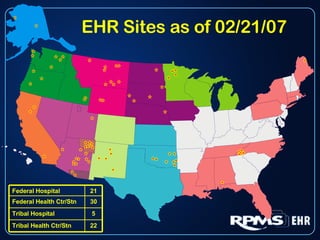
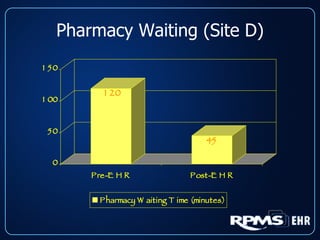
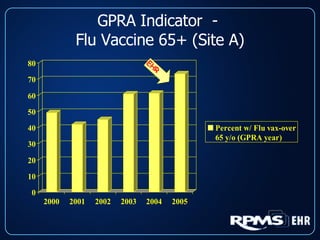
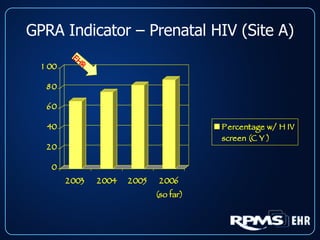
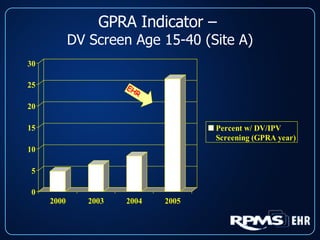
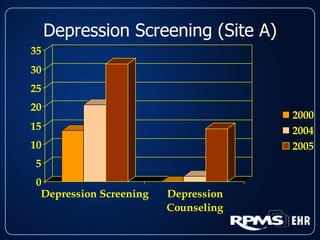
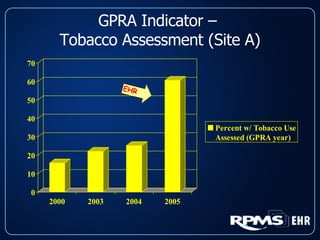
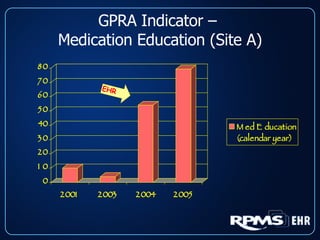
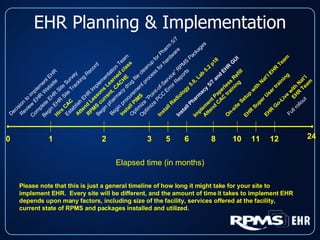
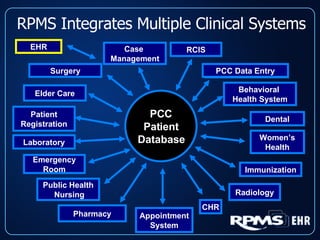
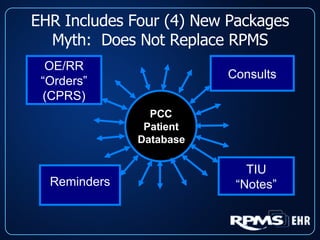
This document provides an overview and status update of the RPMS EHR (Resource and Patient Management System Electronic Health Record) system implemented across Indian Health Service facilities. It discusses the goals of adopting an EHR, the components and functionality of the RPMS EHR, implementation milestones achieved to date, lessons learned from early adopter sites, and how the EHR can help improve patient care, documentation, and metrics. Over 75 facilities are currently using the RPMS EHR, with a goal of all IHS federal sites implementing it by the end of 2008.