Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times

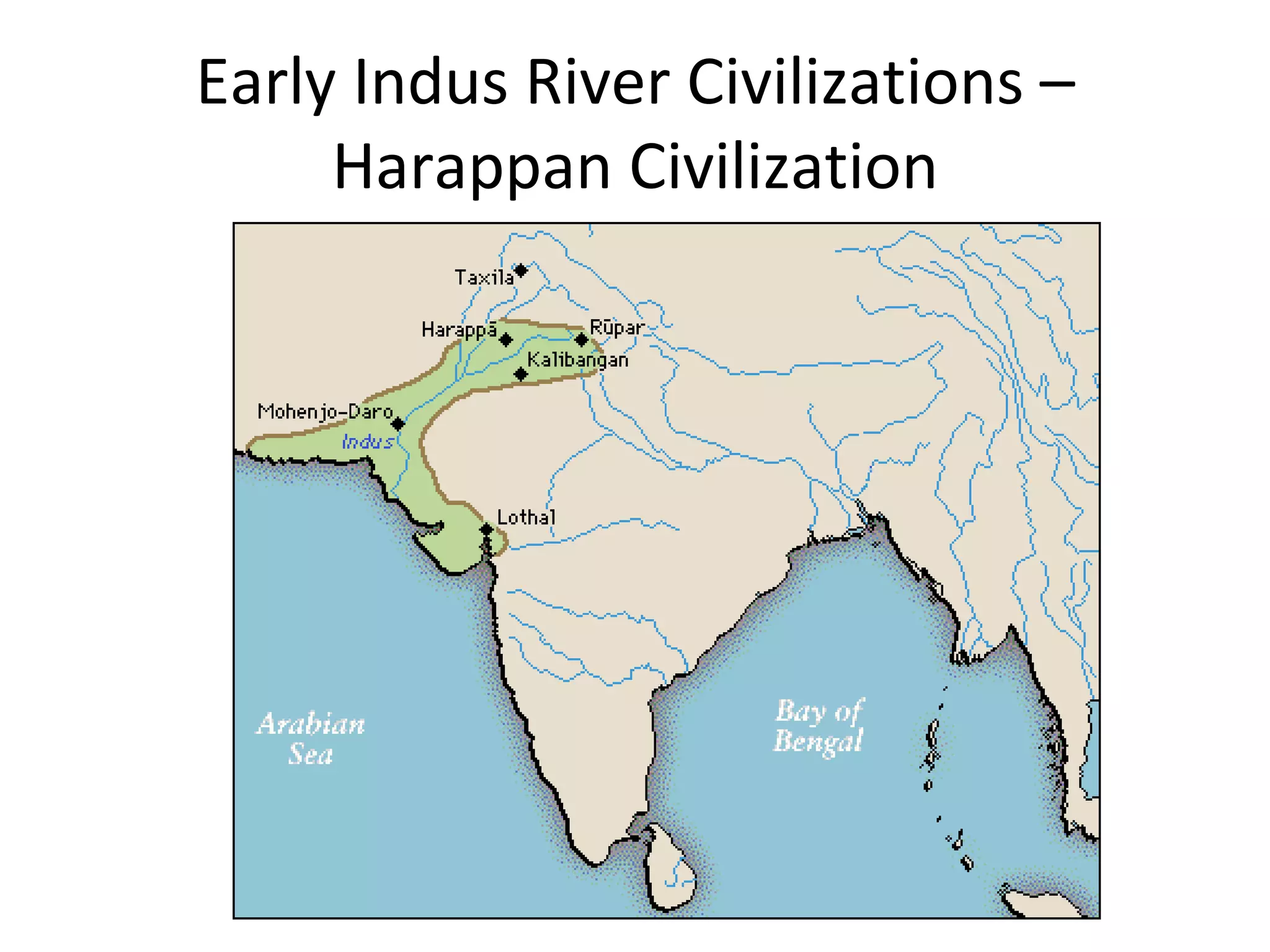




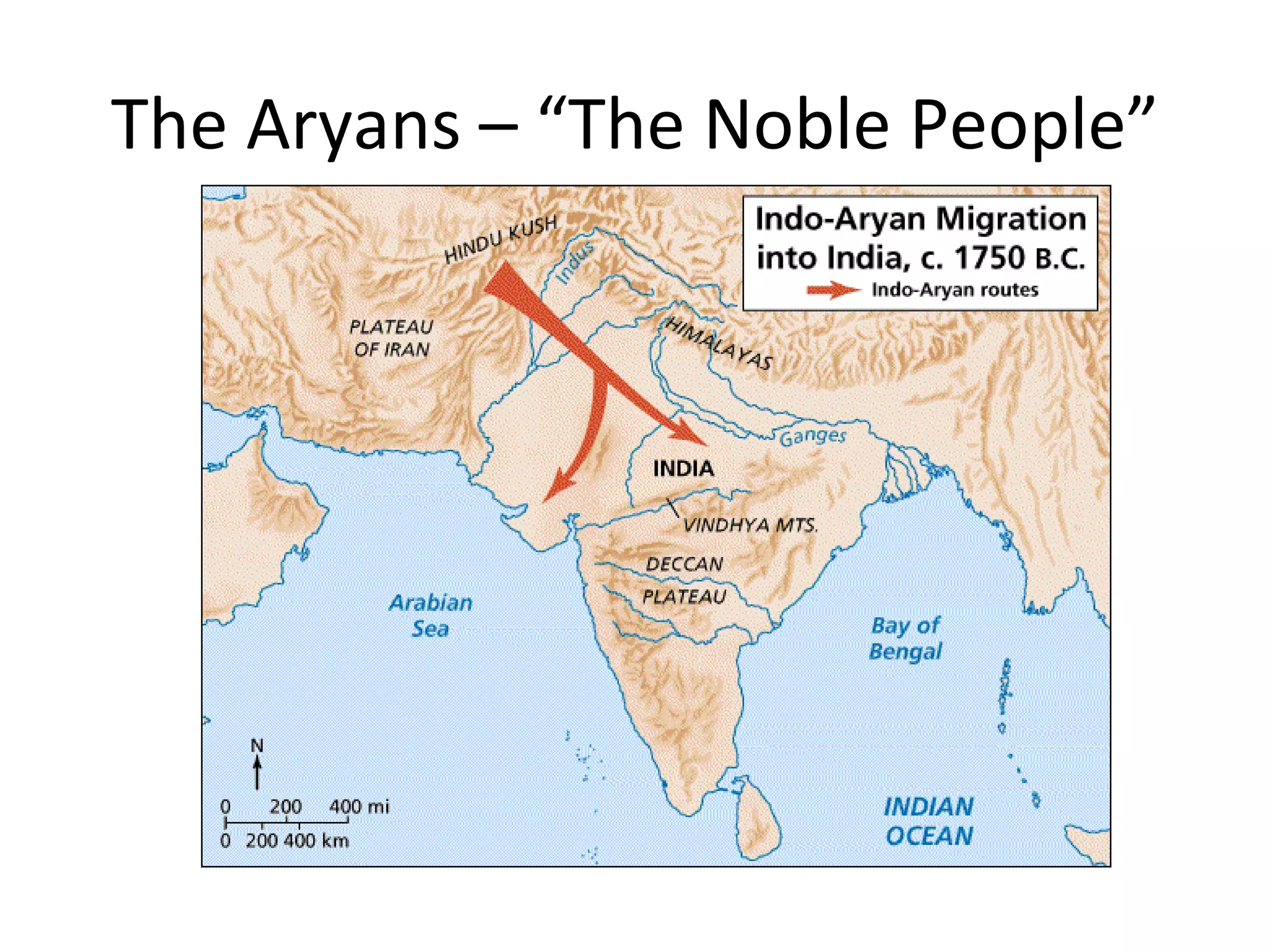





