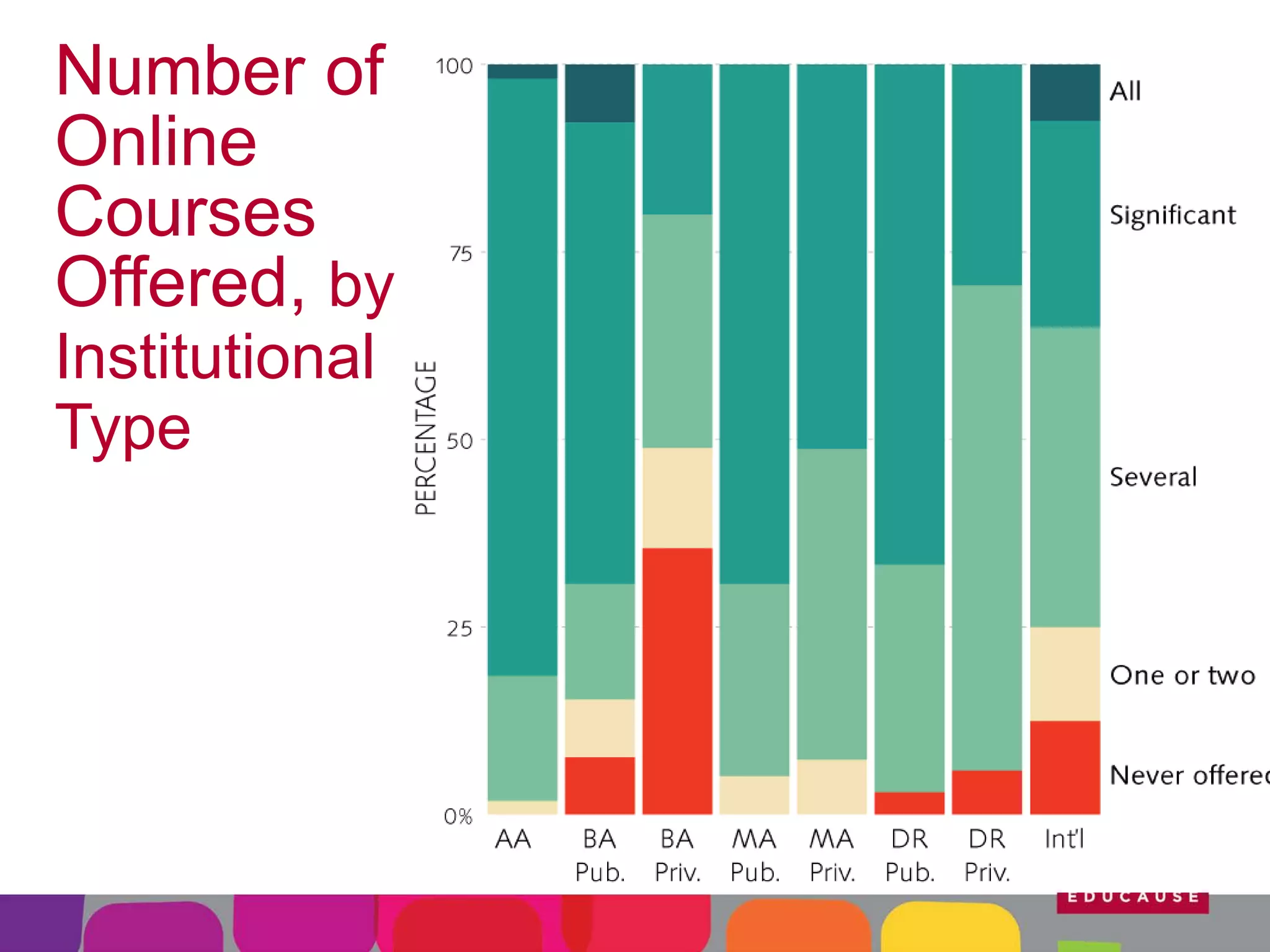
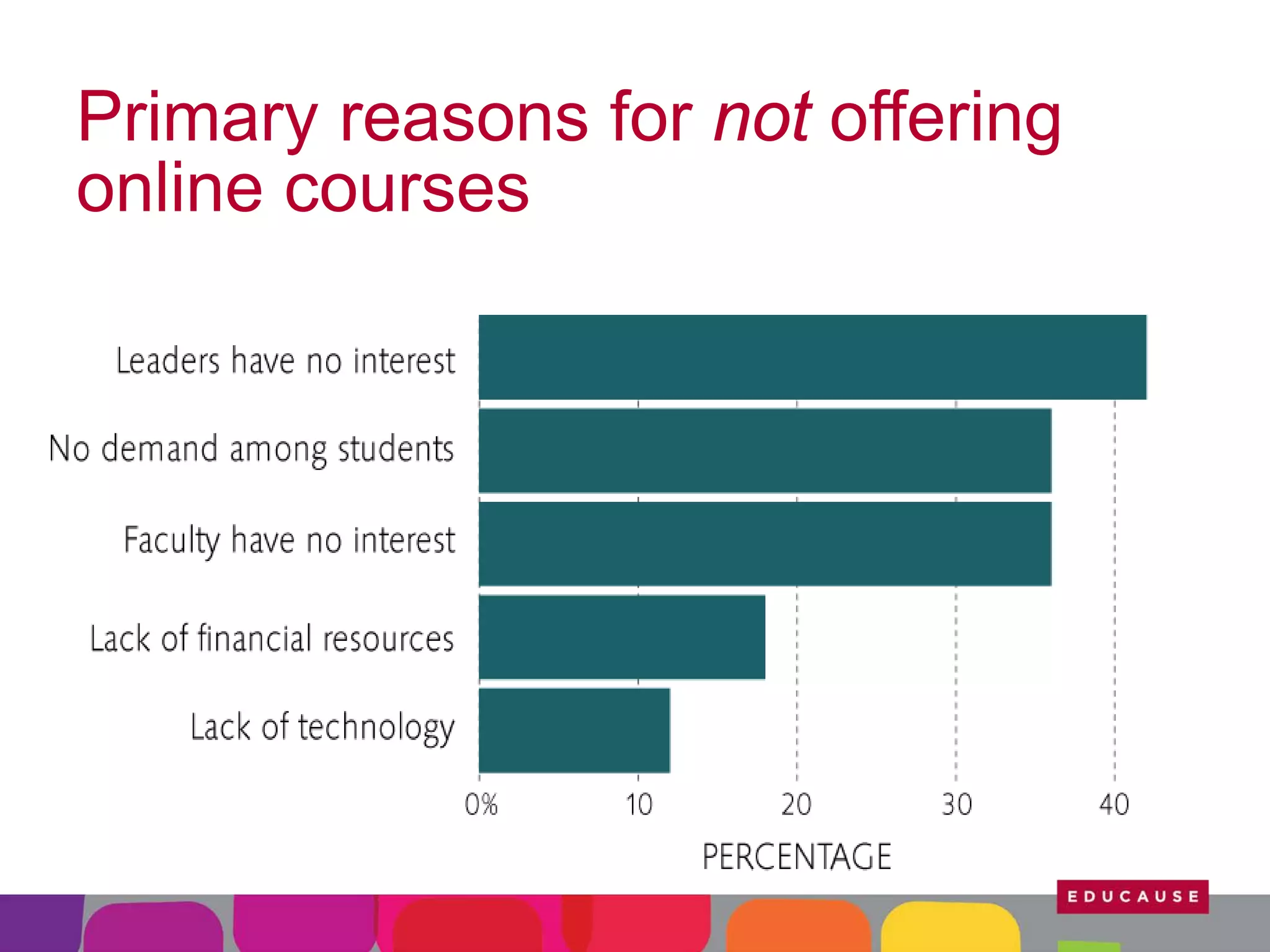
