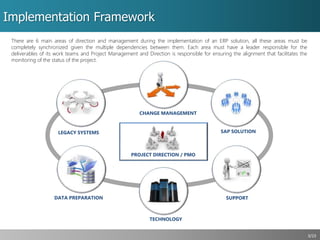
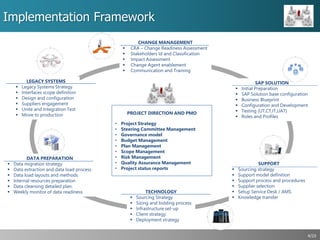
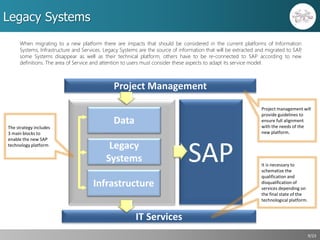
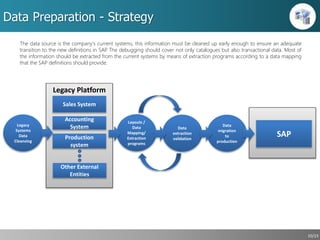
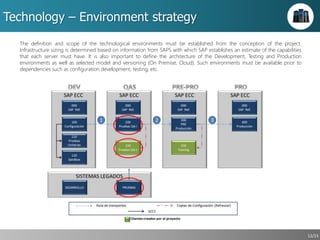
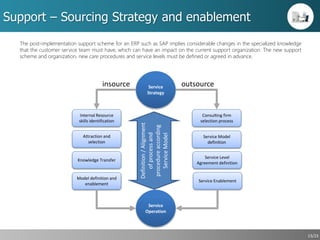
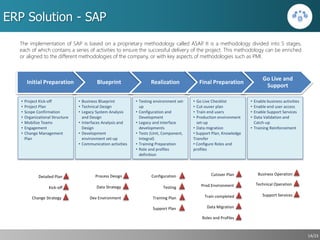
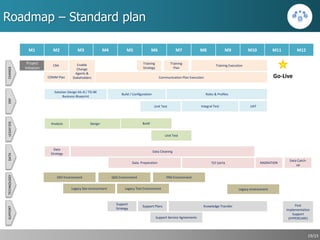
This document outlines a strategic approach for implementing an ERP solution based on SAP, detailing the main areas of project management, change management, and technology support necessary for successful execution. It emphasizes the importance of synchronized leadership across six critical areas, including data preparation, legacy systems management, and comprehensive testing procedures. Additionally, it discusses key constraints and the necessity of stakeholder engagement to ensure a smooth transition to the new ERP platform.