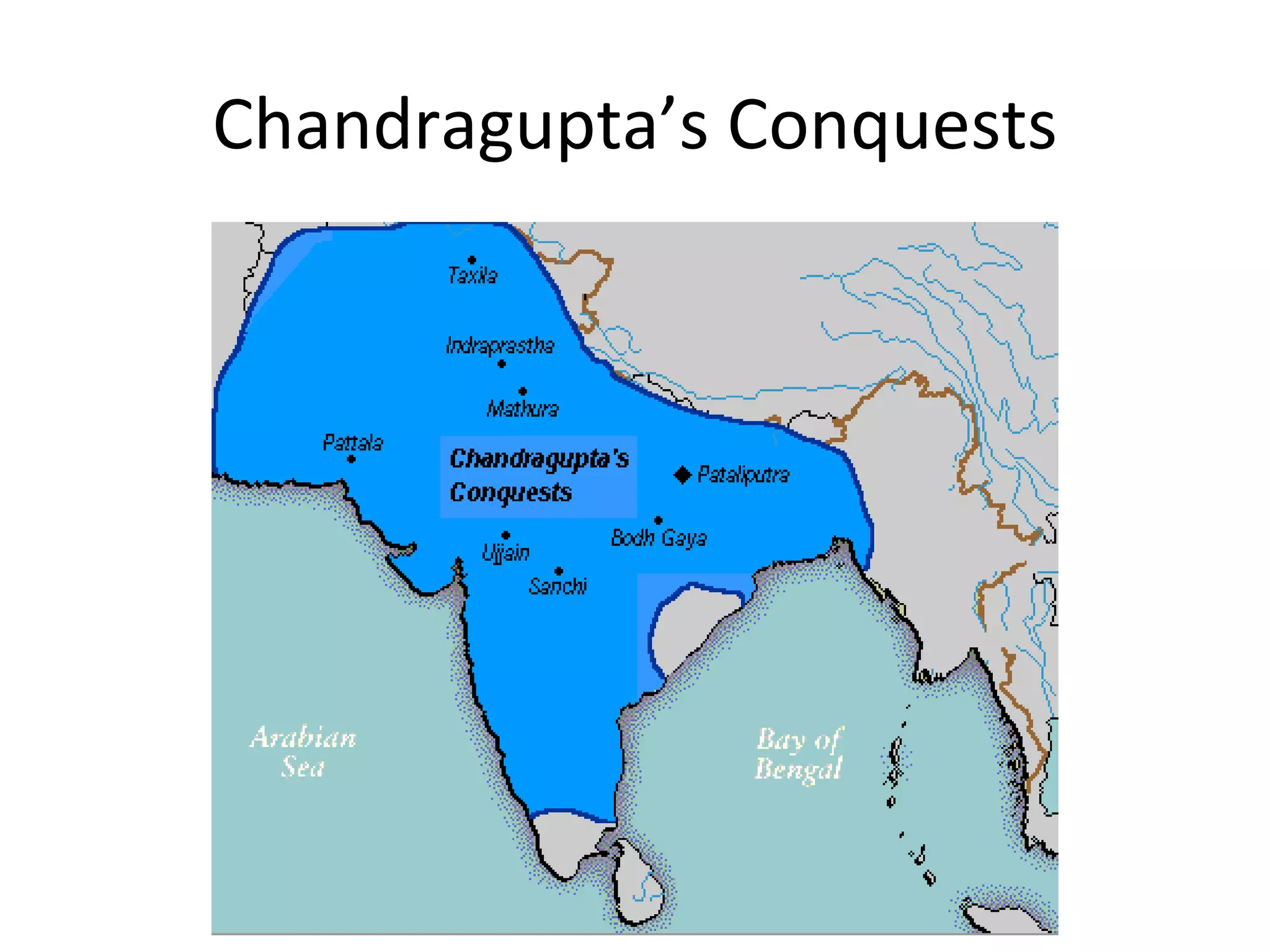

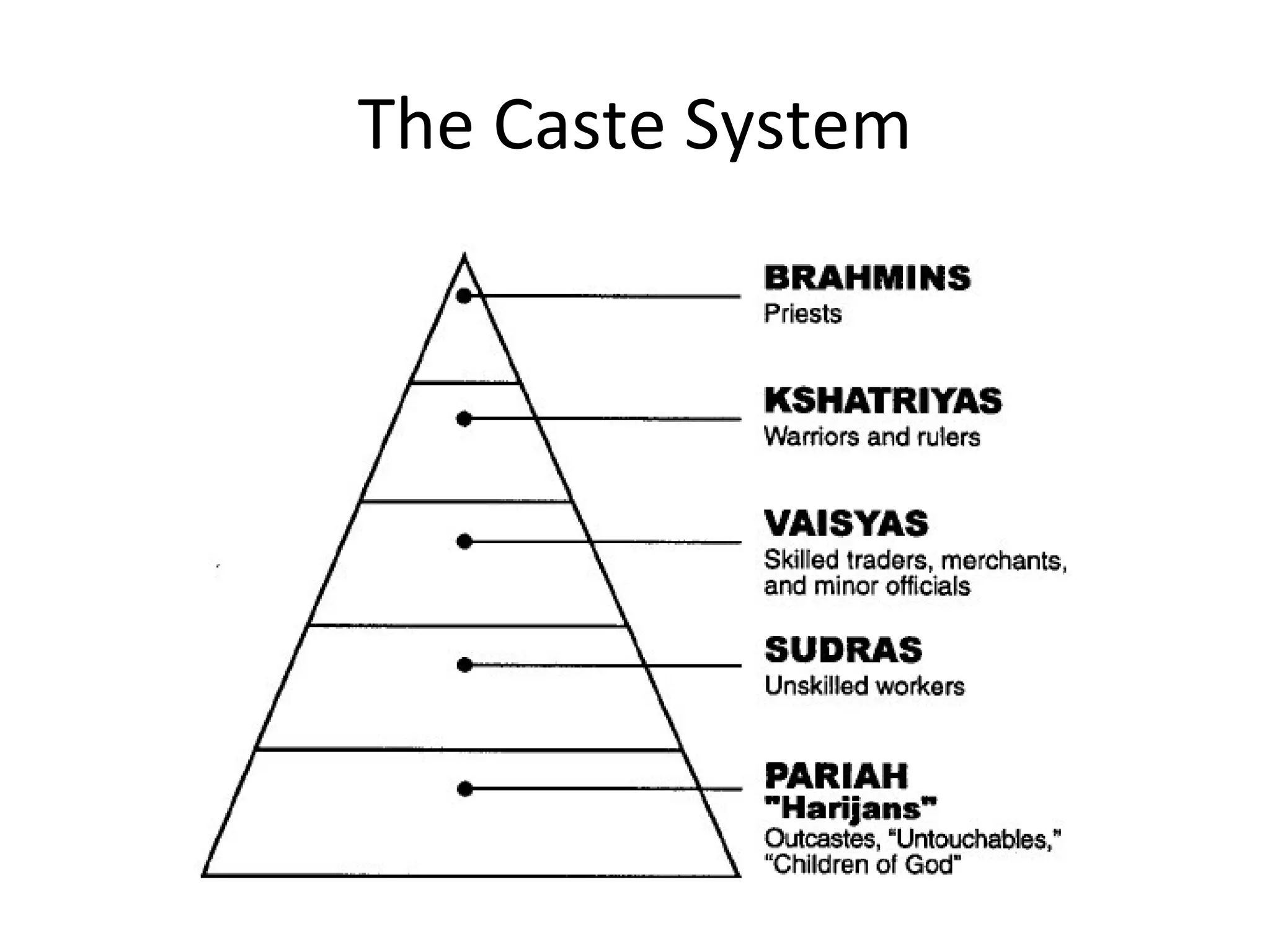





The document summarizes early civilizations and religions in India. It describes the Harappan civilization and the arrival of the Aryans who composed sacred texts known as the Vedas. It also outlines the development of Hinduism, including the caste system, key beliefs like karma and reincarnation, major gods like Brahman, Vishnu, and Shiva, and how Hinduism is also known as Sanatana Dharma.


















