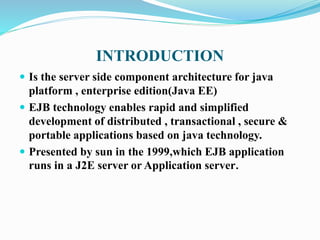
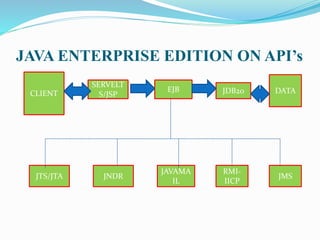
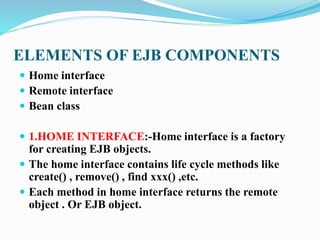
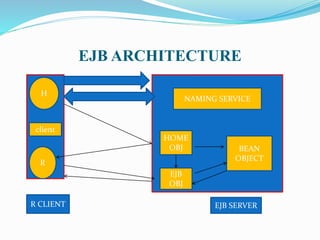
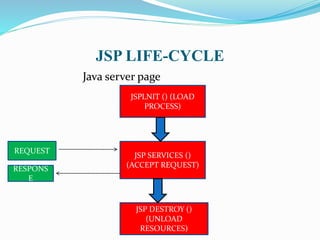
The document discusses Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) and Java Server Pages (JSP). It defines EJB as the server-side component architecture for Java EE that enables development of distributed, transactional, secure applications. EJB components include home interfaces, remote interfaces, and bean classes. JSP is a technology that simplifies development of dynamic web sites, allowing HTML pages to contain embedded Java code. JSP pages are executed by first being translated to servlets, then handled by the web server.