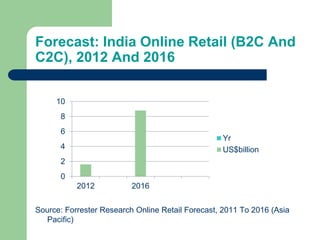
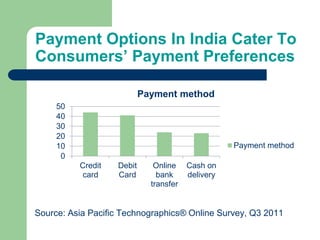
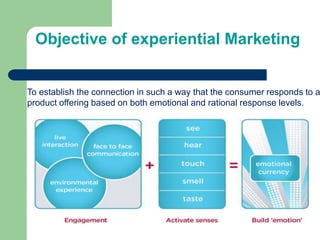
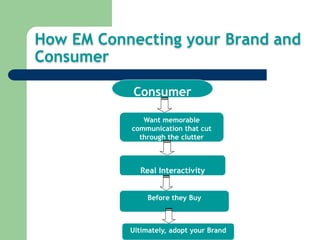
Ecommerce in India is growing rapidly. Online retail sales in India are forecast to increase from $2 billion in 2012 to $10 billion in 2016. Localization is crucial for ecommerce success in India due to specific consumer demands like convenient free shipping and returns. Payment options must also be highly localized to cater to Indian consumers' preferences like cash on delivery. Experiential marketing, buzz marketing, brand communities, and direct marketing are effective strategies for ecommerce retailers to engage customers in India. Flexibility is key as the ecommerce industry and regulatory environment continue to evolve.