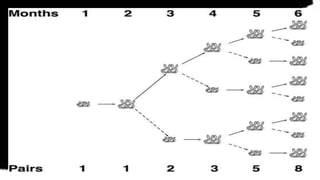
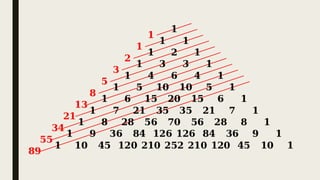
The document discusses the Fibonacci sequence and its applications, highlighting the Fibonacci problem related to rabbit reproduction. It also covers key mathematical developments, including the separation of trigonometry from astronomy, and the contributions of mathematicians like Luca Pacioli and John Napier. Furthermore, it touches on Newton's Principia Mathematica and its foundational role in understanding celestial motions through mathematics.