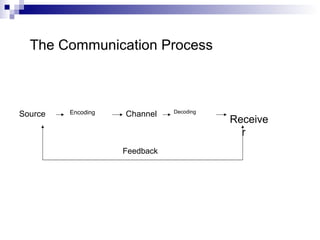
This document discusses effective communication and presentation skills. It covers the communication process, functions of communication, communication fundamentals, key communication skills like listening, feedback, and presentation skills. For presentations, it emphasizes the importance of preparation, structuring the content for the audience, handling stage fright, and delivering effectively through vocal variations, movement, and visual aids. The main points are effective communication requires strong listening, feedback and presentation skills, and preparation is key to successful presentations.