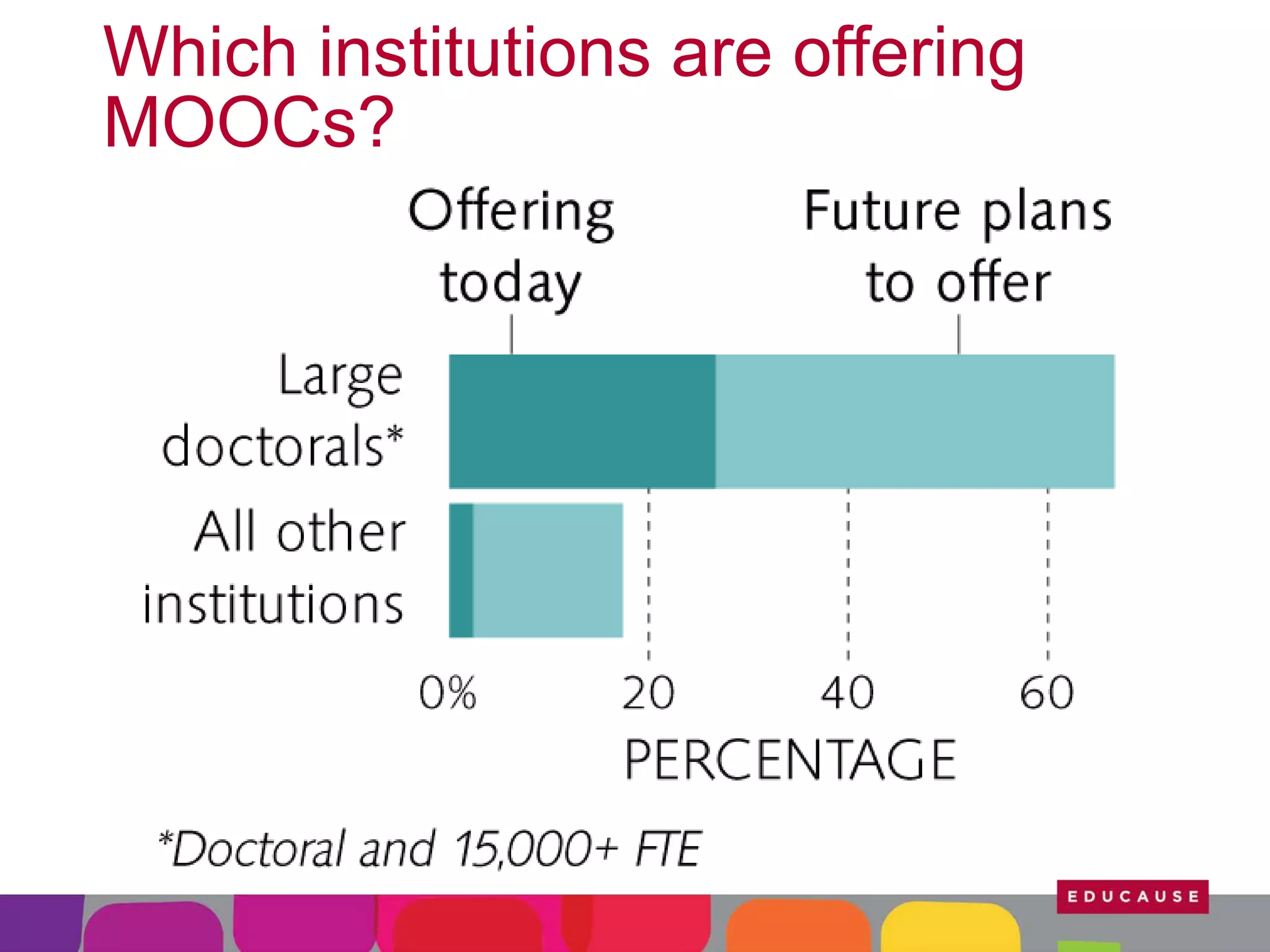
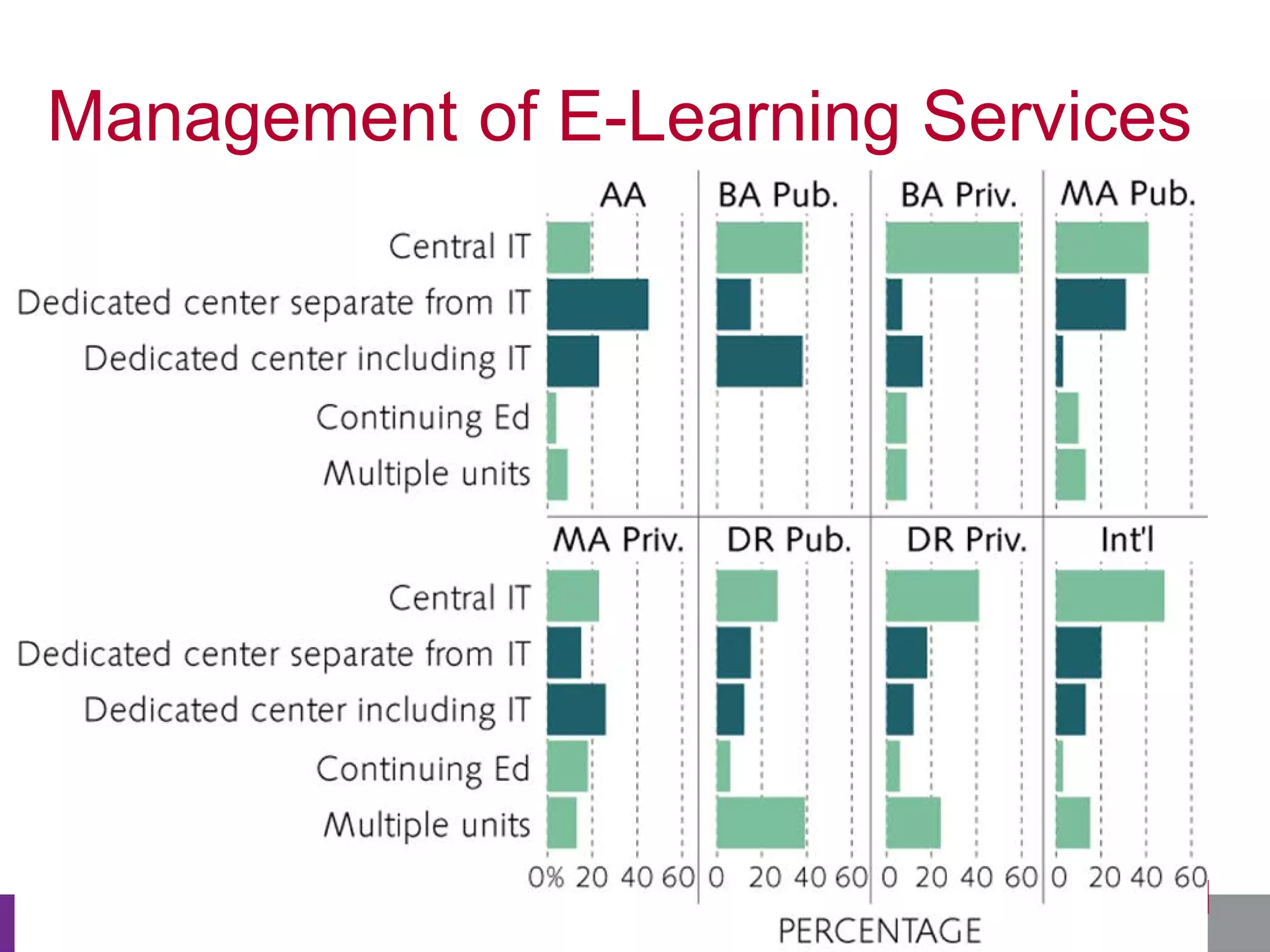
