Embed presentation
Downloaded 41 times



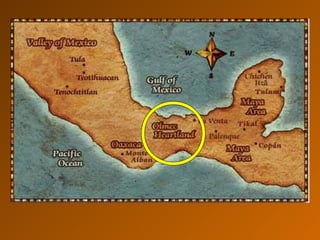








The document summarizes the major Mesoamerican civilizations that flourished between 1200 BCE to the 16th century CE. It discusses the Olmec as the first major civilization, followed by the rise of Teotihuacan as a center of trade and urban growth. The Maya are described as having a complex calendar system, hieroglyphic writing, and women playing important roles. It also covers the Toltecs who created the first conquest state based in Tula and brought metalworking to Mesoamerica.










