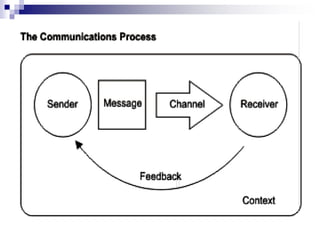
Extension workers need strong communication skills to effectively convey information to farmers. These skills include active listening, public speaking, and providing feedback. When listening, it is important to make eye contact, avoid distractions, and understand different perspectives. When speaking publicly, thorough preparation and understanding audience needs is key. Effective communication allows extension workers to accurately share knowledge and solutions with farmers.