Embed presentation
Download to read offline



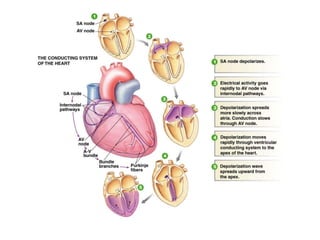
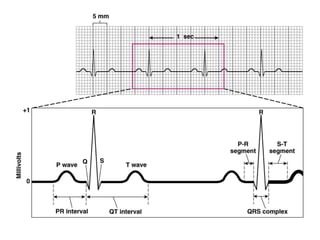
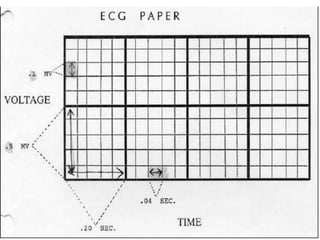
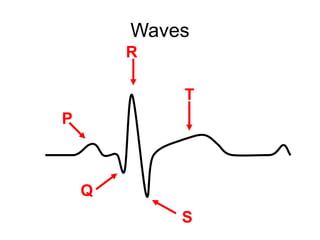



The document discusses electrocardiography (ECG), which is the procedure used to record the electrical activity of the heart. An ECG machine records potential differences between two sites on the body produced by the heart's electrical activity. The ECG provides a characteristic waveform due to the spread of depolarization and repolarization with each heartbeat. Key aspects of the ECG include the P, Q, R, S, and T waves which correspond to atrial and ventricular depolarization and repolarization, and intervals like the P-R and Q-T that measure timing of these processes. The ECG remains one of the most commonly used cardiovascular diagnostic procedures over 100 years after its introduction.