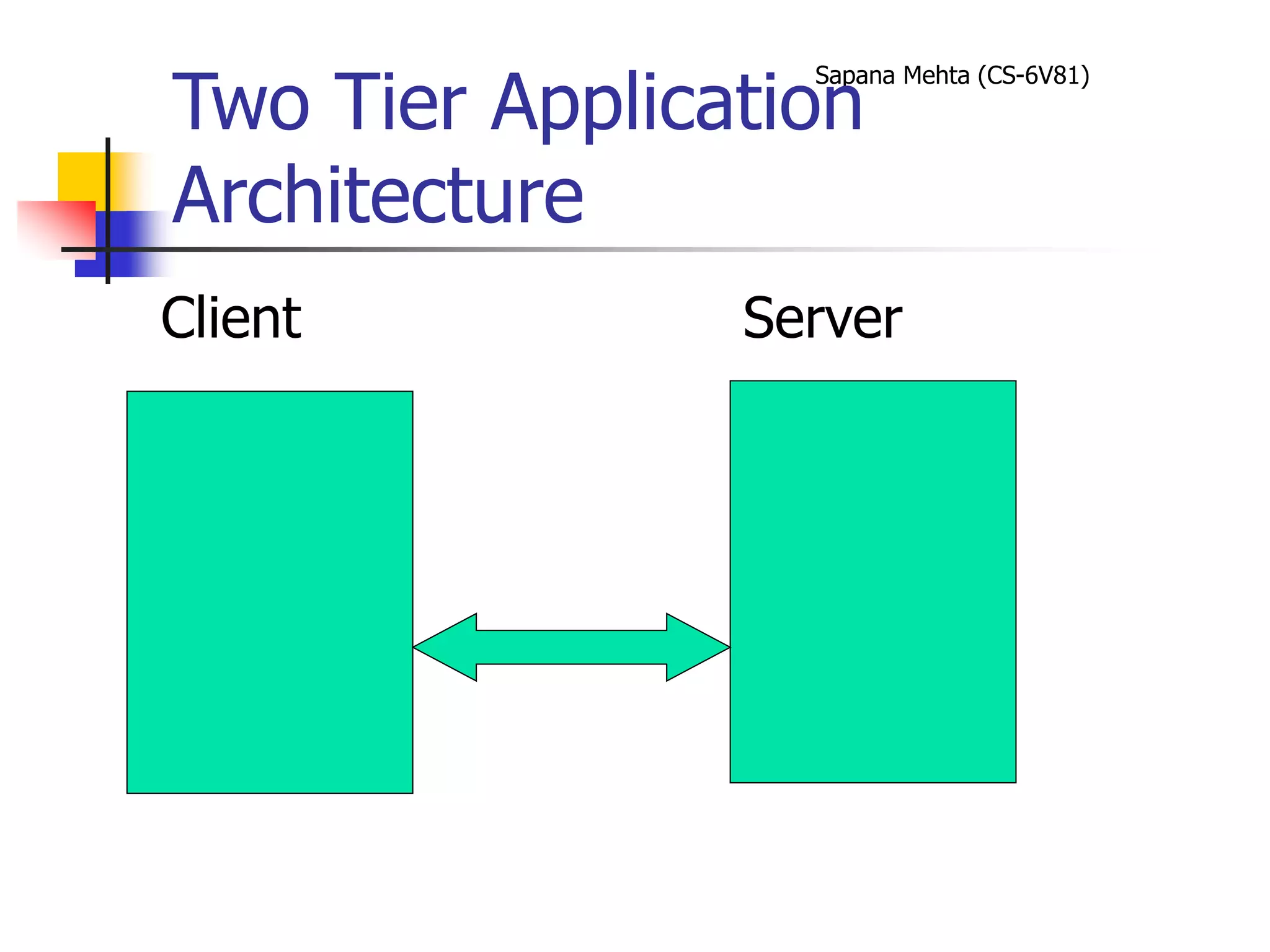
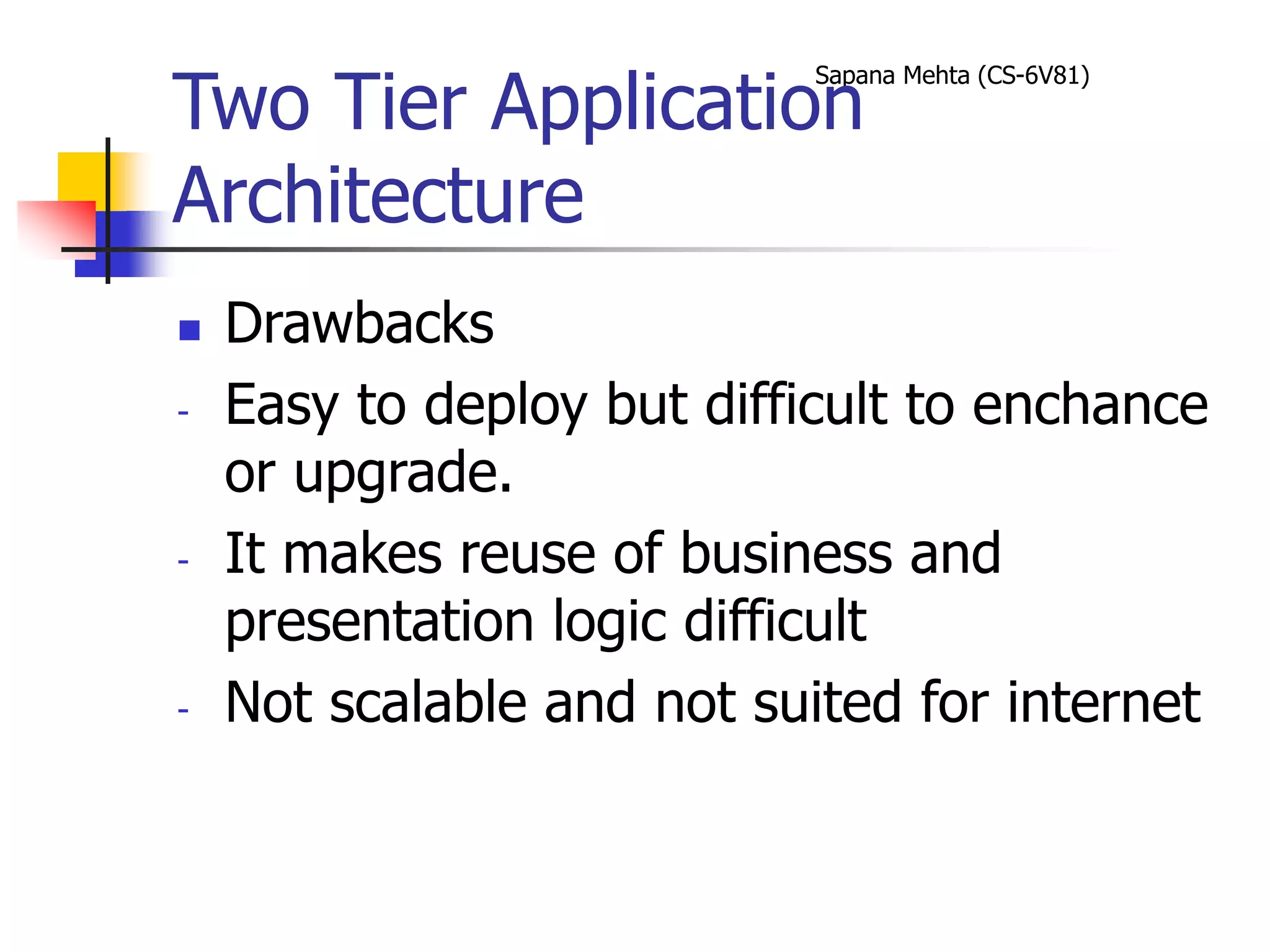