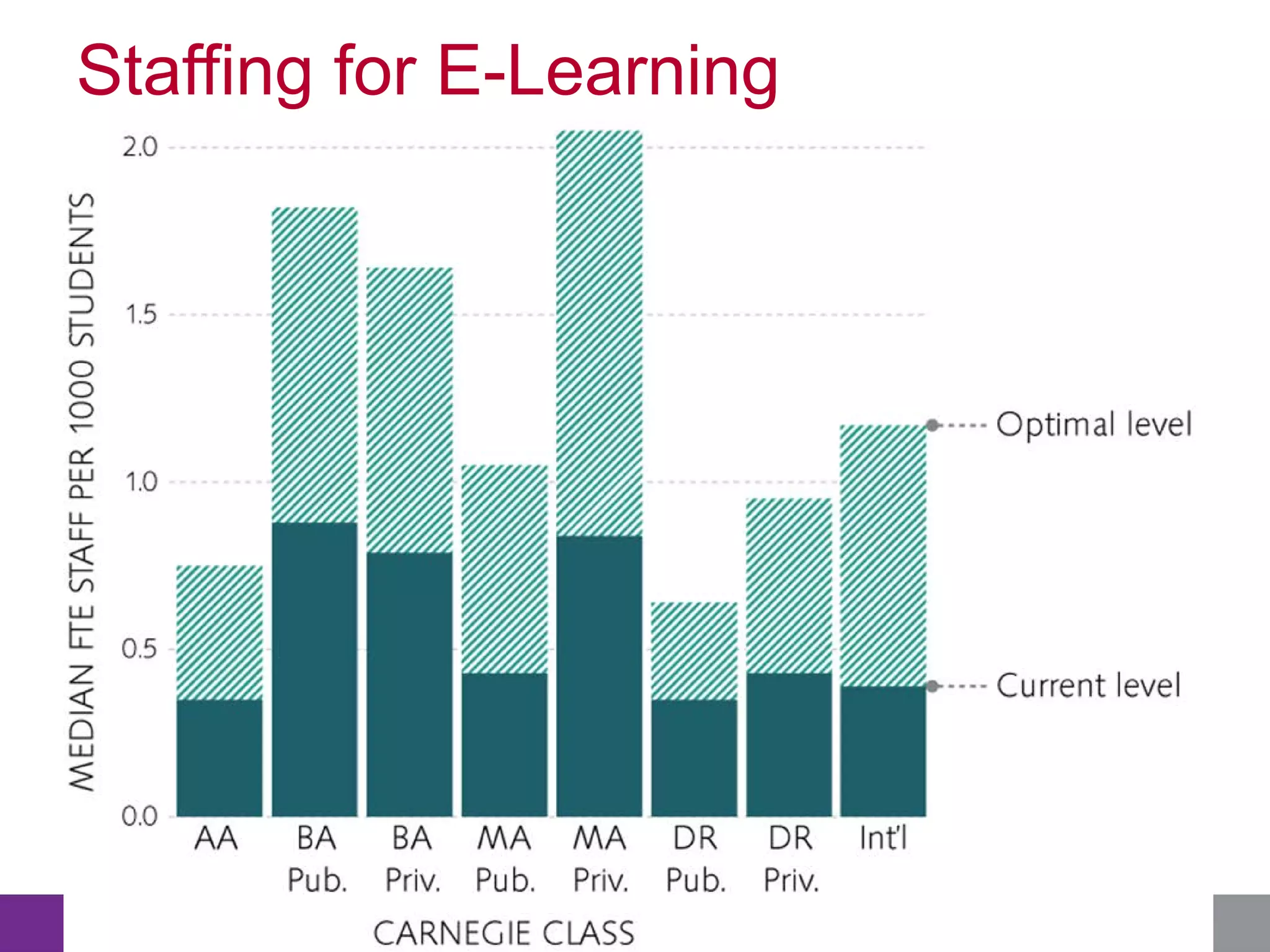
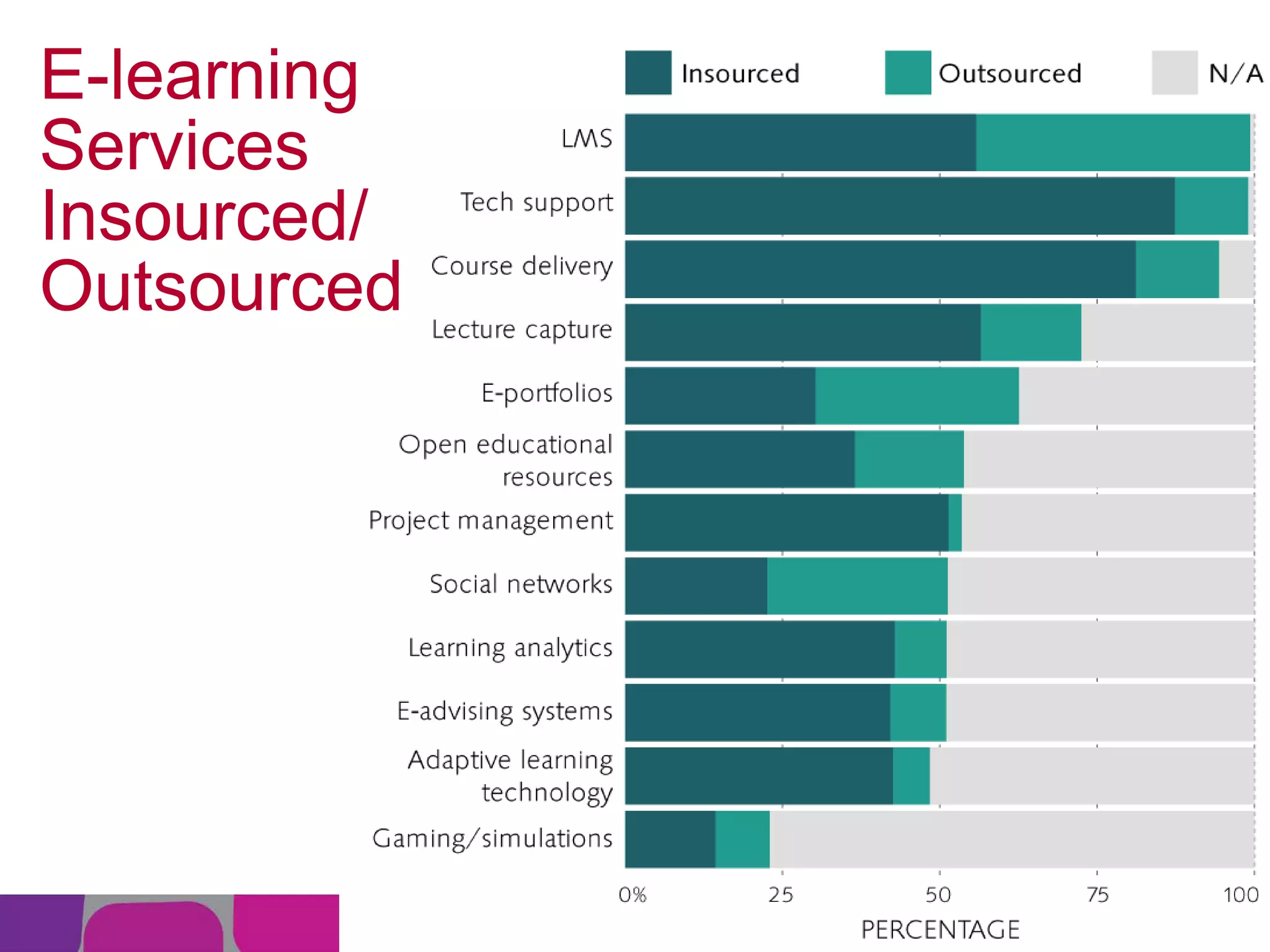
