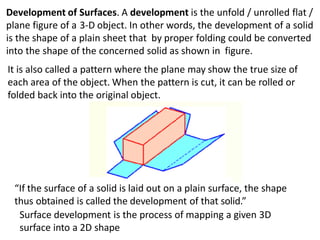
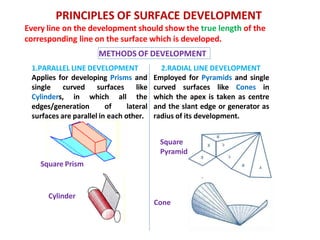
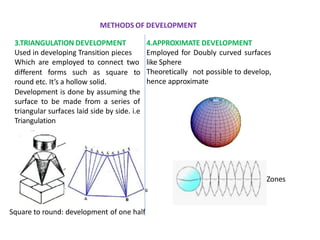
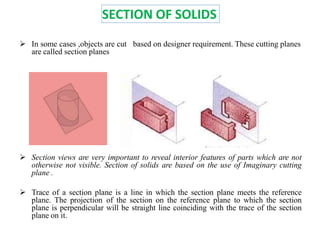
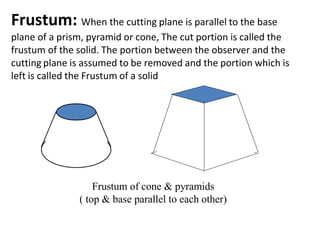
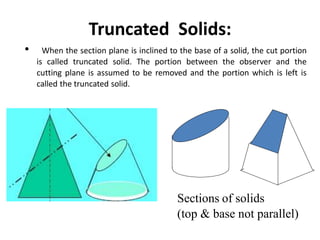
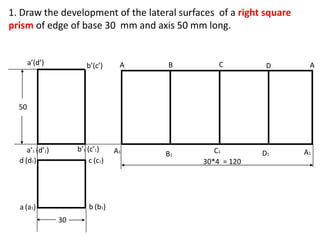
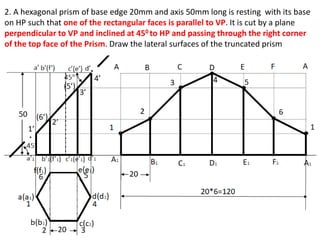
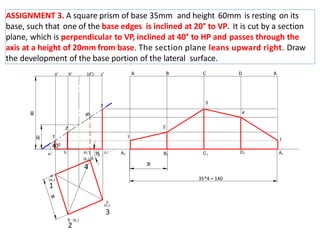
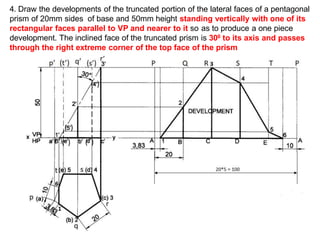
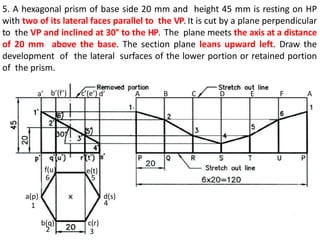
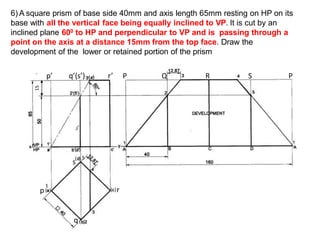
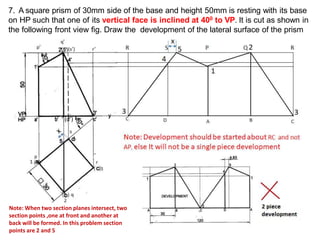
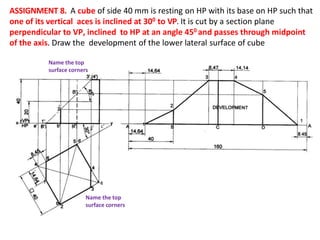
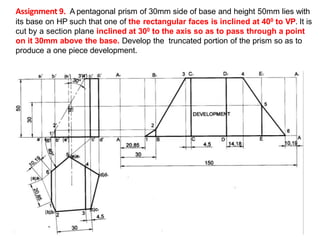
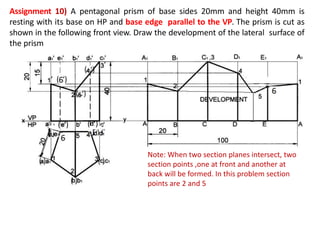
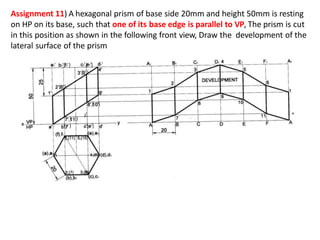
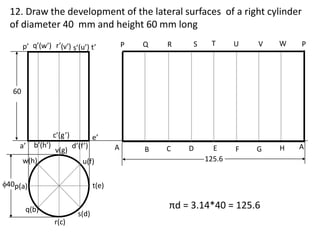
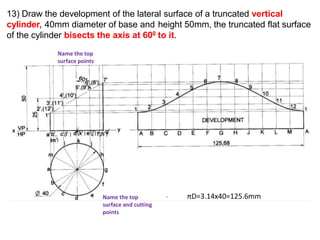