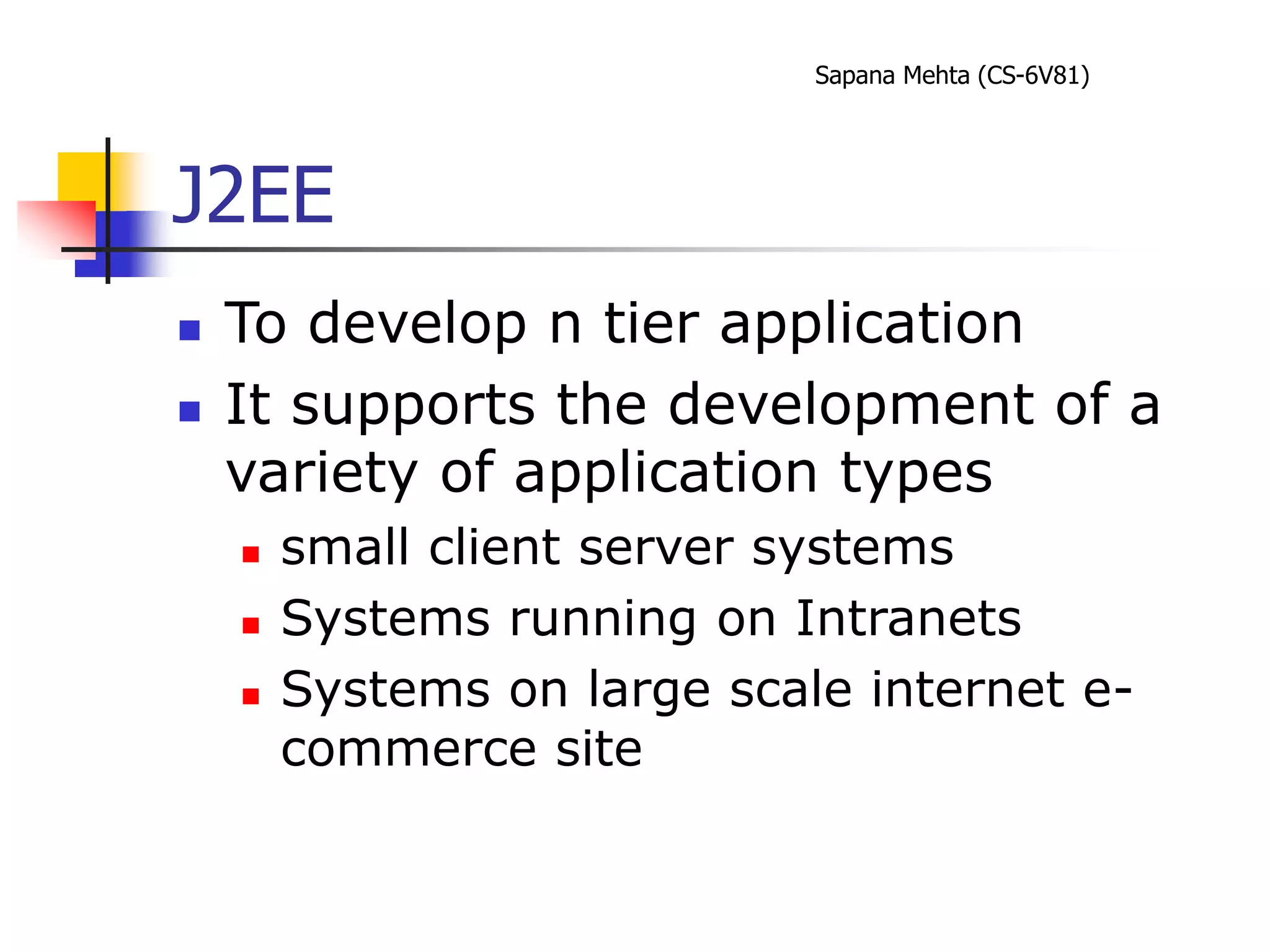
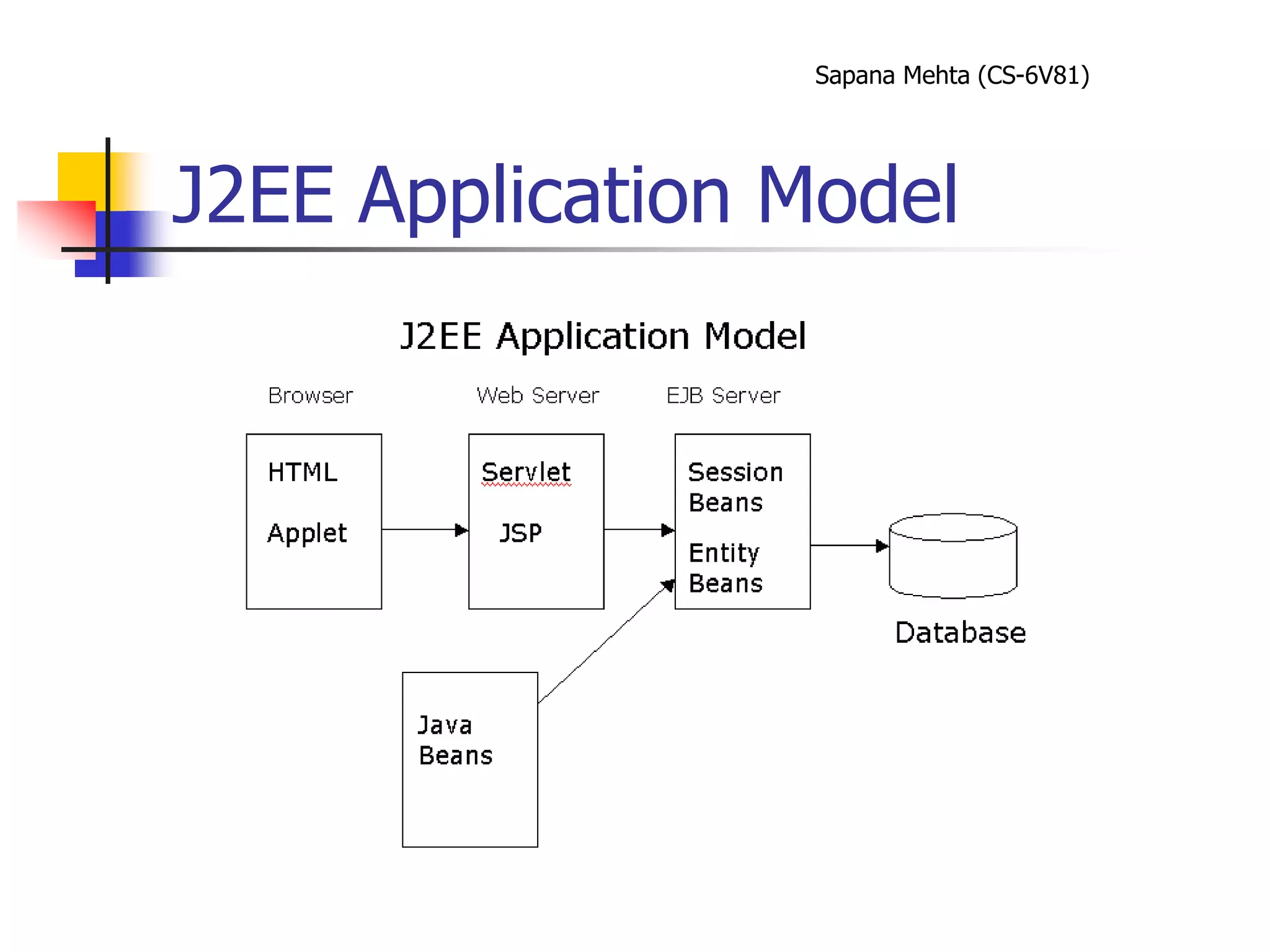
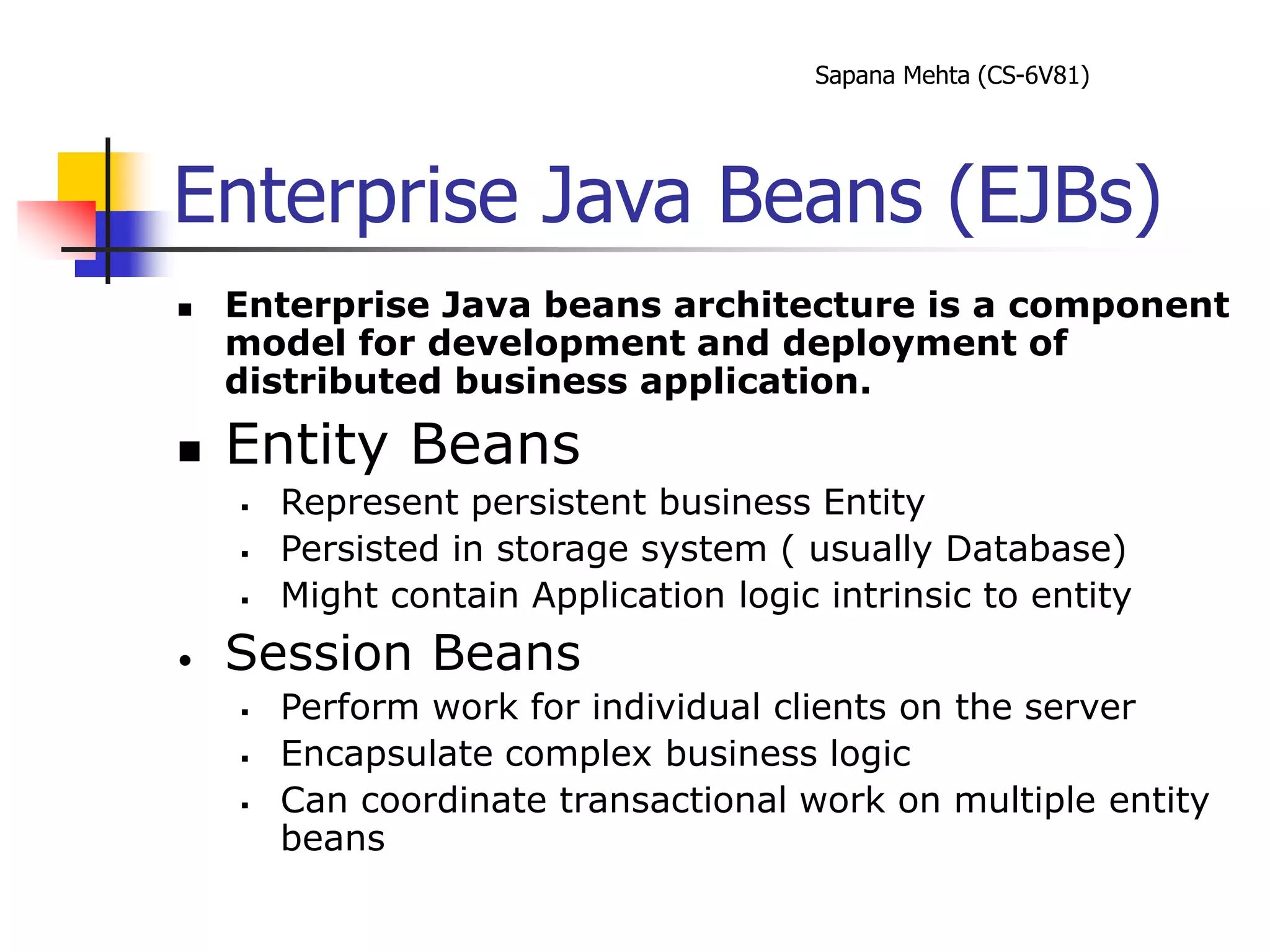
