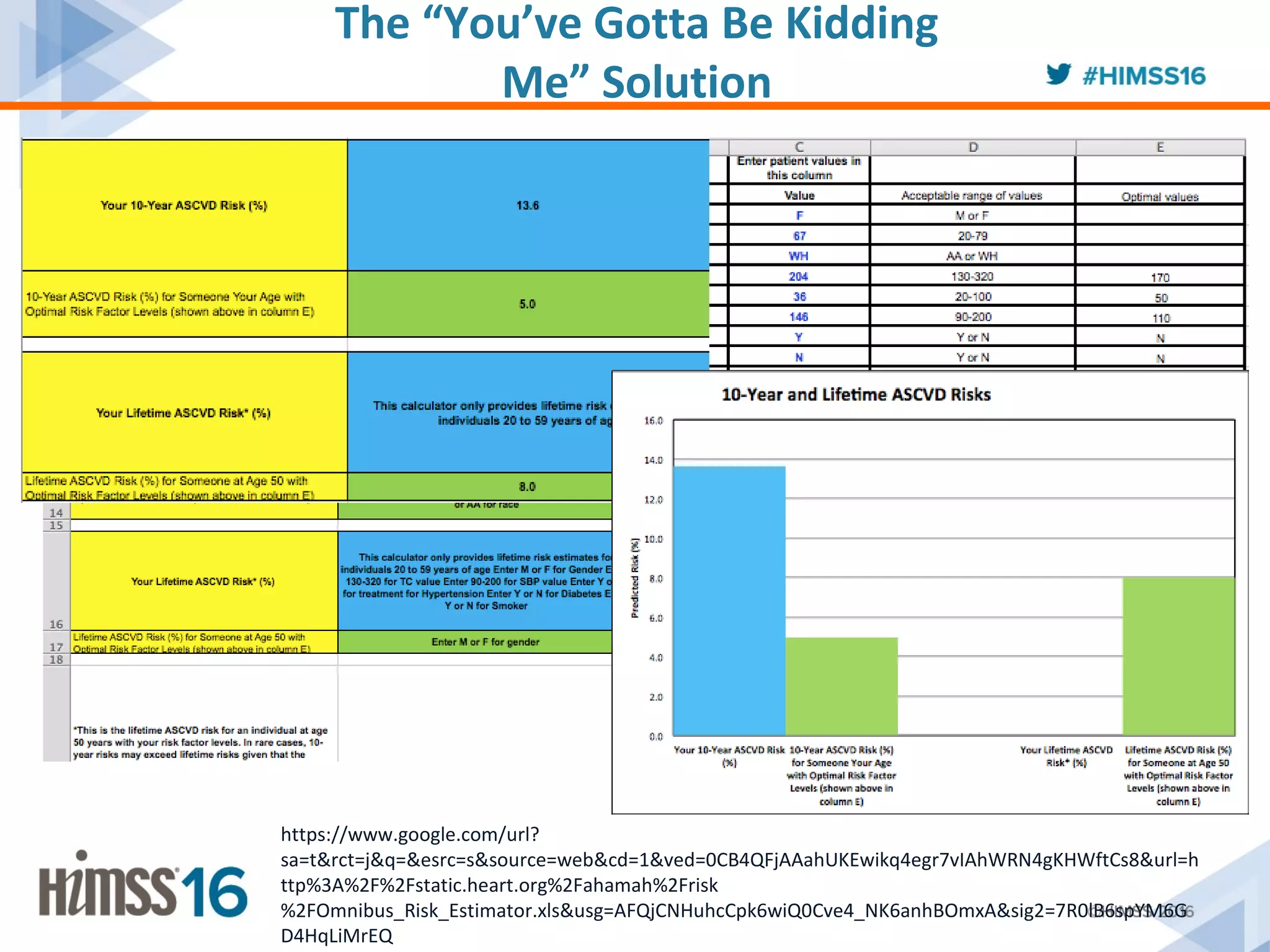
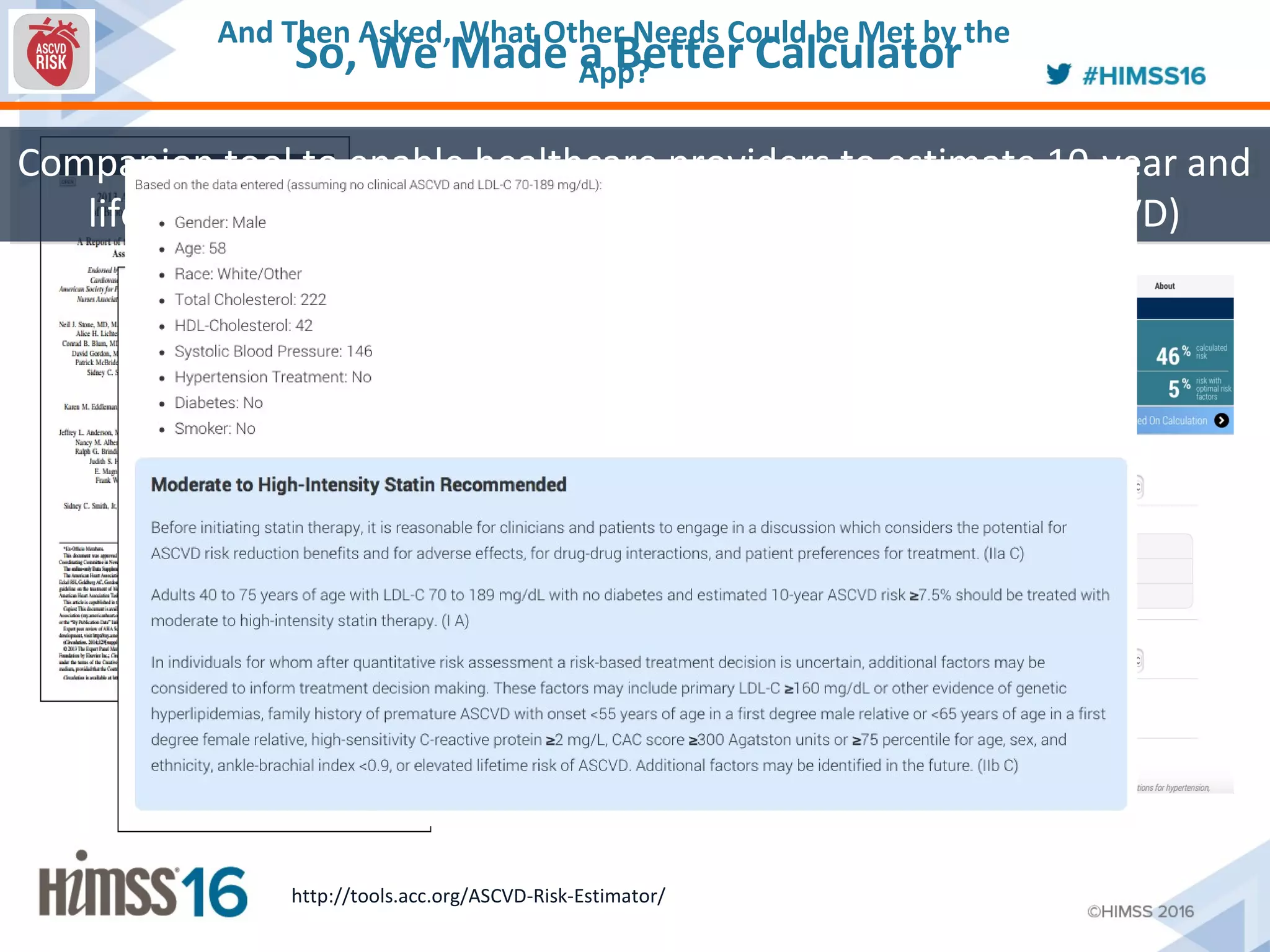
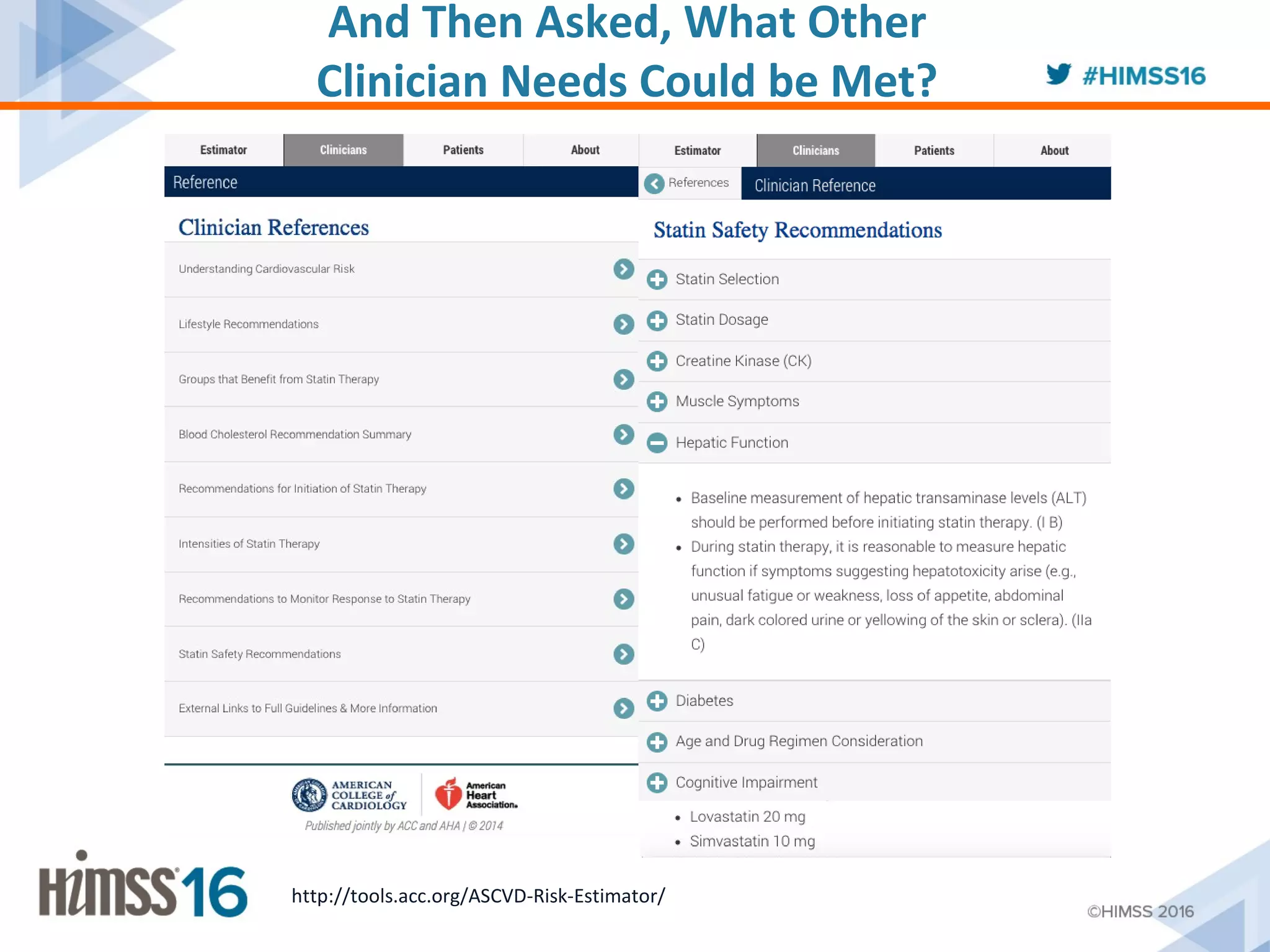
