Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times

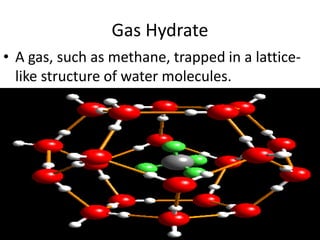




Gas hydrates are structures where gas like methane is trapped in a crystalline lattice of water molecules. Manganese nodules are rounded lumps on the ocean floor made of manganese and iron that also contain small amounts of copper, nickel and cobalt. While oil and natural gas from the ocean floor currently provide energy, gas hydrates form as bacteria break down organic matter trapped in ocean sediments and other resources extracted include salts, sand, gravel and manganese nodules.