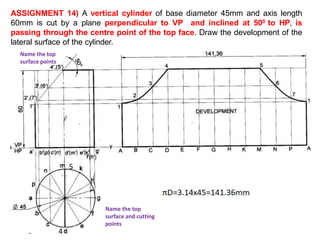
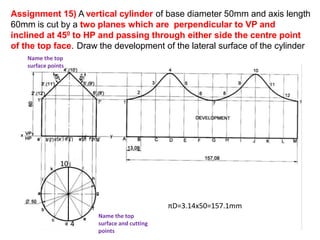
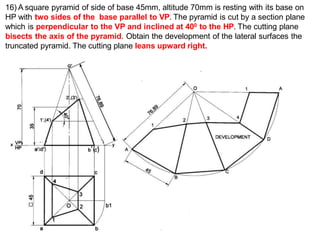
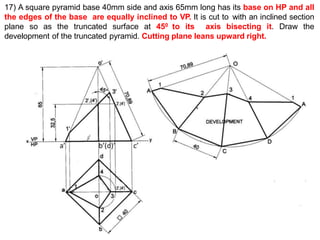
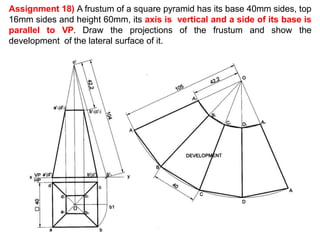
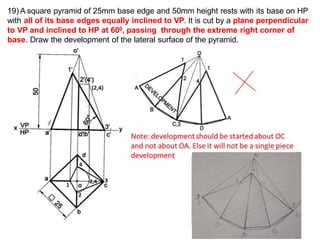
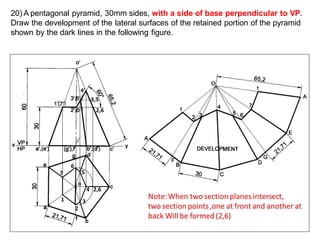
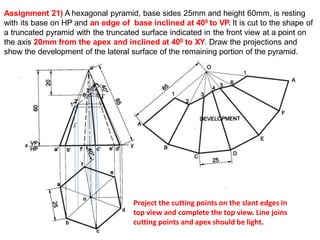
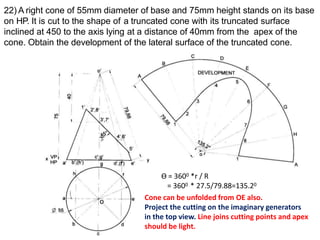
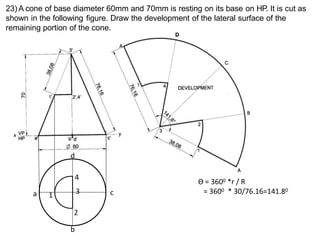
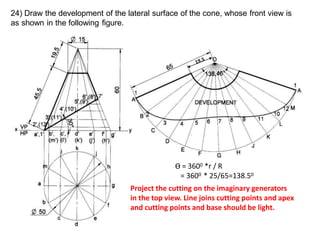
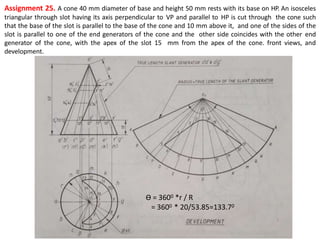
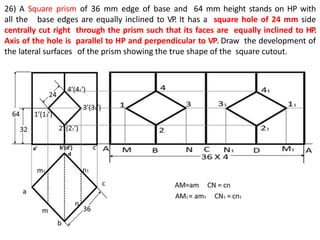
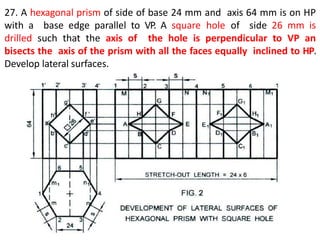
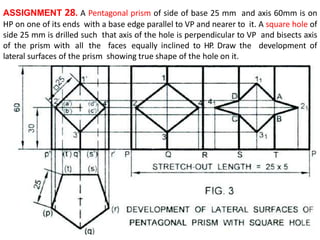
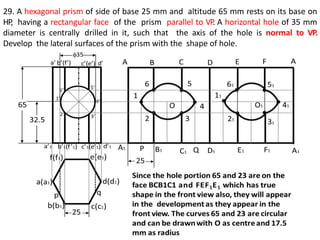
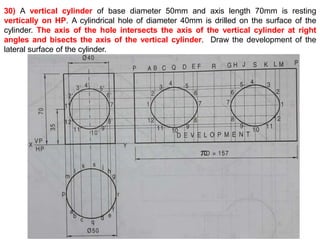
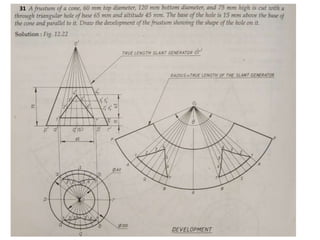
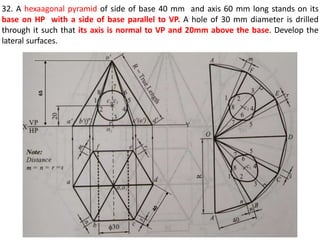