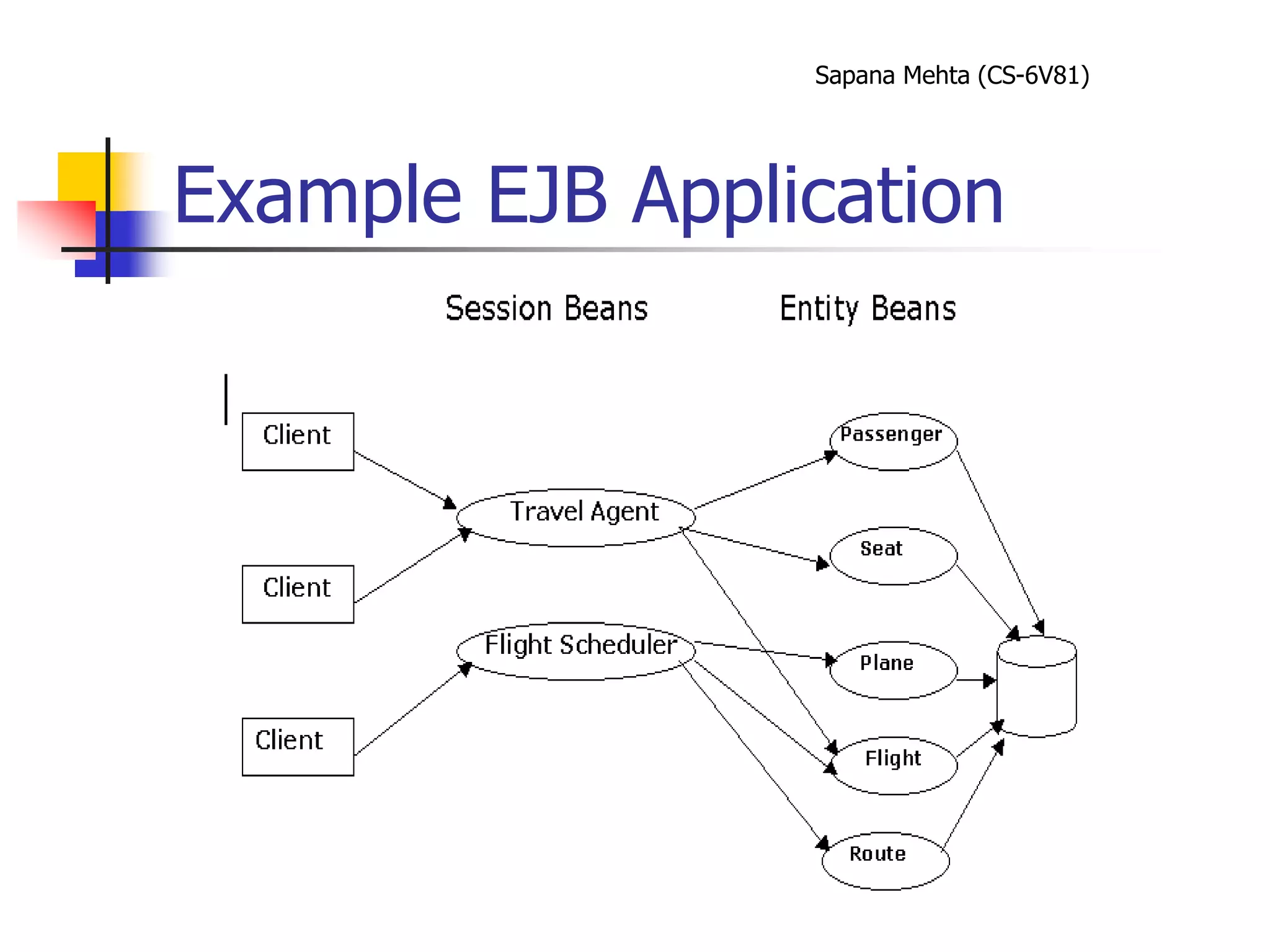
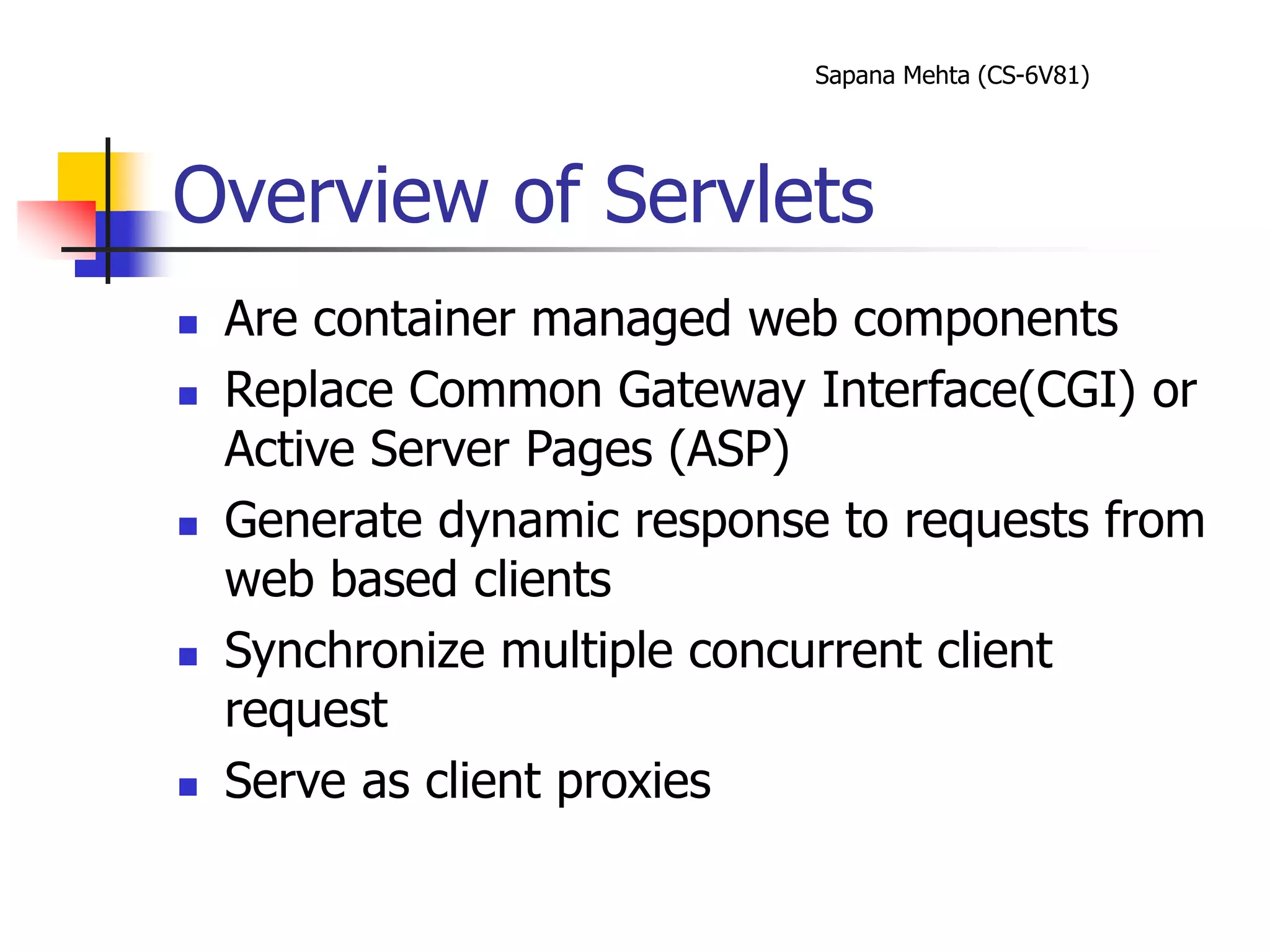
