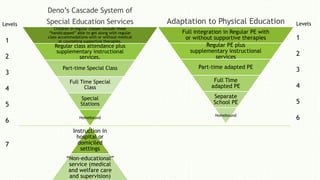
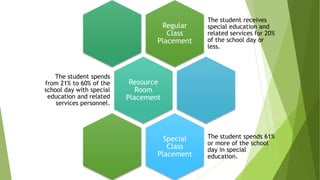
The document discusses the cascade system of special education services developed by Evelyn Deno, which emphasizes a continuum of services in the least restrictive environment, aimed at effectively integrating students with disabilities into regular educational settings. It details various placement types defined by the U.S. Department of Education, the principles of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), and the importance of tailored evaluation procedures for appropriate educational placements. The overarching goal is to match each student's abilities with optimal support services to enhance learning while ensuring compliance with legal standards.