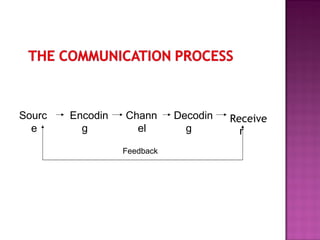
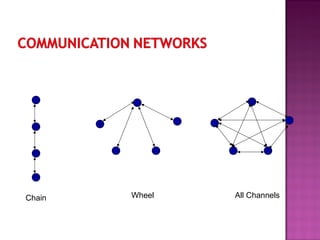
This document discusses key aspects of effective communication and public speaking. It covers preparing for a presentation by understanding the audience and structuring the content. Presentations should have a clear beginning, middle, and end. Effective delivery involves active movement, controlled gestures, and varying vocal tones. Questions from the audience should be anticipated and handled confidently. Visual aids require proper lighting and visibility to enhance the presentation. Overall success requires preparing thoroughly, using stage fright constructively, and interacting closely with the audience.