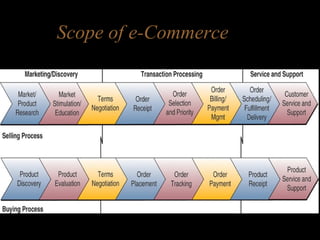
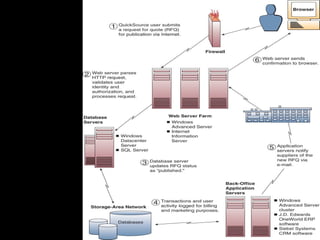
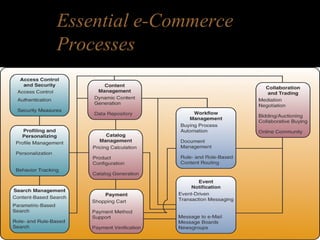
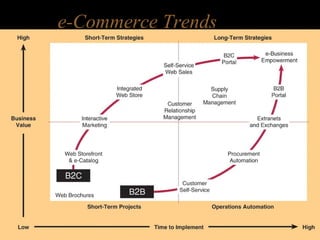
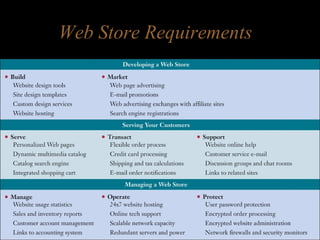
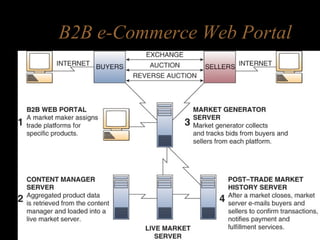
Electronic commerce encompasses the entire online process of developing, marketing, selling, delivering, servicing, and paying for products and services. It occurs through various models including business-to-consumer, business-to-business, and consumer-to-consumer. Successful e-commerce requires integrated customer-focused processes, secure transactions, interactive catalogs and ordering, and online customer support.