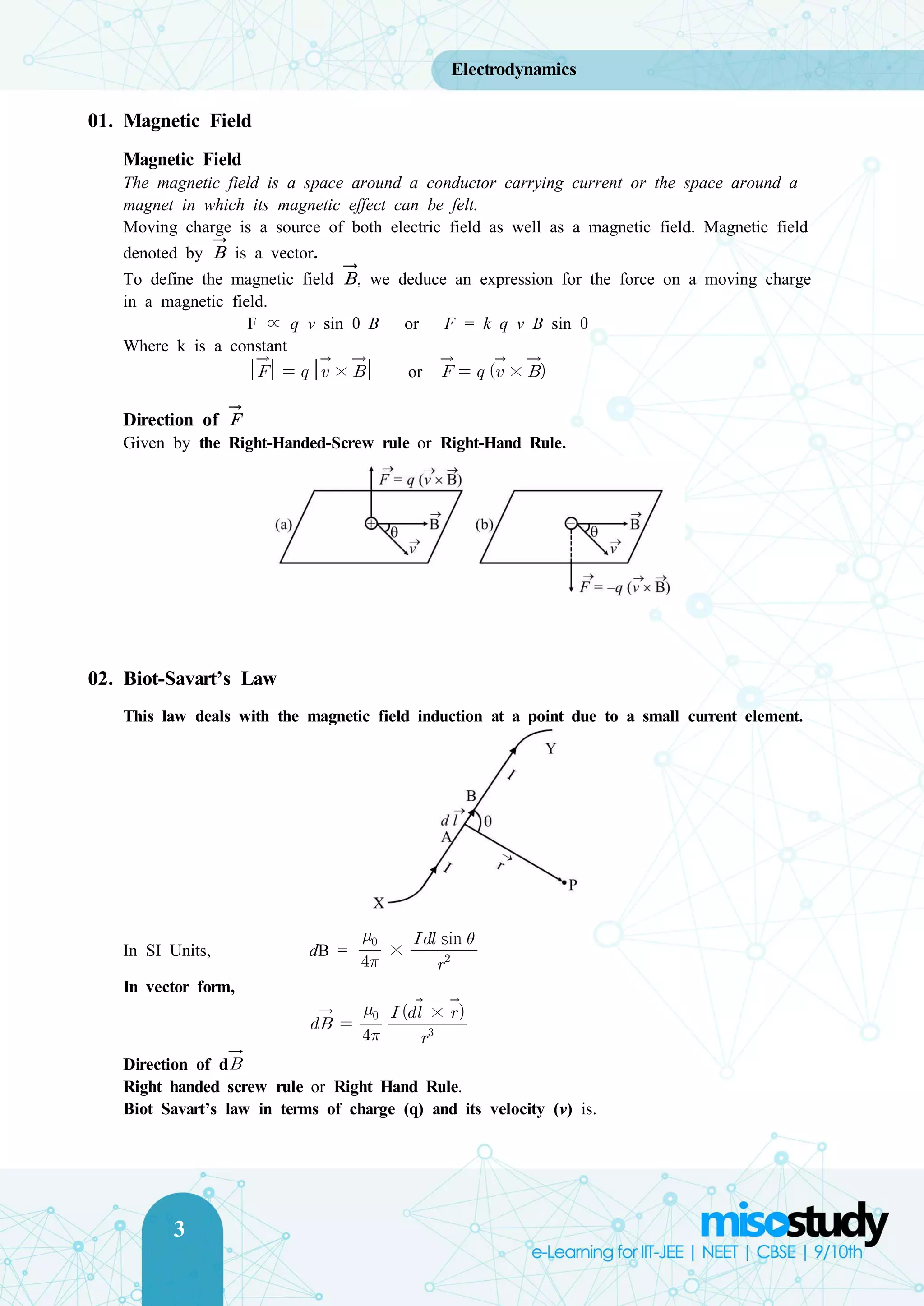

The document discusses key concepts in electrodynamics, focusing on magnetic fields and the Biot-Savart law. It explains that a magnetic field surrounds a conductor carrying current, with forces on moving charges expressed through equations utilizing sine and cosine functions. Additionally, it highlights important features of the Biot-Savart law, including its similarities to Coulomb's law and its application to symmetrical current distributions.



