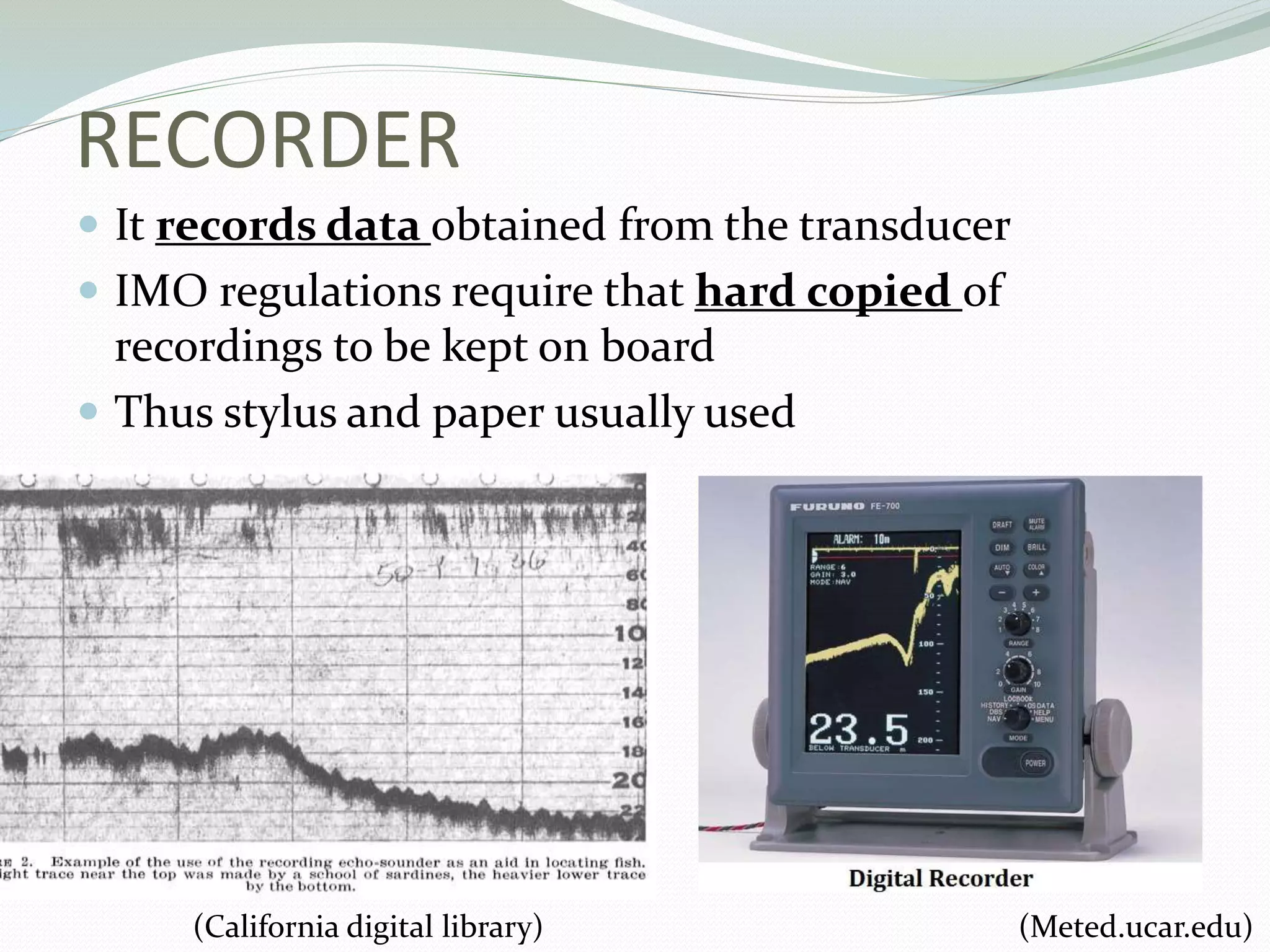
The document provides a comprehensive overview of echo sounders, which are devices used to measure water depth by sending sound pulses and measuring the time taken for echoes to return. It discusses the working mechanism, key components such as transducers and recorders, and factors that affect accuracy, including temperature and salinity variations. Additionally, the document highlights potential errors in measurements and includes a bibliography for further reference.