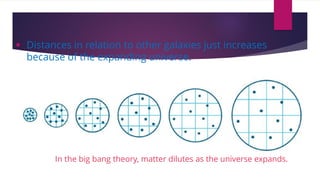
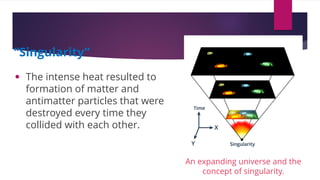
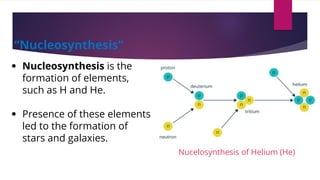
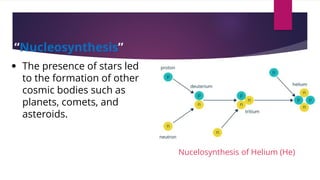
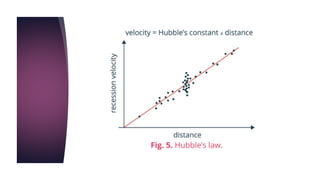
The big bang theory explains how the universe began approximately 13.8 billion years ago from a dense, hot singularity. The universe expanded rapidly from this initial state in a process known as inflation. As it expanded, light elements like hydrogen and helium formed. Evidence for the big bang includes the expansion of the universe observed through Hubble's law, the cosmic microwave background radiation leftover from the early universe, and abundances of light elements. Georges Lemaître first proposed the theory in the 1920s, with Edwin Hubble and later Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson providing crucial observational evidence through their discoveries.