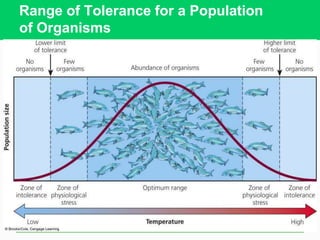
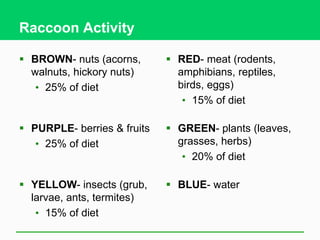
Populations can be limited by abiotic factors like temperature, space, and food availability. A population's size is determined by its habitat's carrying capacity, which is the maximum population it can sustain indefinitely without degradation. For example, if food becomes scarce it can limit a raccoon population from growing further. In an activity where students gather different colored "food" items as raccoons, some raccoons faced limitations like poor health that prevented them from obtaining a balanced diet, demonstrating how factors in the environment can impact population growth and survival.