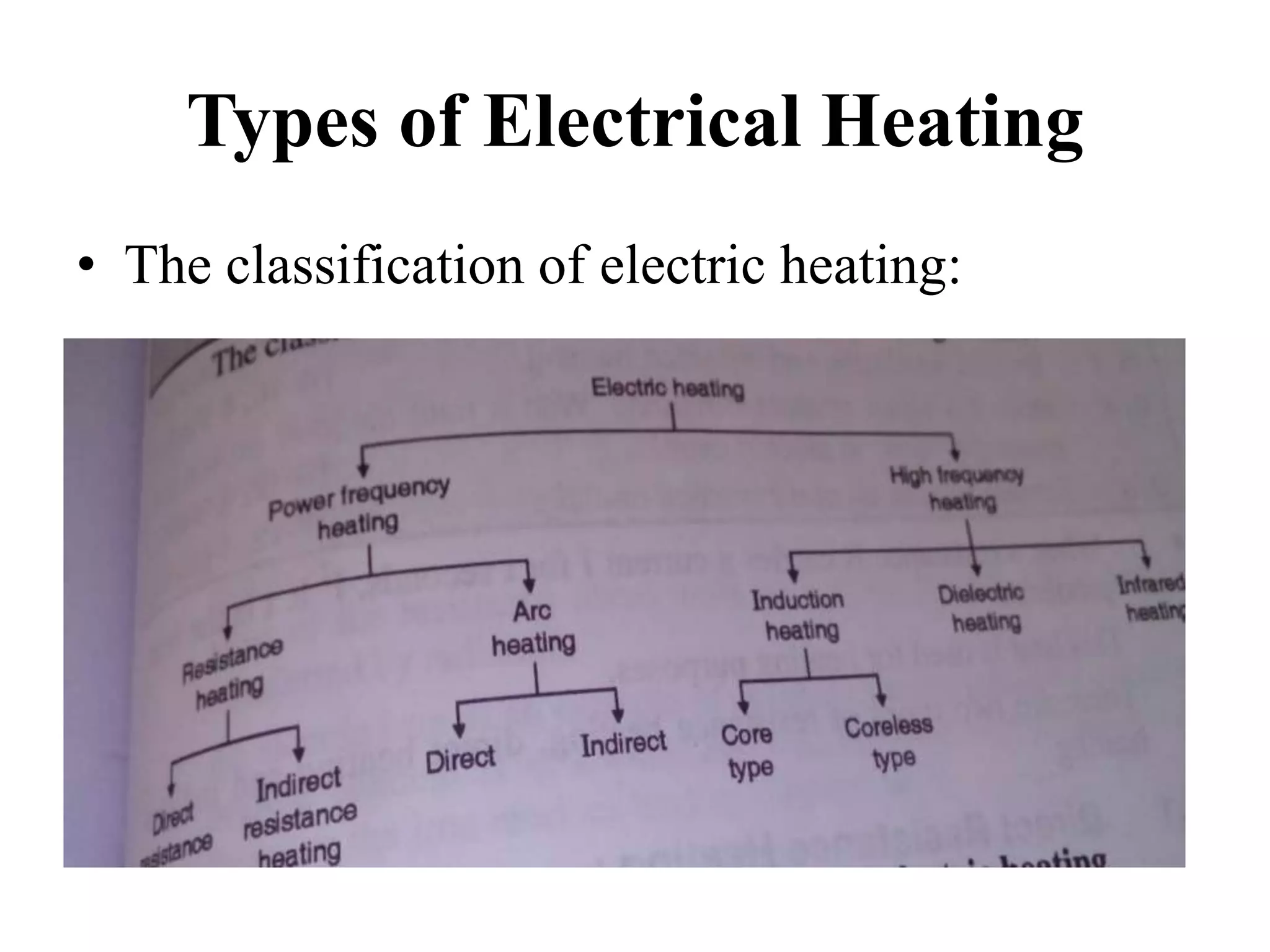
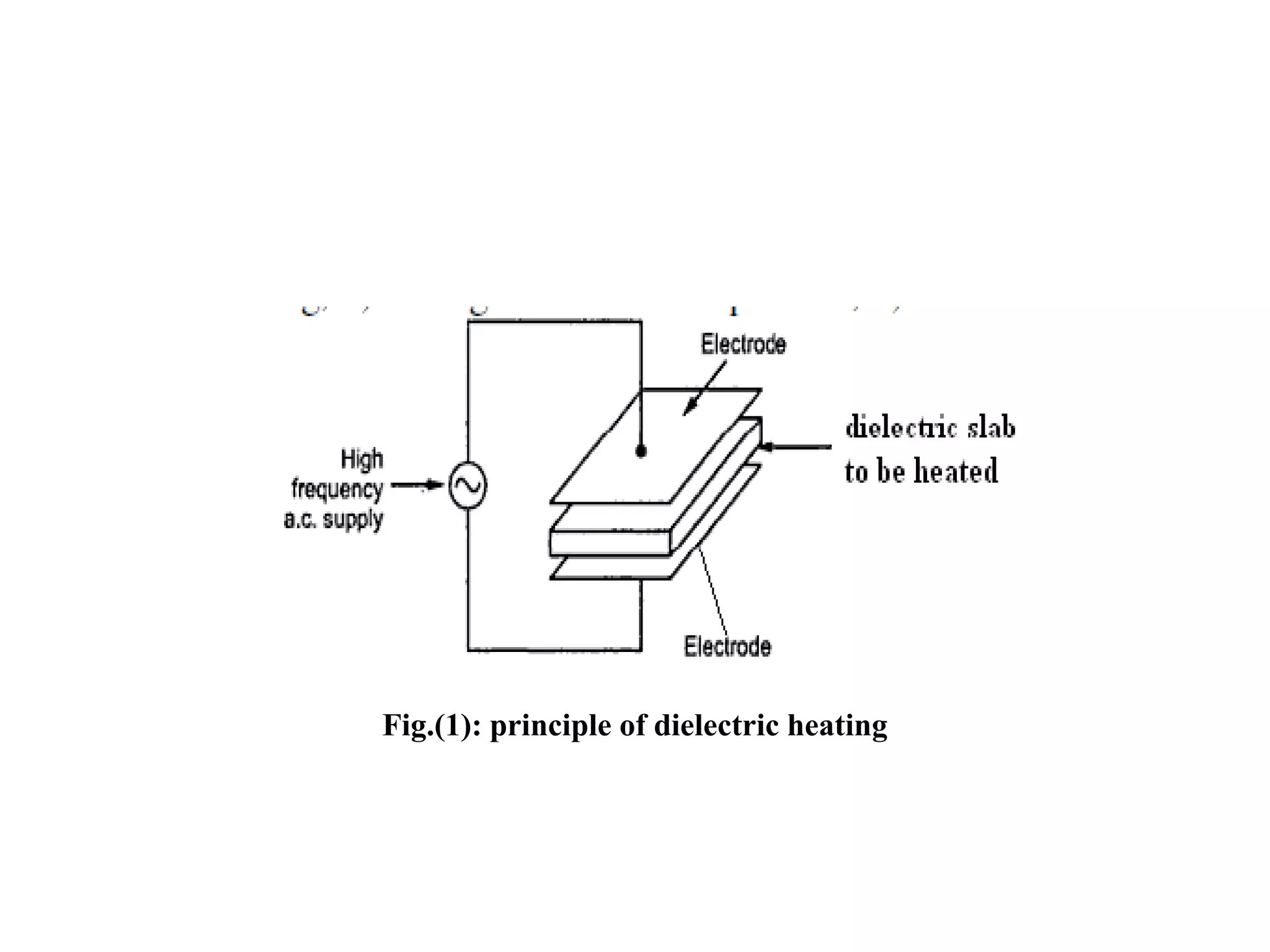
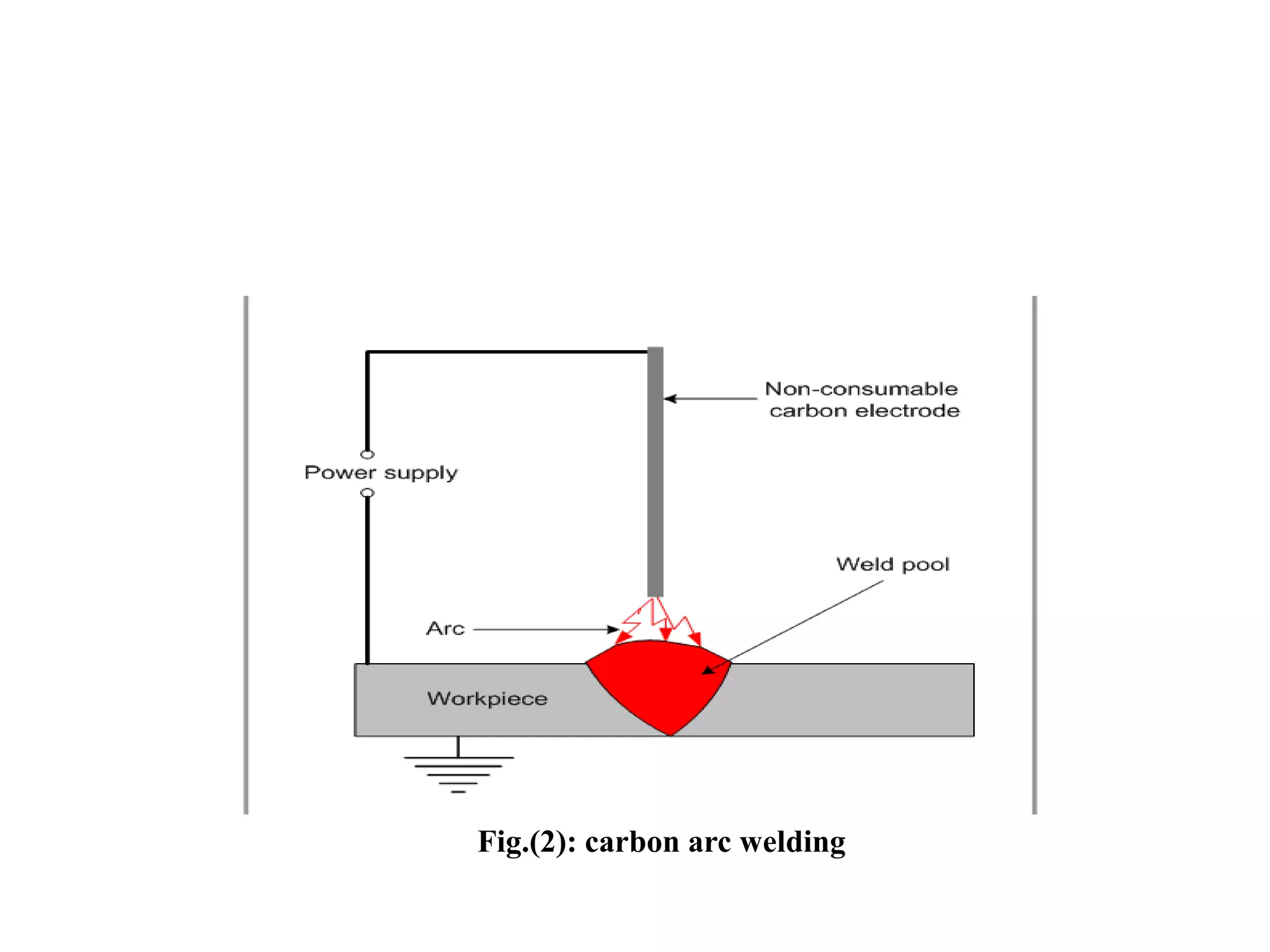
This document discusses different types of electric heating and welding. It describes domestic and industrial applications of electric heating such as electric irons, kettles, ovens, and heaters. The main types of electric heating are resistance heating, induction heating, eddy current heating, and dielectric heating. It also discusses different welding techniques including arc welding, metal arc welding, carbon arc welding, and atomic hydrogen welding.