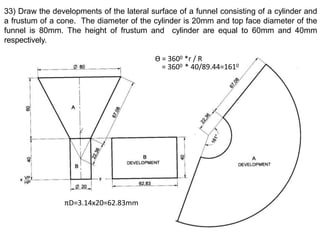
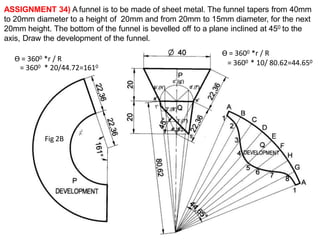
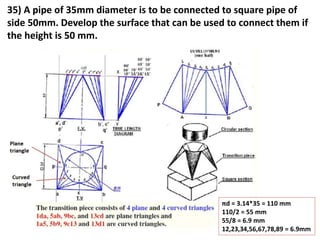
The document discusses the development of lateral surfaces of 3D objects. It defines a development as the unrolled flat shape of a 3D solid that can be folded back into the original shape. There are different methods of developing surfaces - parallel line development for prisms and cylinders, radial line development for pyramids and cones, triangulation development for transition pieces, and approximate development for curved surfaces like spheres. It also discusses sectioning of solids using cutting planes and the development of truncated and frustum shapes. Examples are provided for developing various prisms, pyramids, cylinders and cones.