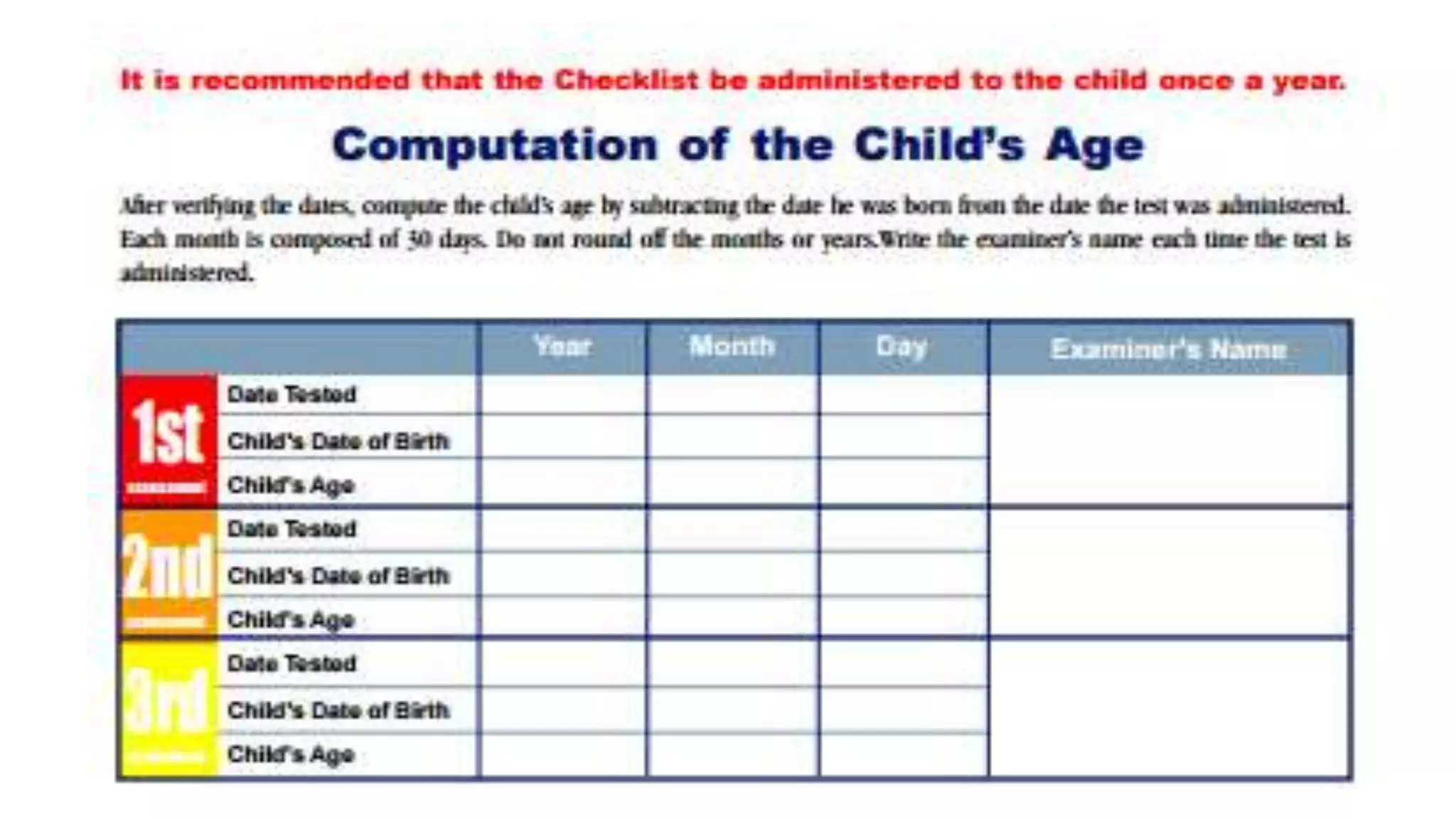
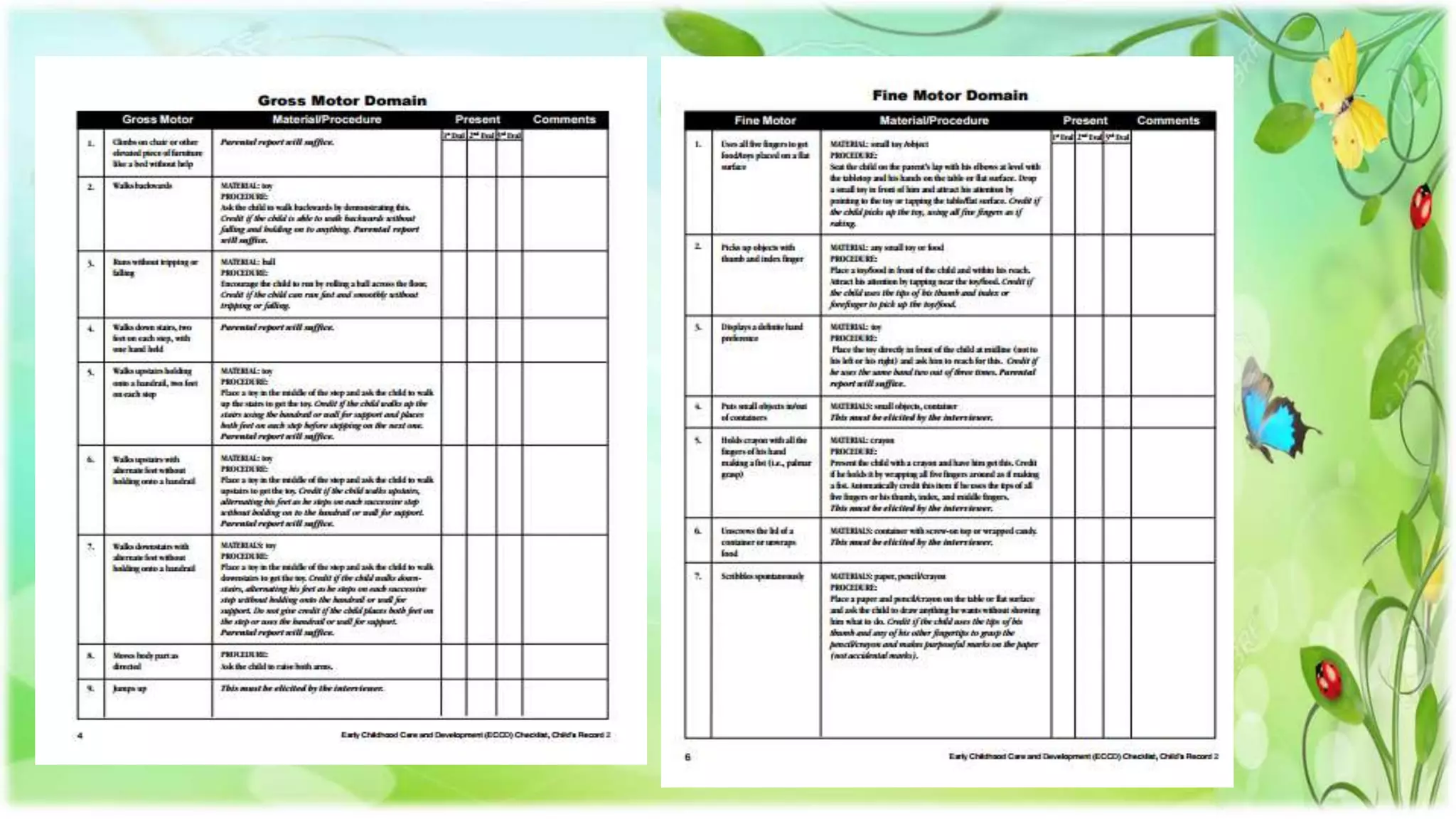
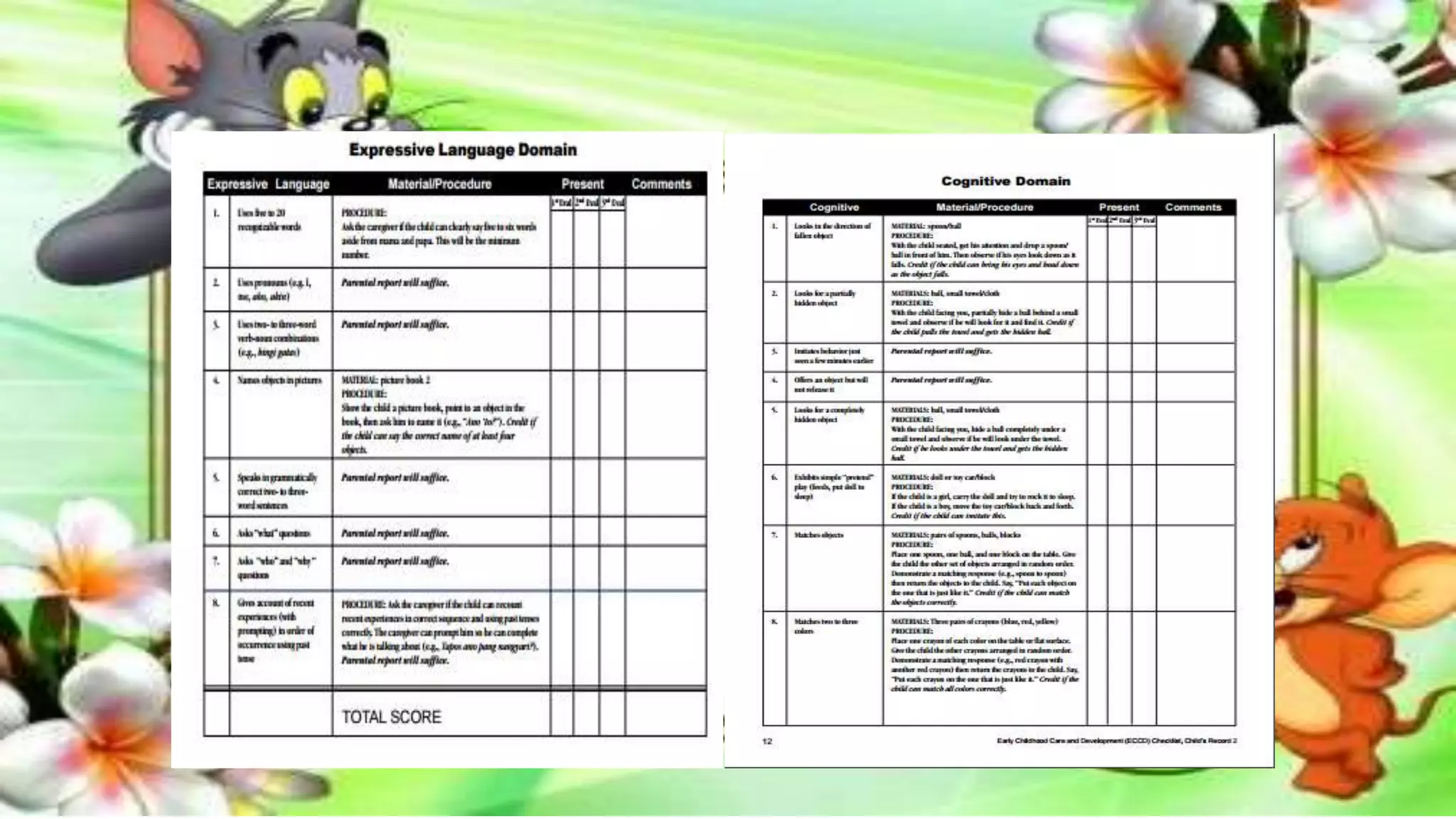
