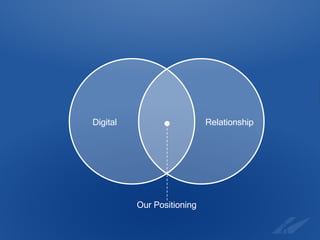
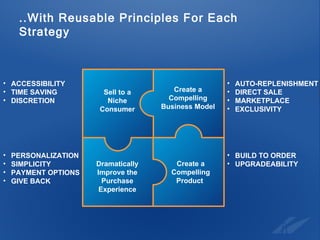
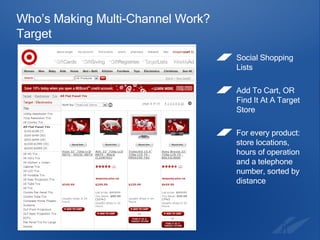
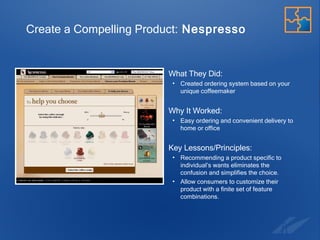
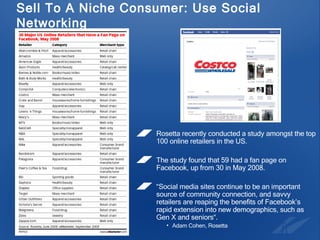
The document discusses the evolution and strategies of e-commerce, highlighting its growth to a $12 billion market and the importance of collaboration in the industry. It emphasizes the need for businesses to create compelling products, improve the purchasing experience, and effectively sell to niche consumers. Recommendations for future e-commerce practices include fostering brand-retailer collaboration and utilizing insights to enhance customer engagement and satisfaction.