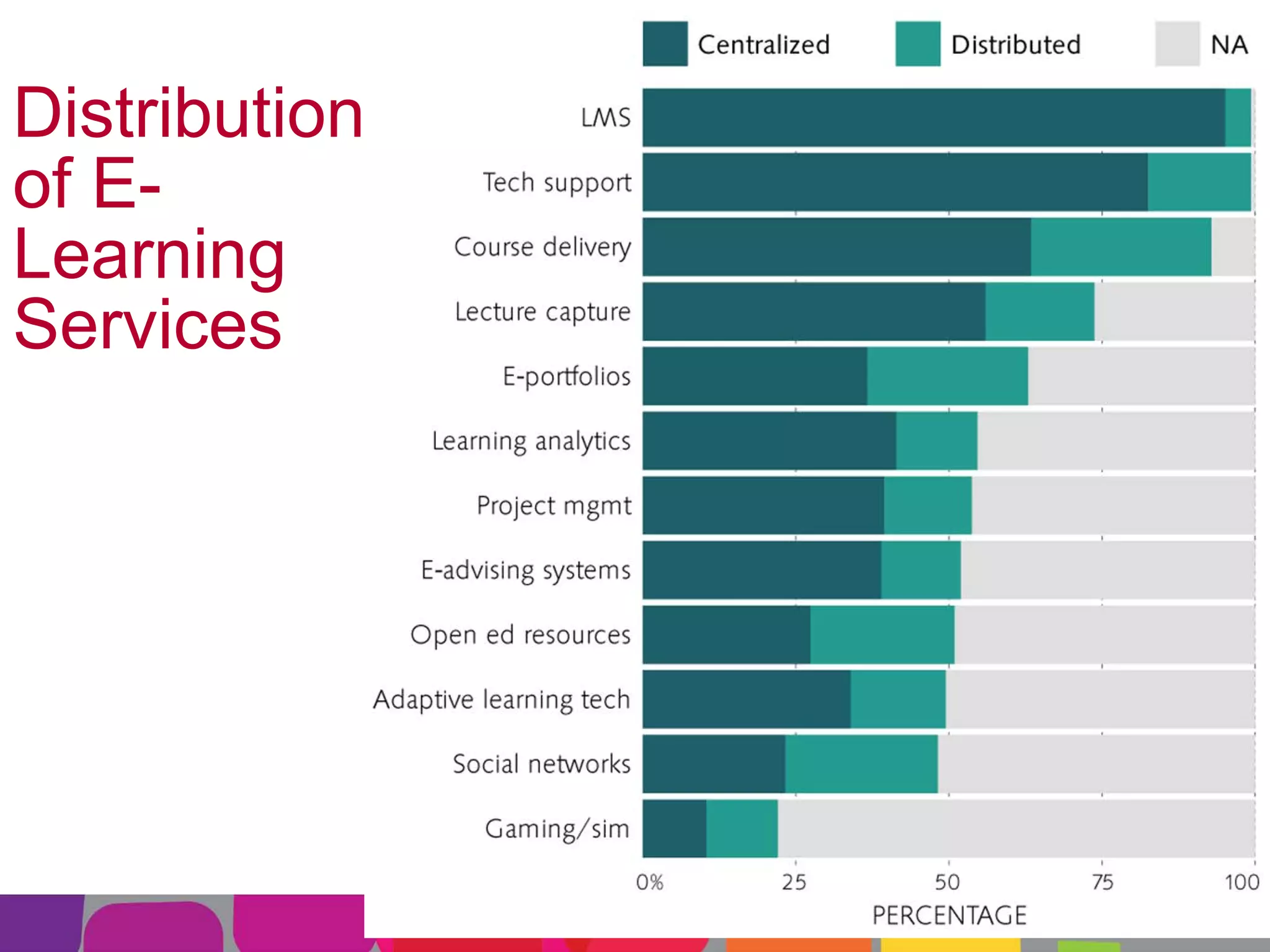
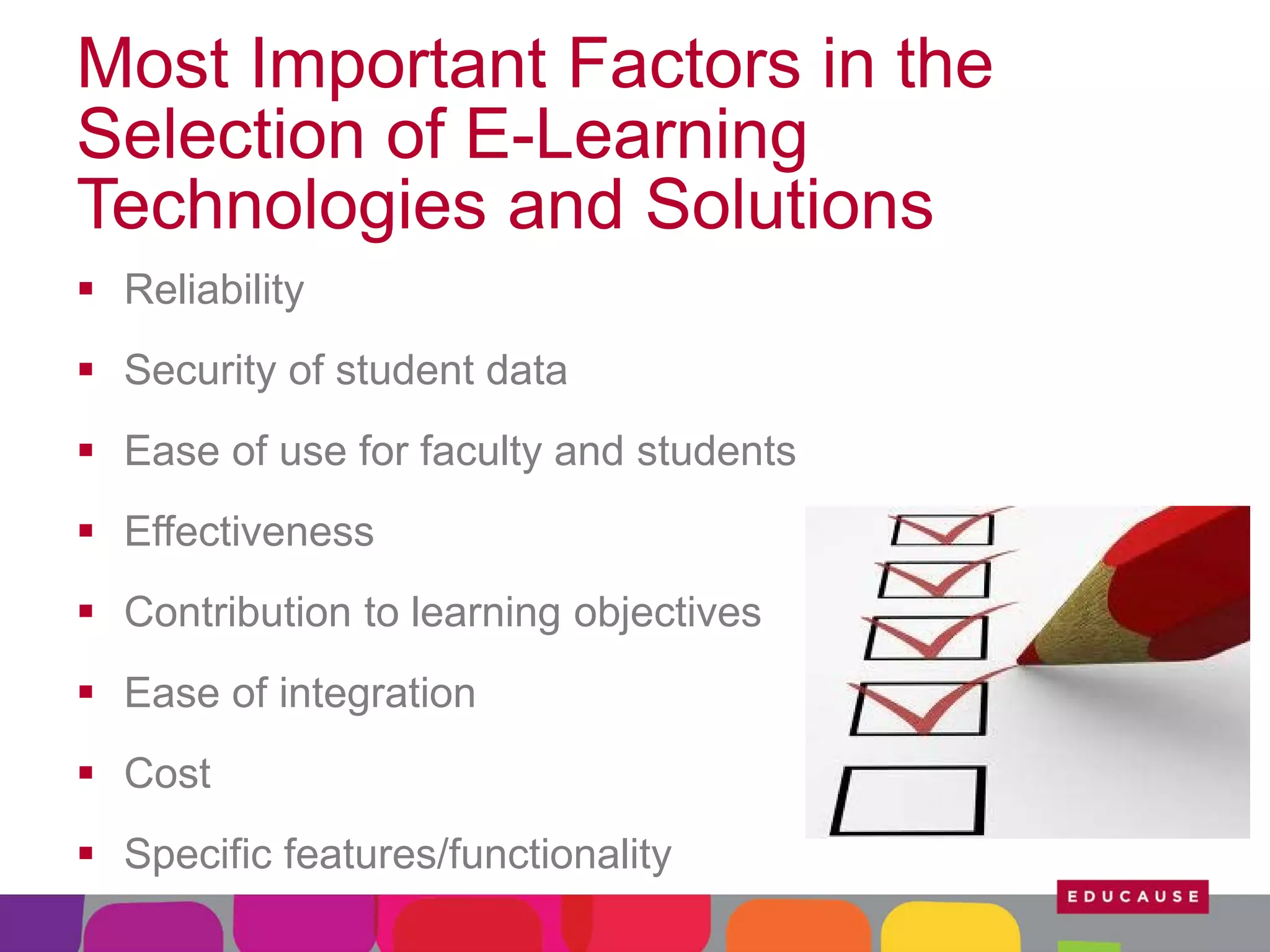