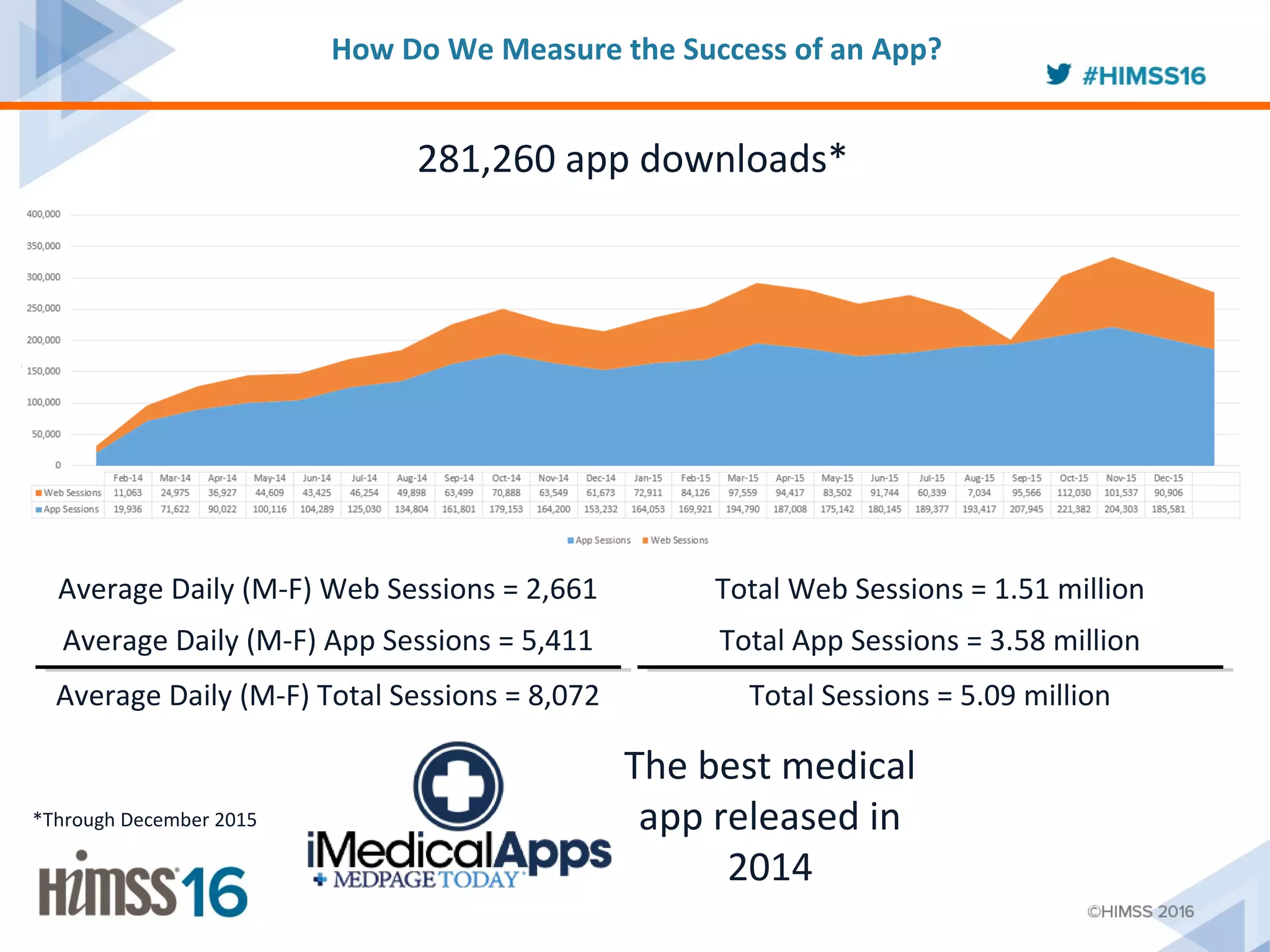
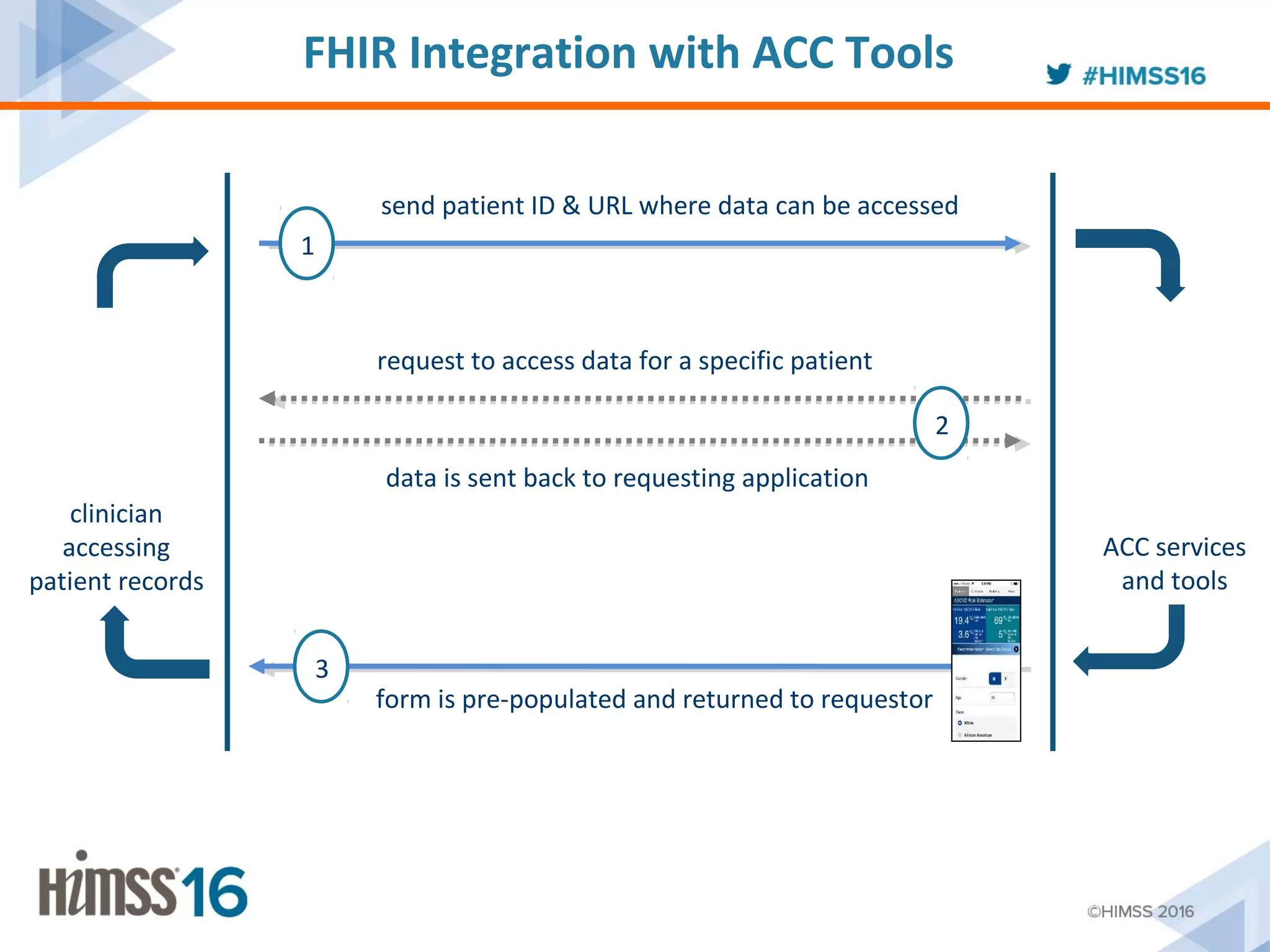
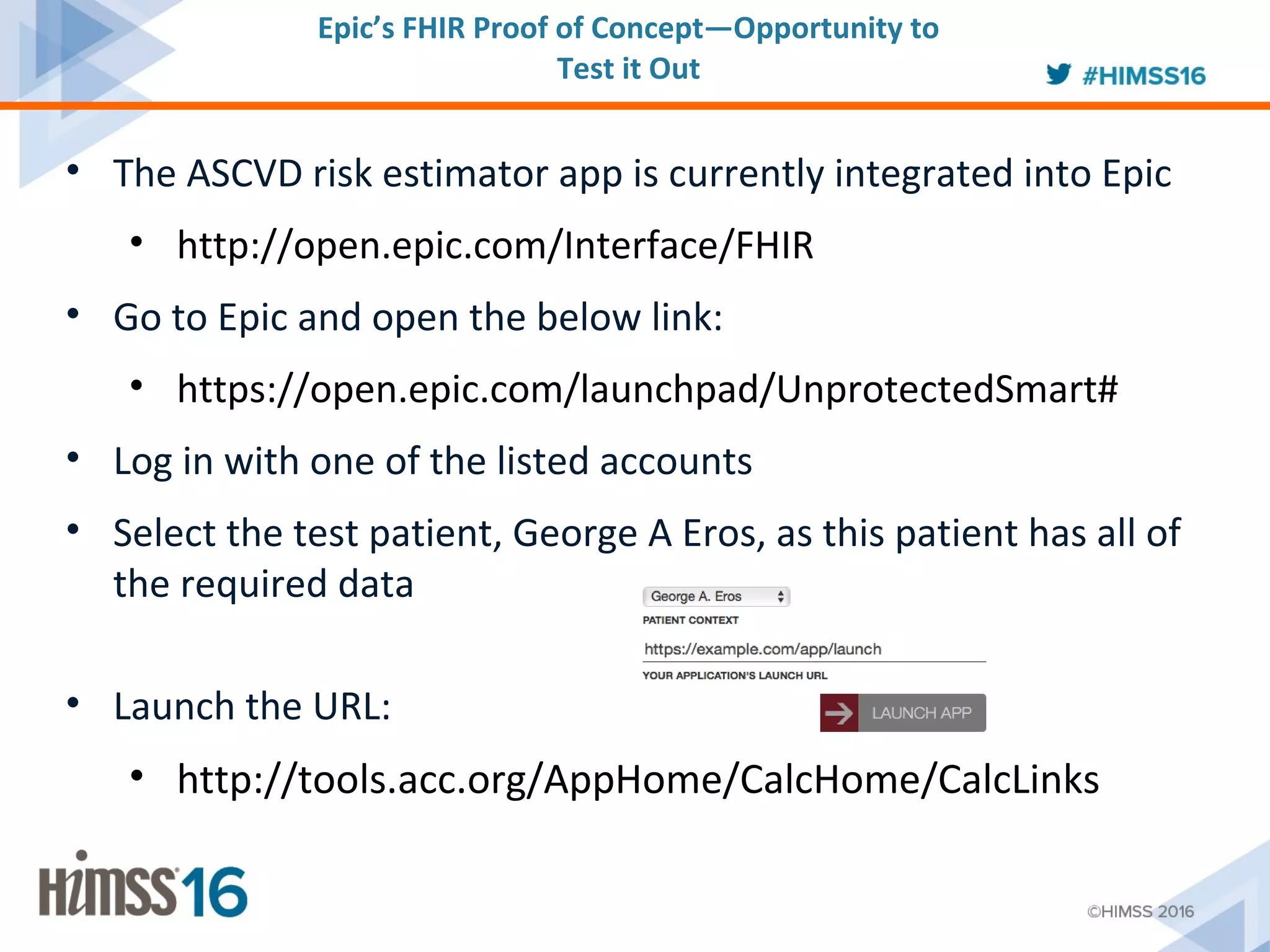