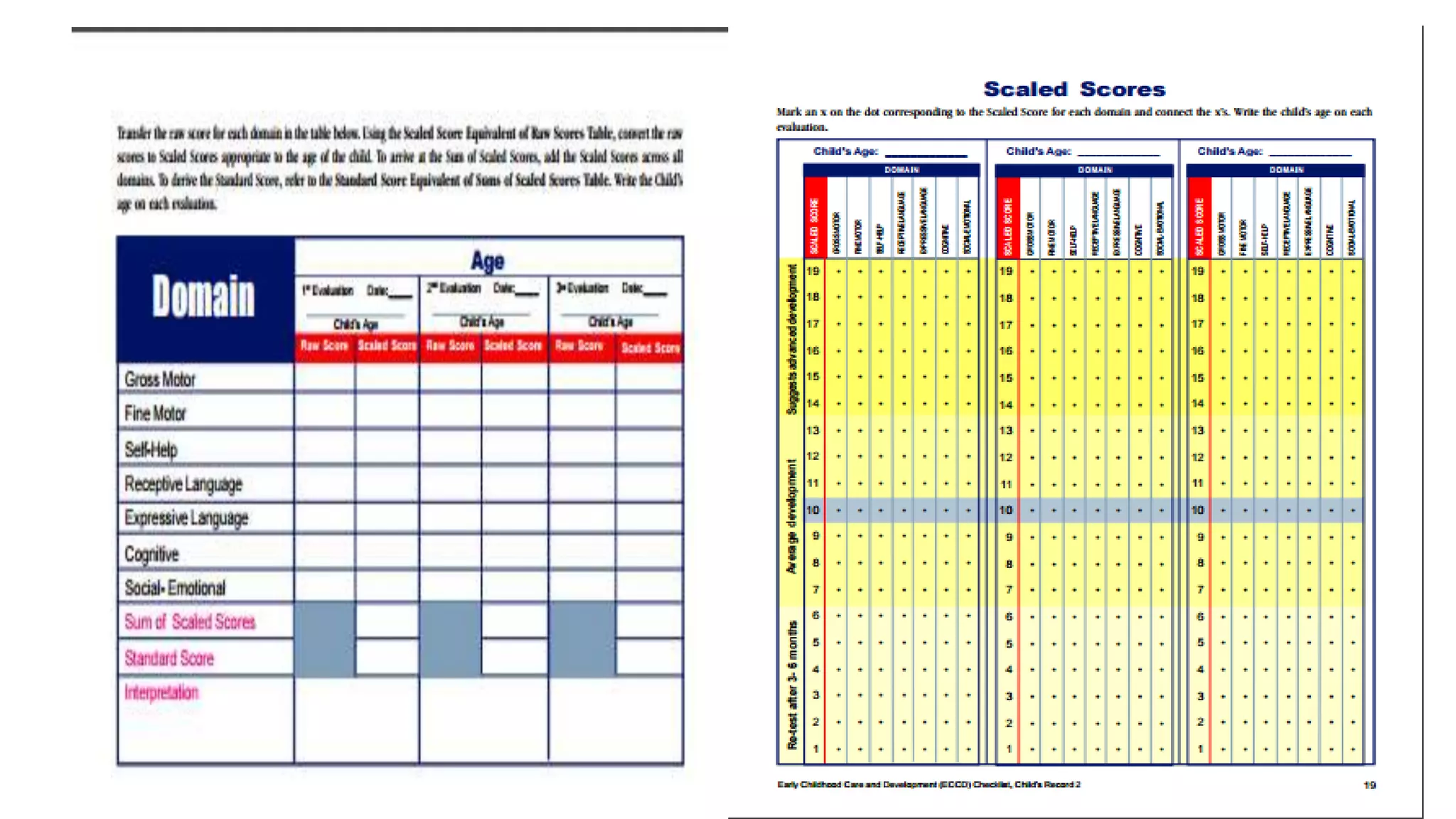
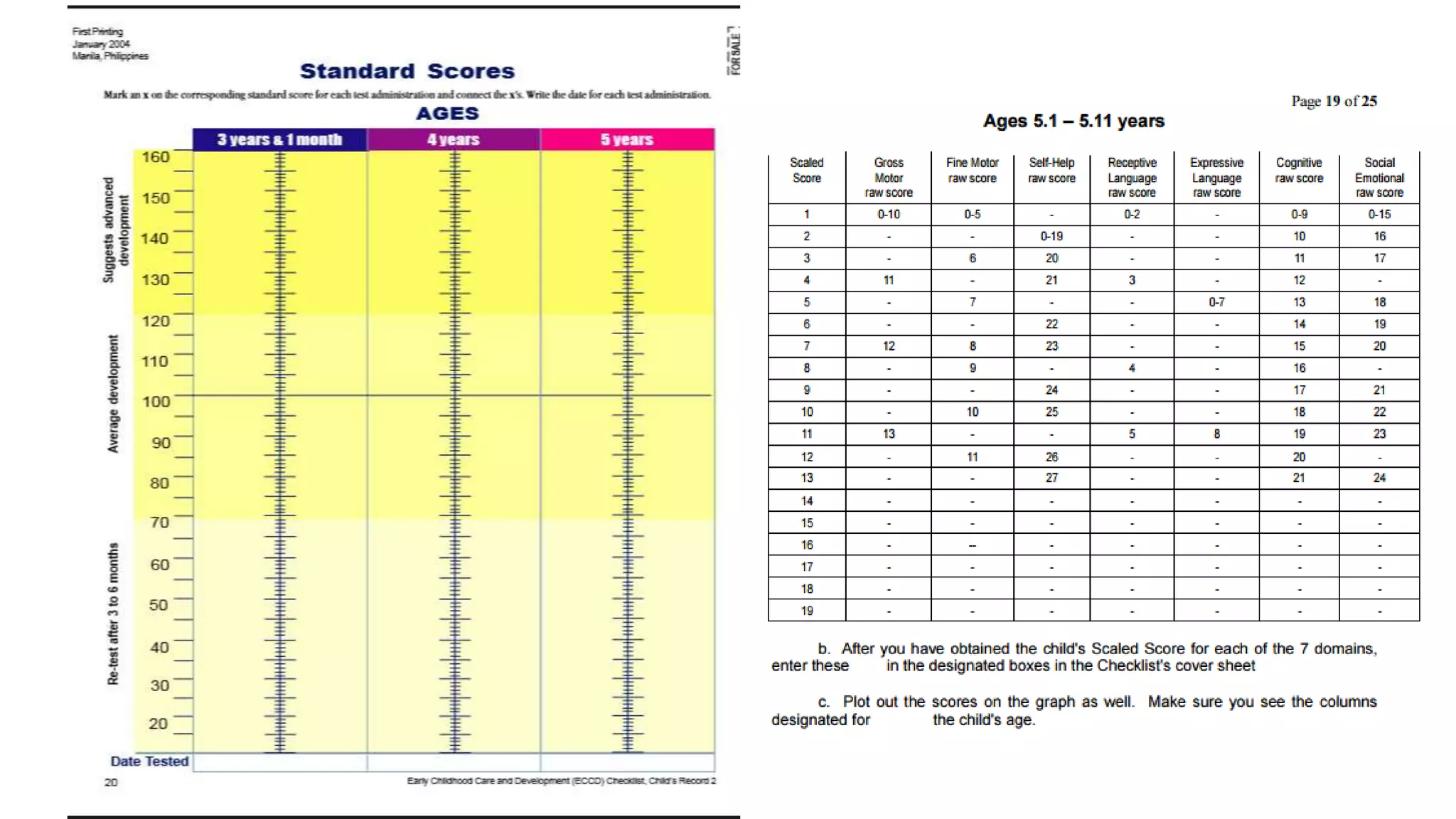
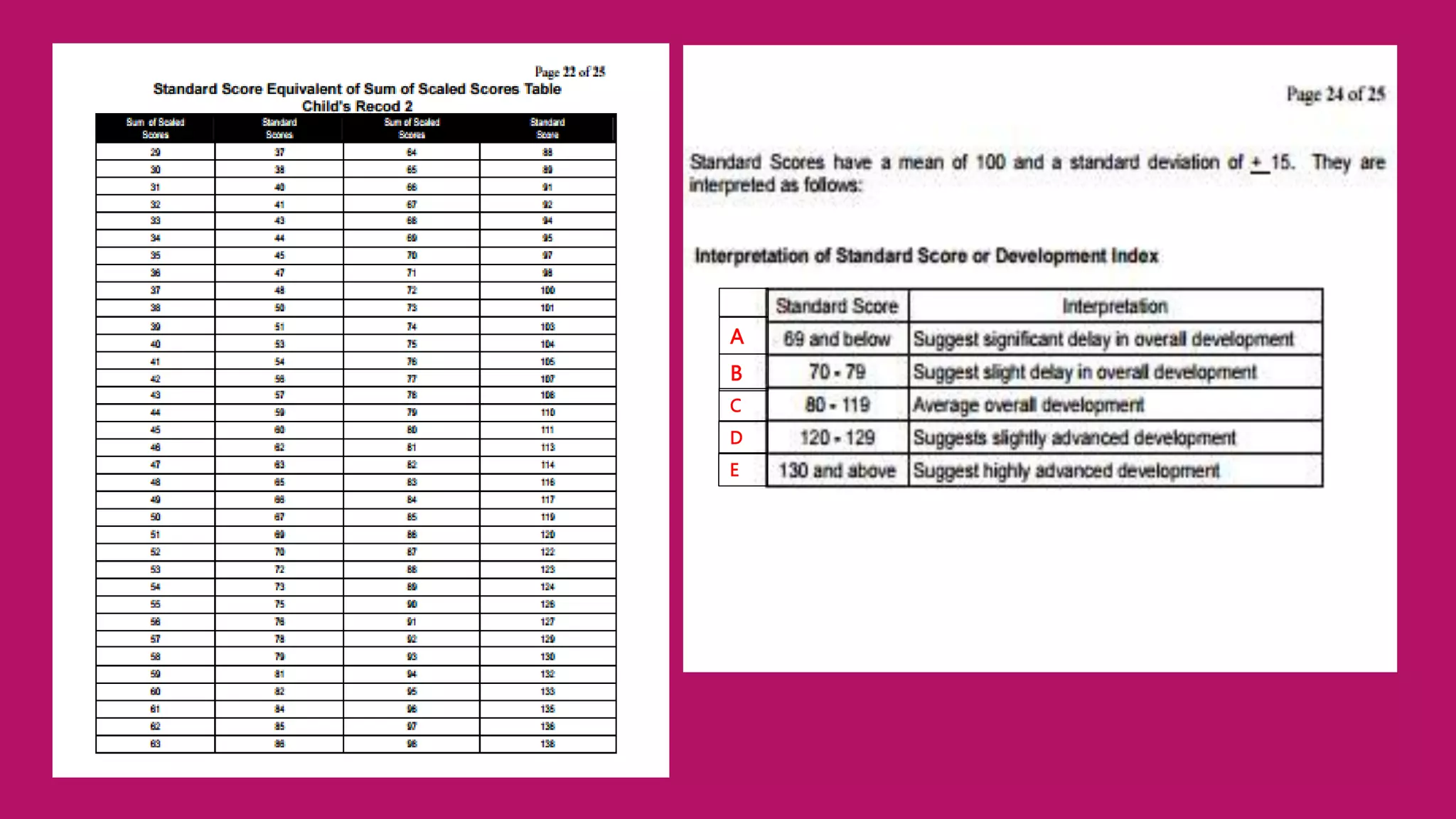
The revised Philippine ECCD checklist is administered to Filipino children ages 3-5 to assess their development across 7 domains: gross motor skills, fine motor skills, self-help, receptive language, expressive language, cognitive skills, and social-emotional skills. It is administered quarterly for children aged 5 and aims to evaluate larger movements, hand-eye coordination, independence with routines, understanding of language, ability to communicate, thinking processes, and ability to interact with others.