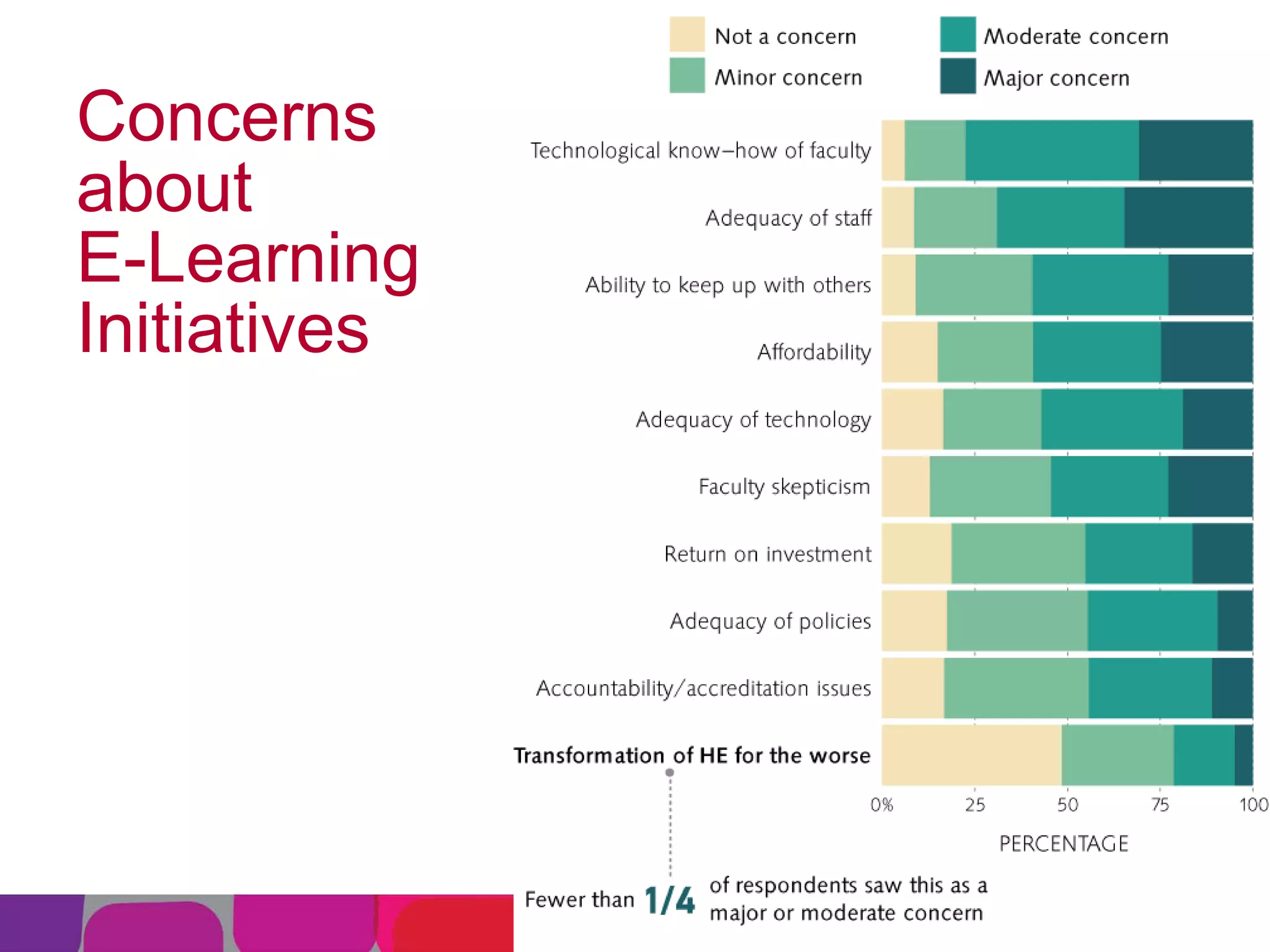