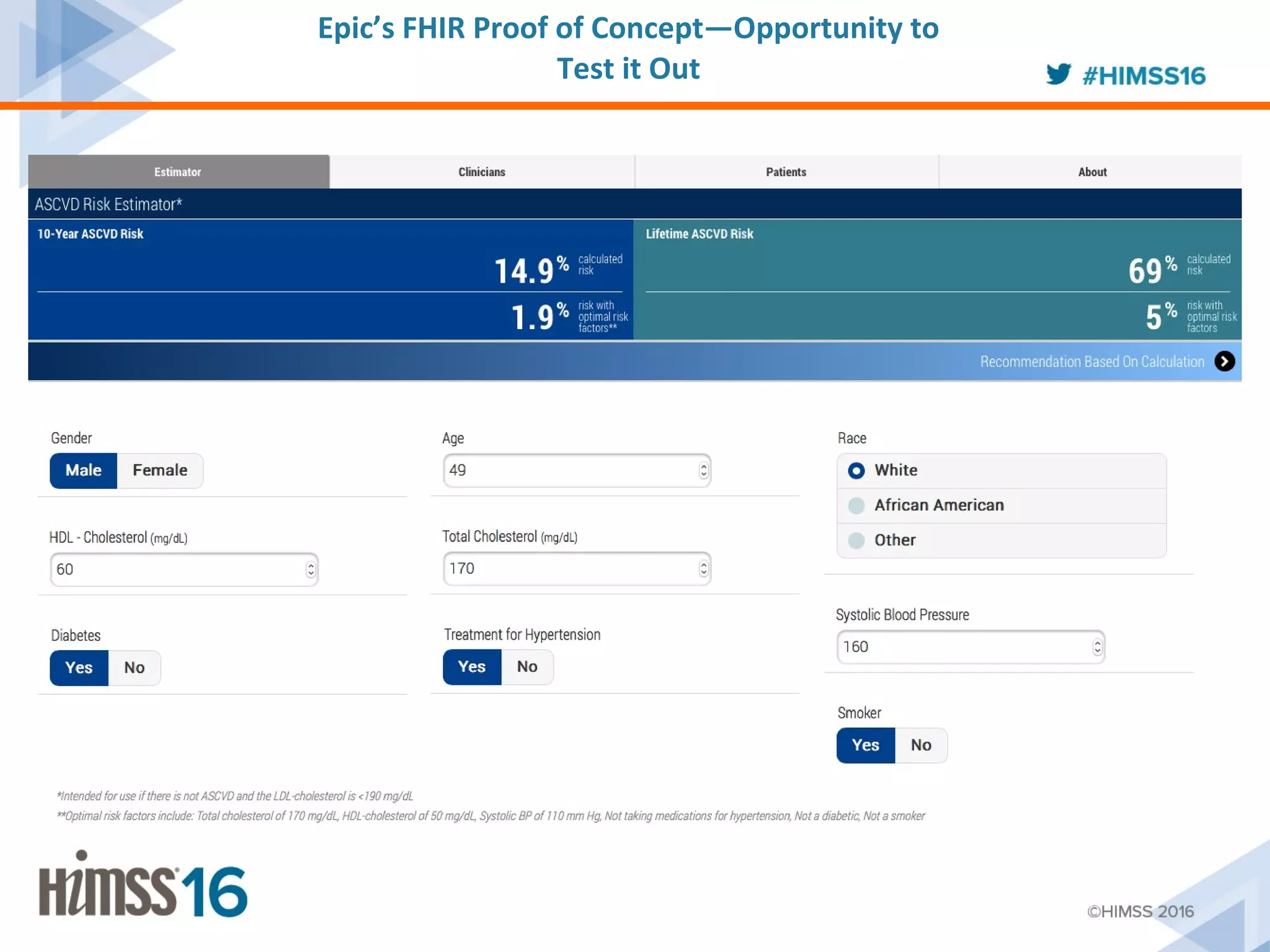
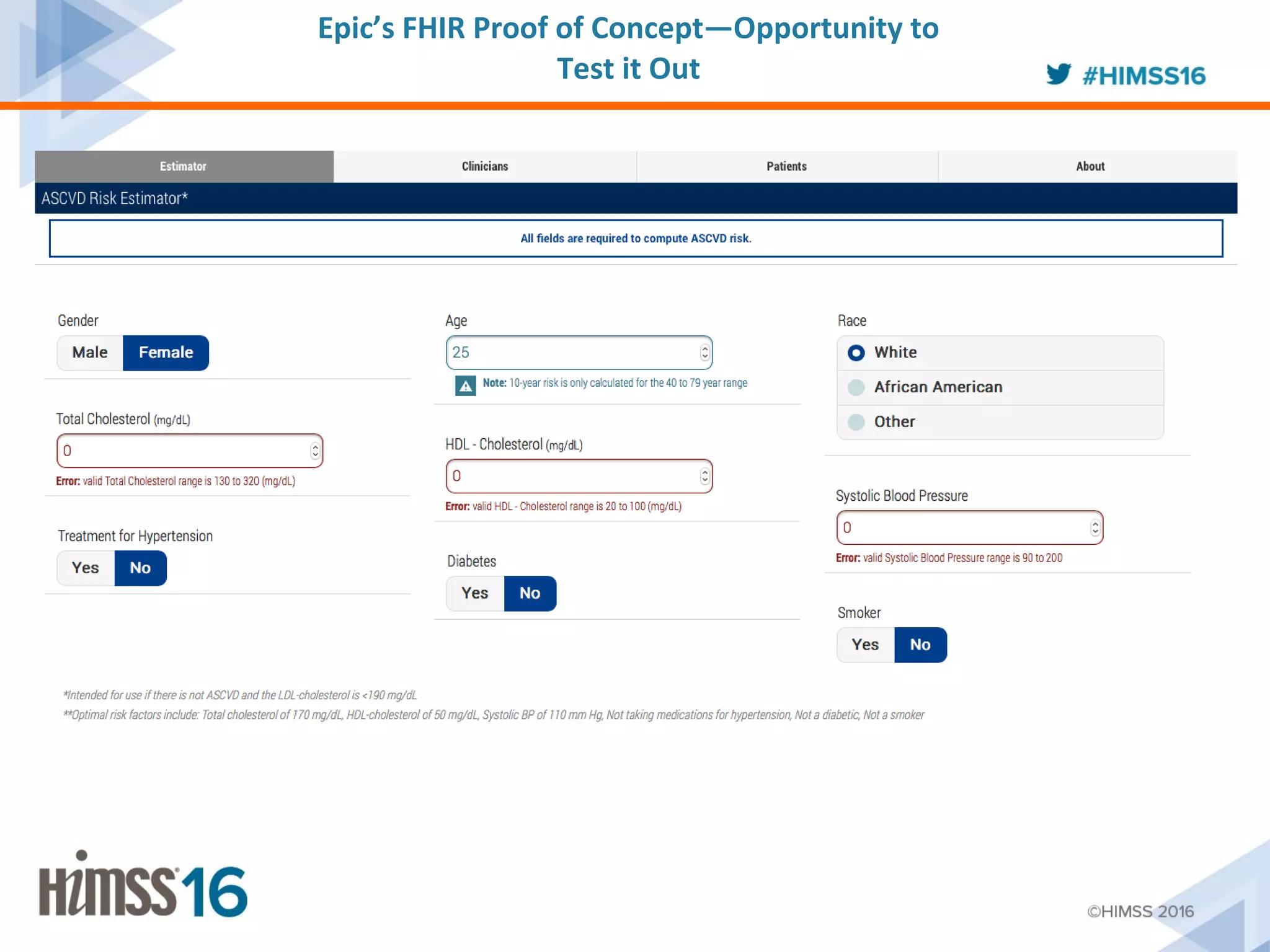
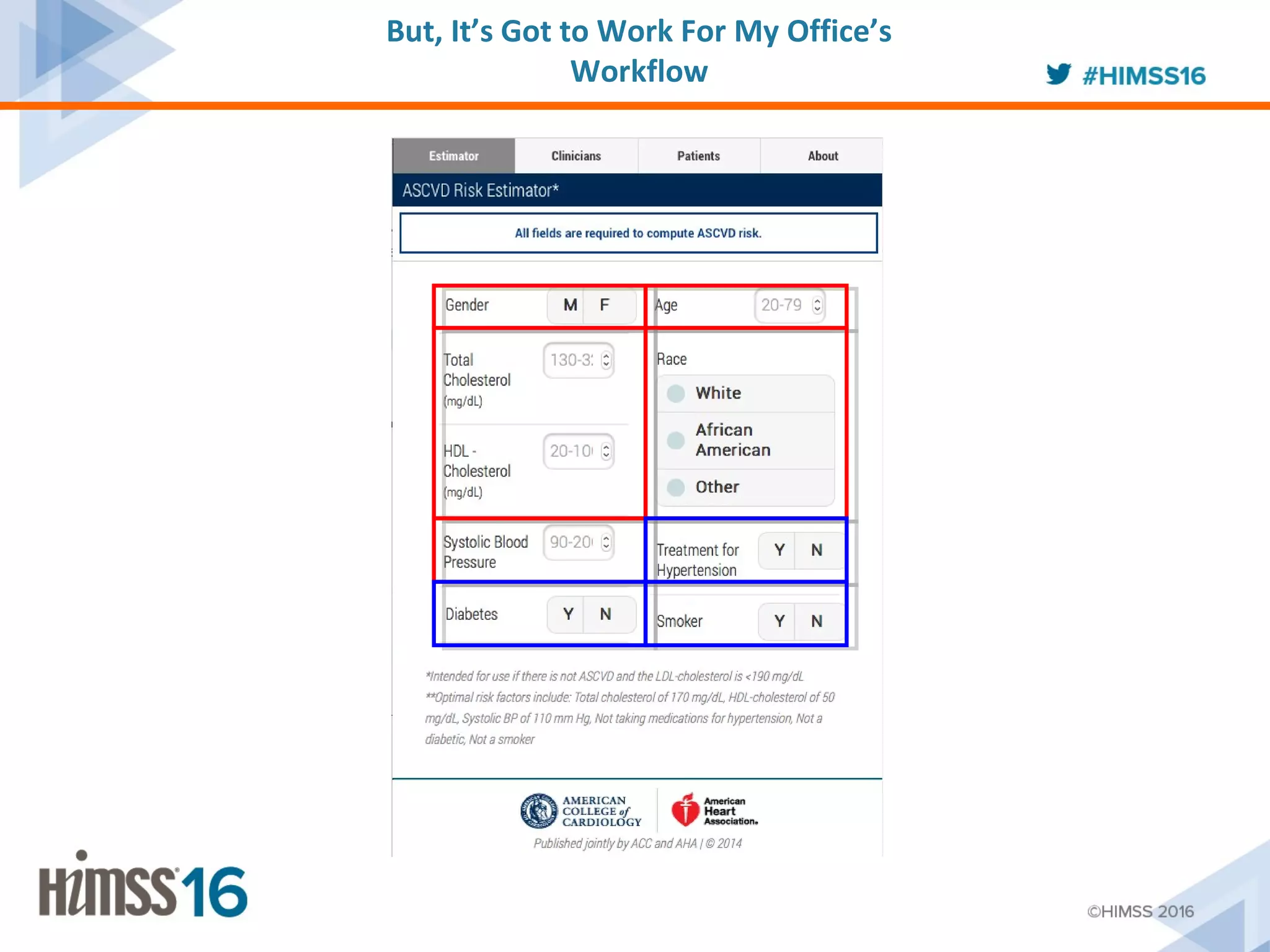
