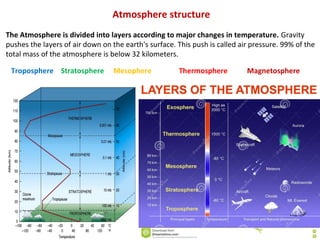
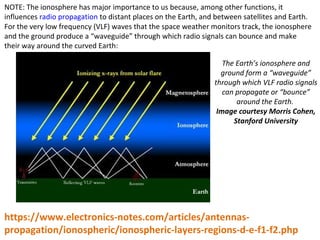
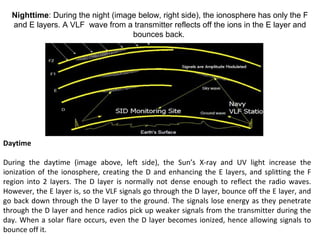
The atmosphere is structured in layers, each having distinct temperature variations and functions, including the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and magnetosphere. The ionosphere, a critical part of the atmosphere, influences radio wave propagation, particularly through the D, E, and F regions, which vary in ionization based on solar and cosmic activity. Additionally, phenomena such as solar flares and lightning can dramatically impact radio communications by altering ionospheric density and layers.