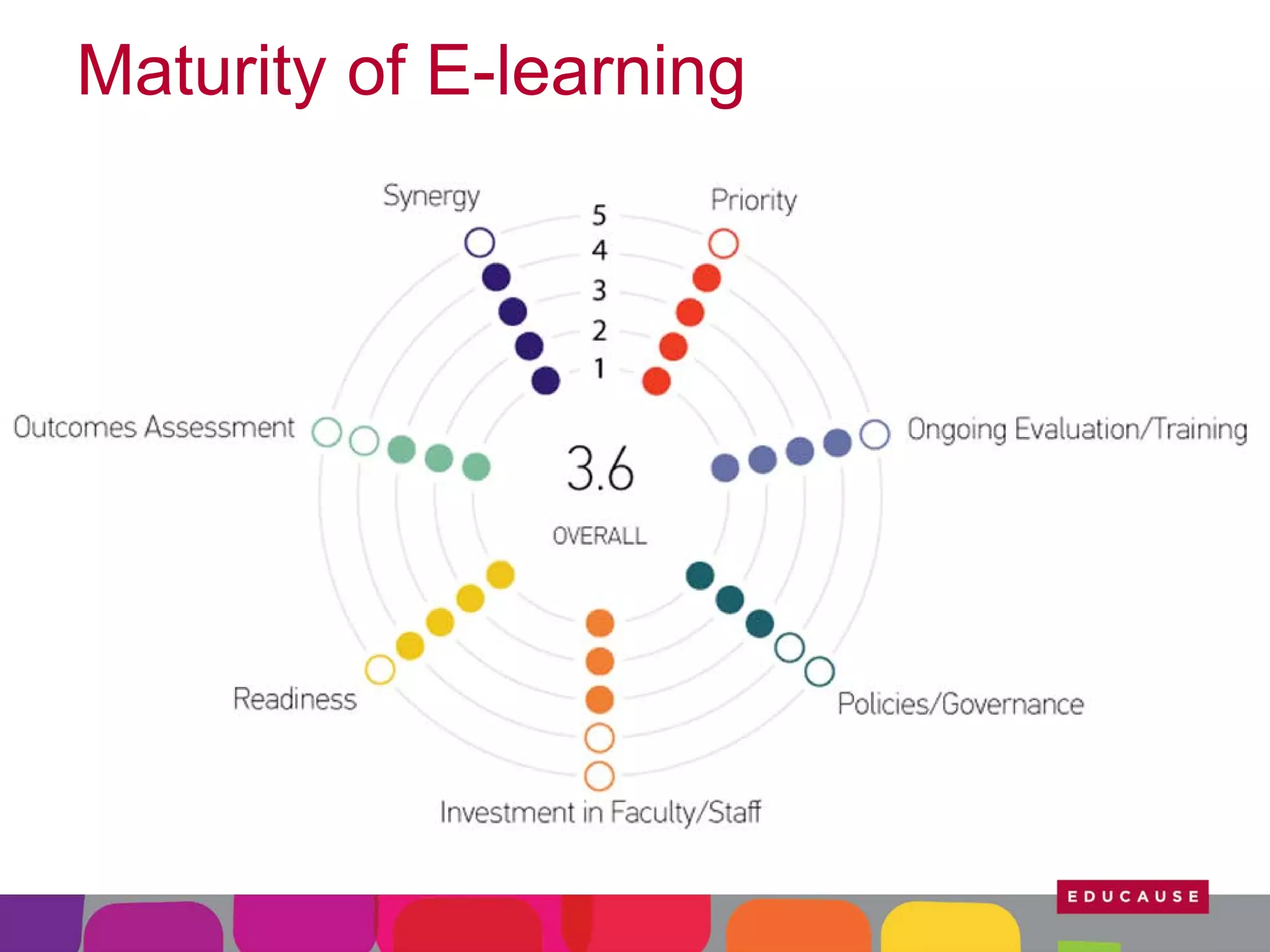
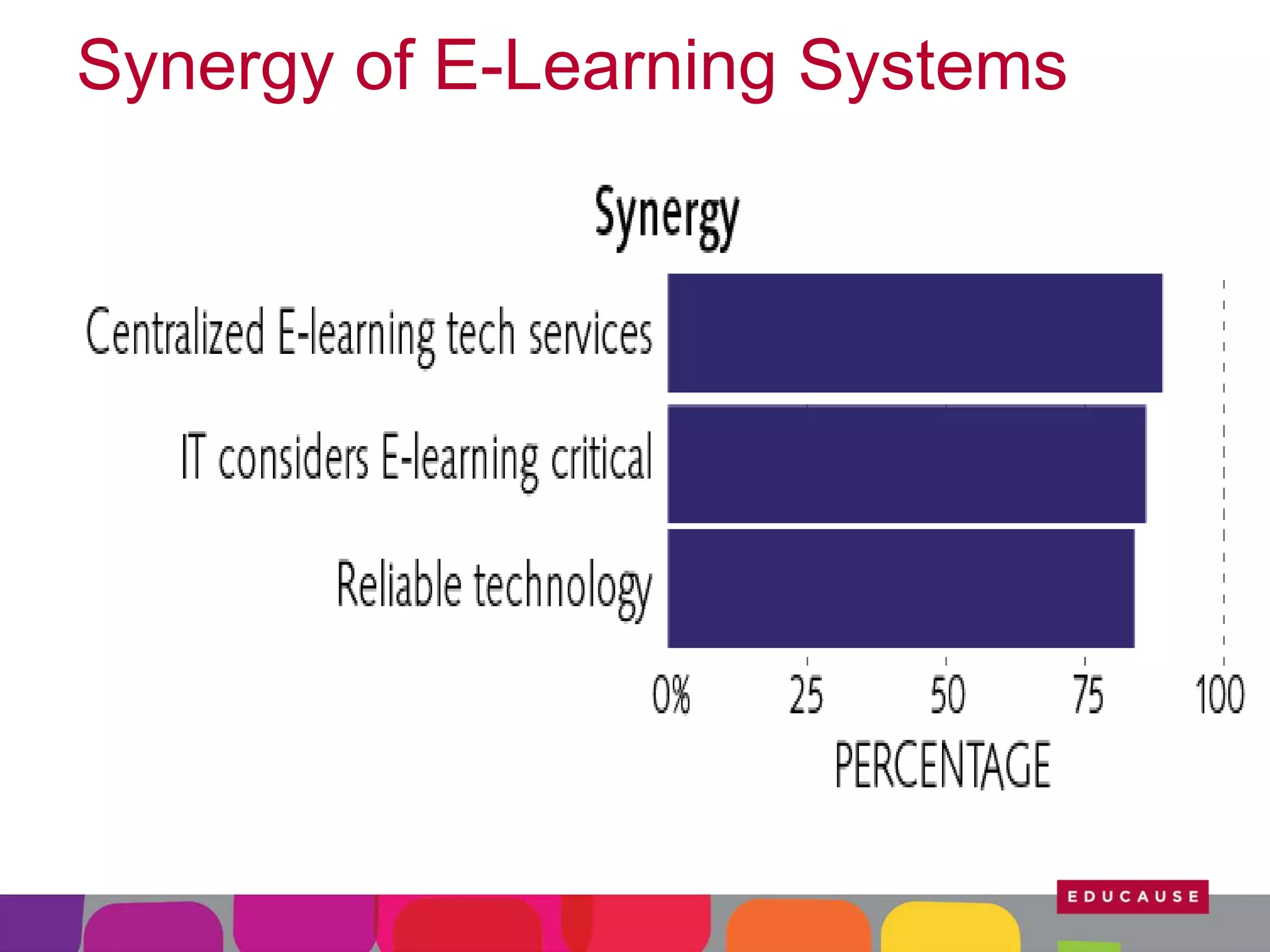
