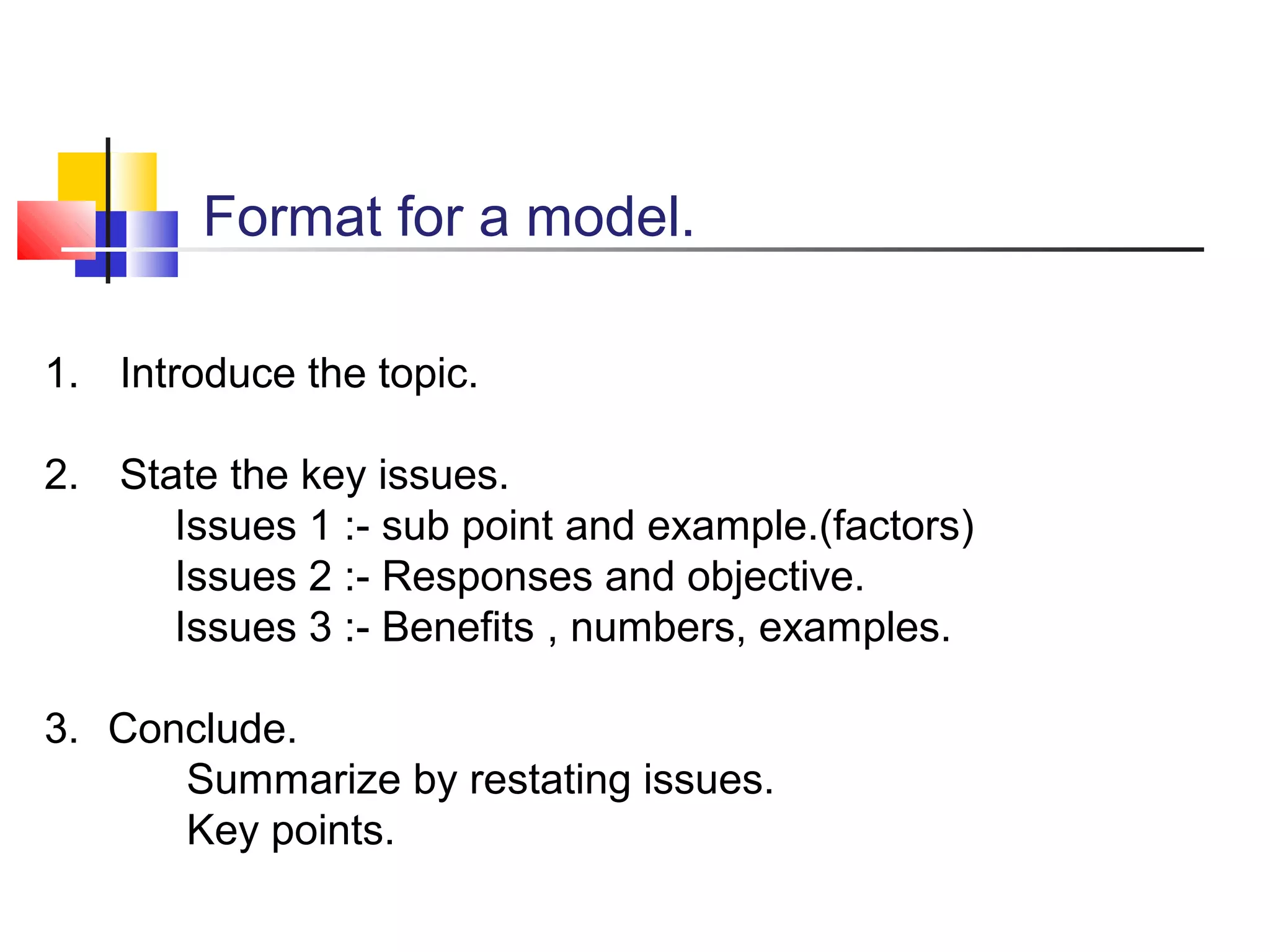
This presentation summarizes how to give an effective presentation. It discusses the different types of presentations, including informal presentations among friends and family and formal presentations for business. Good presentation skills can be developed through practice and include speaking clearly on the topic, engaging the audience, and using body language effectively. The presentation should have a clear introduction, discussion of key issues, and conclusion. Proper posture, eye contact, gestures, and facial expressions are important for connecting with the audience. Preparation, understanding the audience, and channeling nerves into positive energy are also emphasized for successful presentations.