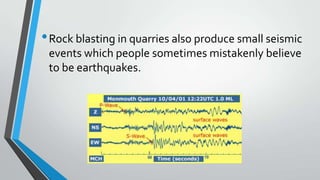
Earthquakes can be caused both naturally and artificially. Naturally occurring earthquakes are the result of seismic activity in the earth's crust. They can be measured using seismometers and are reported on the moment magnitude scale or Richter scale depending on their size. Artificial earthquakes have been caused by underground nuclear explosions, which have generated moderate quakes felt up to 50km away. Rock blasting in quarries can also cause small seismic events that are sometimes misidentified as natural earthquakes. Recent examples include North Korea's nuclear tests in 2006 and 2009, which were detected as earthquakes of magnitudes 3.9 and 4.5 in South Korea.