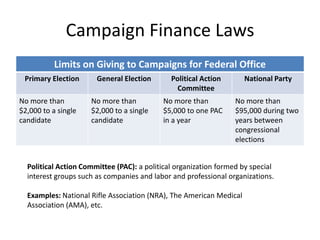
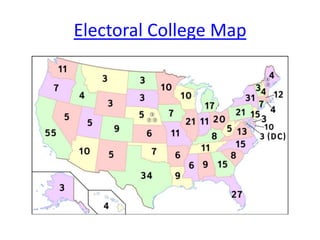
Elections, Voting, and Voter Behavior outlines the process of nominating and electing candidates in the United States. There are four main methods for nominating candidates: caucuses, conventions, direct primaries, and petitions. Primary elections allow members of political parties to vote for their preferred nominee, while the general election is held on the first Tuesday following the first Monday in November. Voter behavior is influenced by demographics like age, education level, income, and religion, as well as feelings of political efficacy. Historically, voting rights have expanded to include more groups, but some citizens still do not vote due to issues like lack of registration, indifference, or a sense that their vote does not matter.