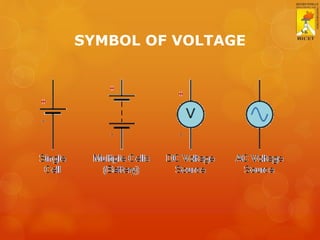
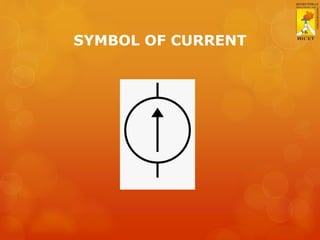
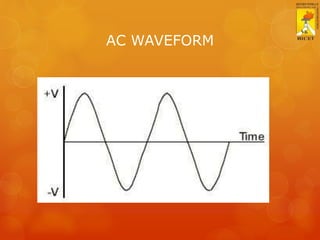
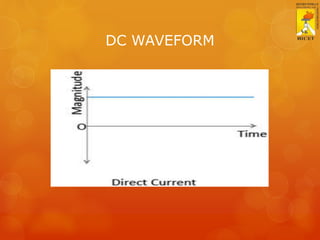
This document provides an overview of basic electricity concepts. It discusses voltage, current, resistance, and Ohm's law. Voltage is defined as potential difference and is symbolized by V. Current is defined as the rate of flow of electric charge and is symbolized by I. Resistance opposes current flow and is measured in ohms (Ω). Ohm's law states that voltage is directly proportional to current, where the constant of proportionality is resistance. The standard voltage for single-phase AC supply in homes is 230V.