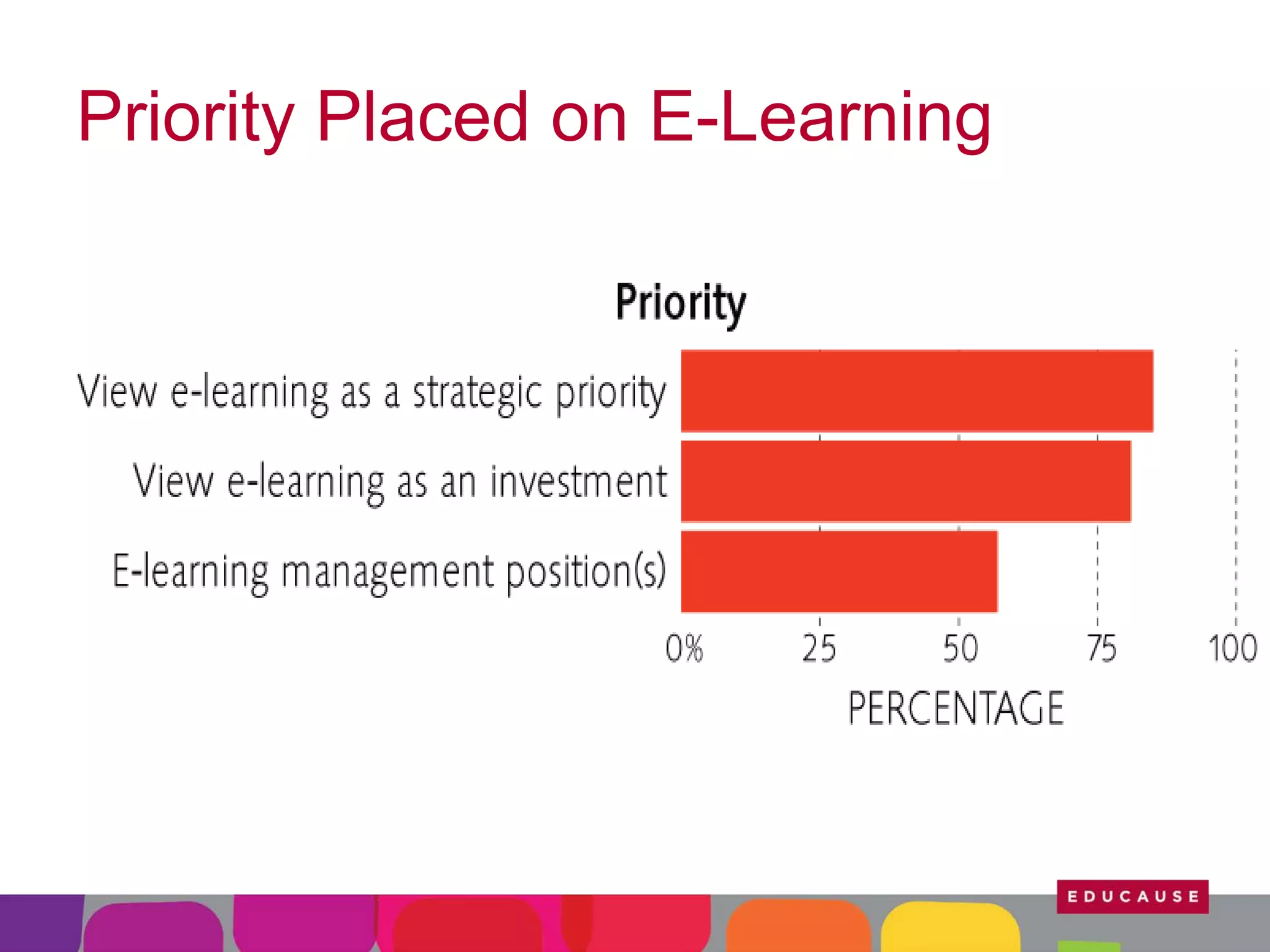
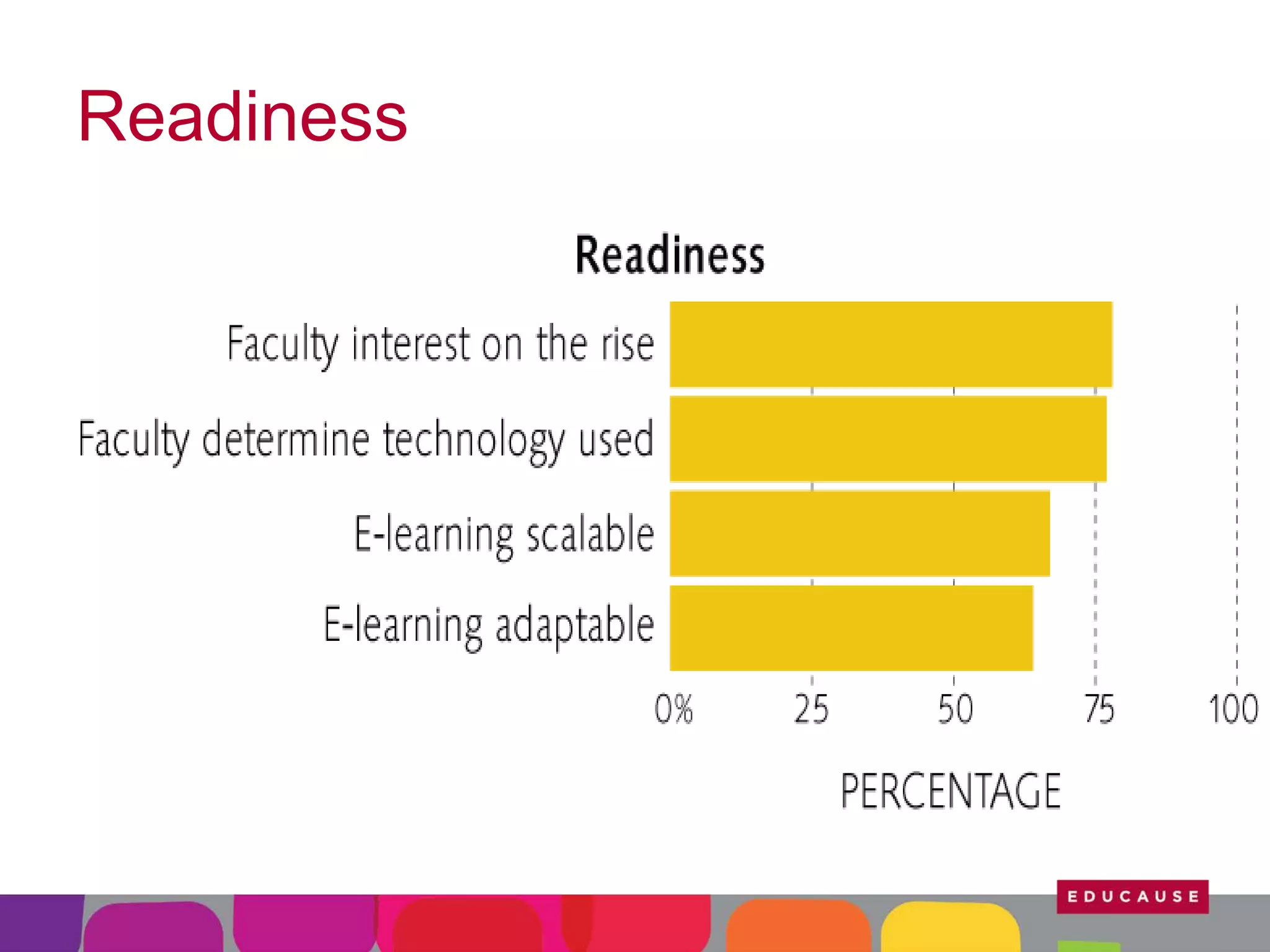
