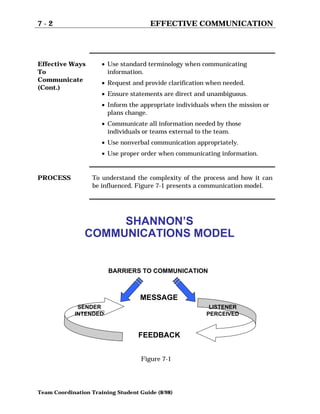
Communication is the process of exchanging information through words, tone of voice, and body language. Shannon's communication model identifies the key parts of communication as the sender, message, receiver, feedback, and potential barriers. Effective communication requires acknowledging messages, using standard terminology, requesting clarification when needed, and ensuring statements are unambiguous. Active listening from the receiver involves focusing on the message, observing nonverbal cues, keeping an open mind, and verifying understanding through paraphrasing.