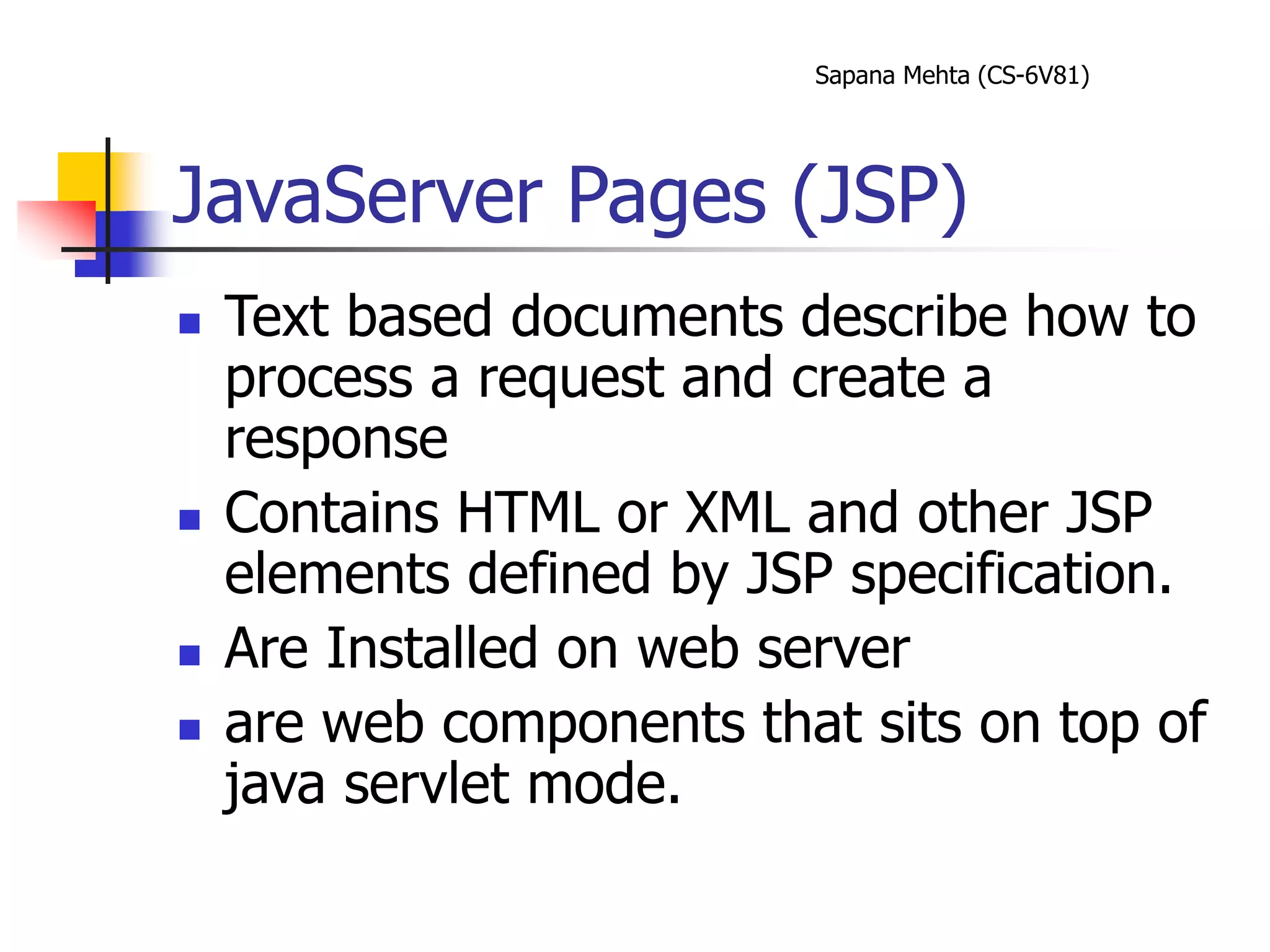
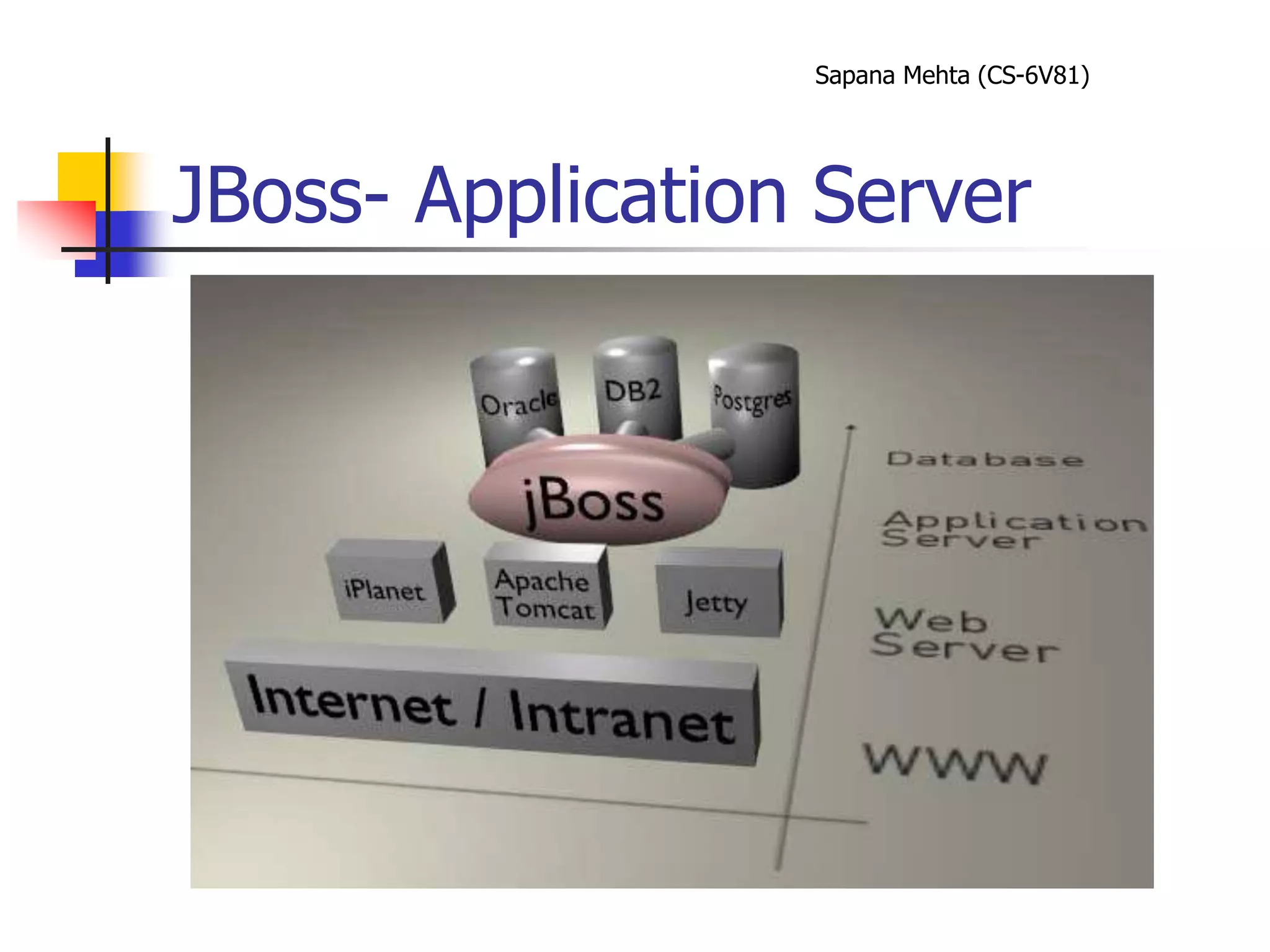
The document provides an overview of J2EE and JBoss. It discusses the evolution from two-tier architectures to n-tier architectures with J2EE. Key components of J2EE are then described, including Enterprise JavaBeans, servlets, JavaServer Pages, and their roles in the J2EE architecture. The document also provides a brief introduction to what JBoss is and its role as an open source application server.