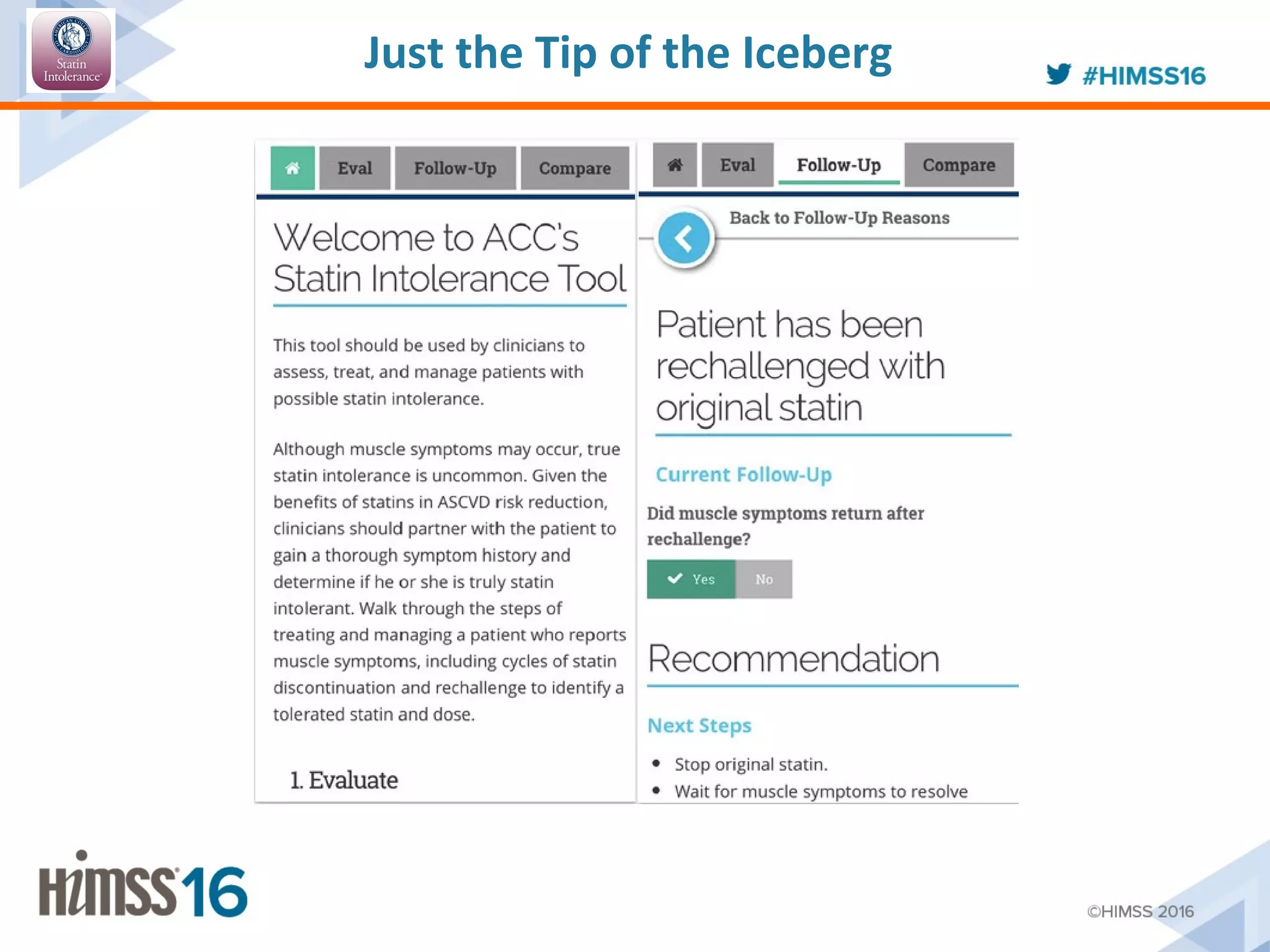
The ACC/AHA ASCVD risk estimator app aims to provide healthcare providers with a tool to estimate 10-year and lifetime risks for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, enhancing clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. Integration with electronic health records (EHR) using Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) is emphasized to streamline workflows and documentation. The initiative seeks to further expand its capabilities by collaborating with various EHR vendors to improve the use and functionality of the risk estimator app.