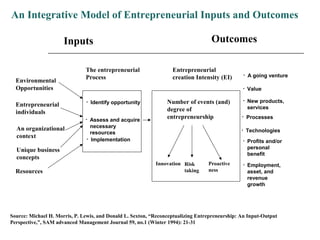
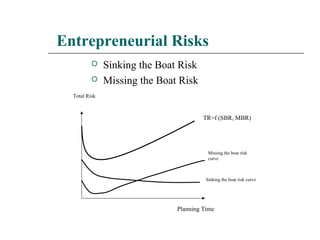
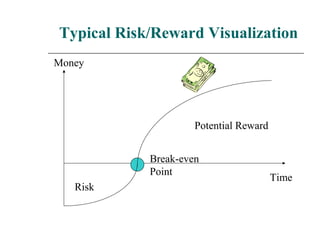
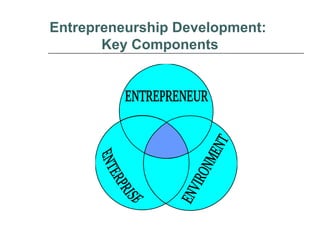
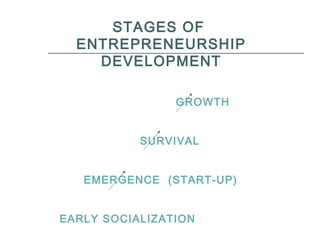
The document outlines the essence of entrepreneurship, highlighting it as a purposeful activity aimed at generating profit through innovative production and distribution. It describes the entrepreneurial process, including opportunity identification, resource acquisition, implementation, and emphasizes the importance of psychological traits such as motivation, risk tolerance, and adaptability. Additionally, it discusses the stages of entrepreneurship development, key constraints, and the rewards associated with successful entrepreneurial ventures.