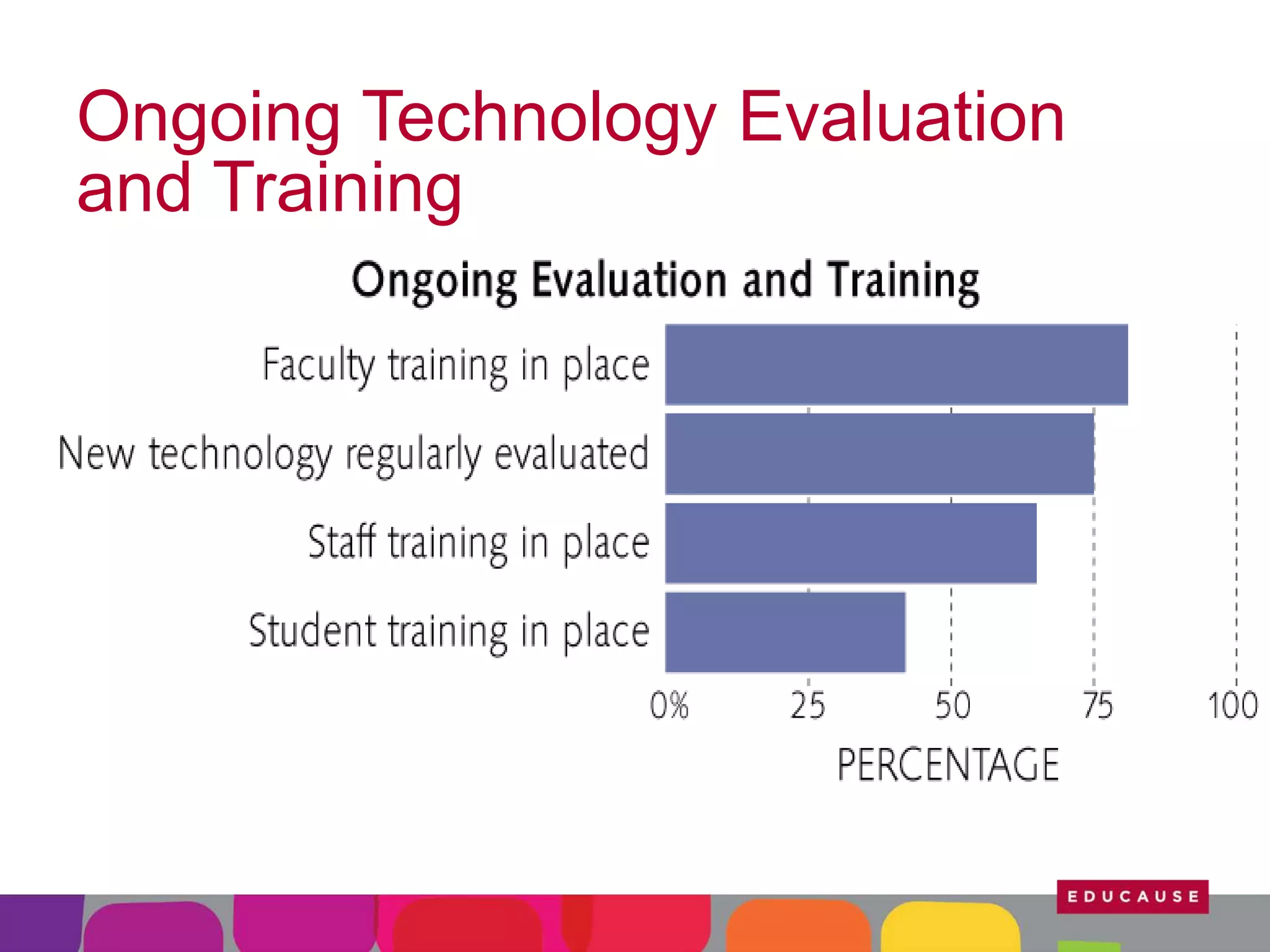
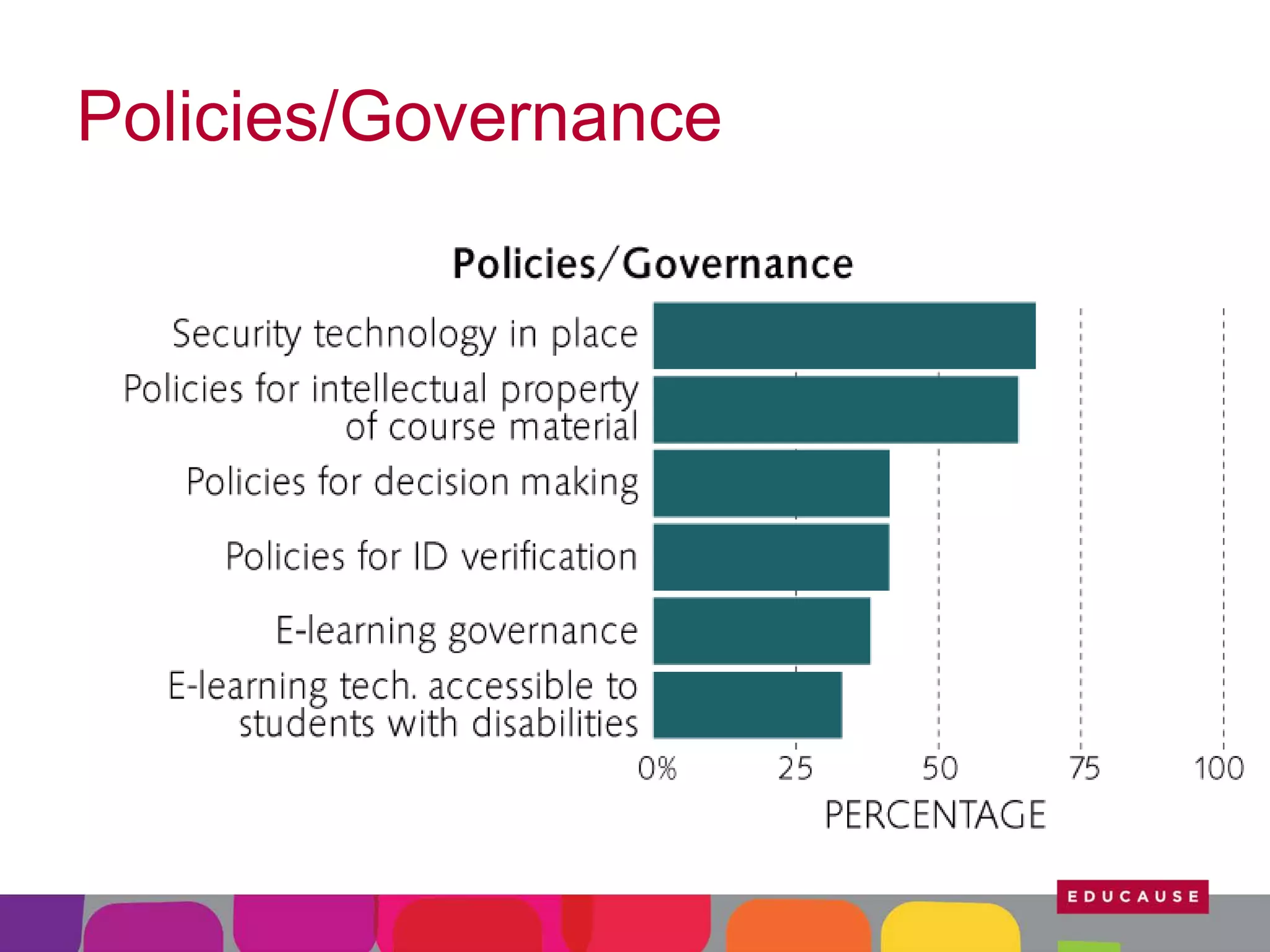
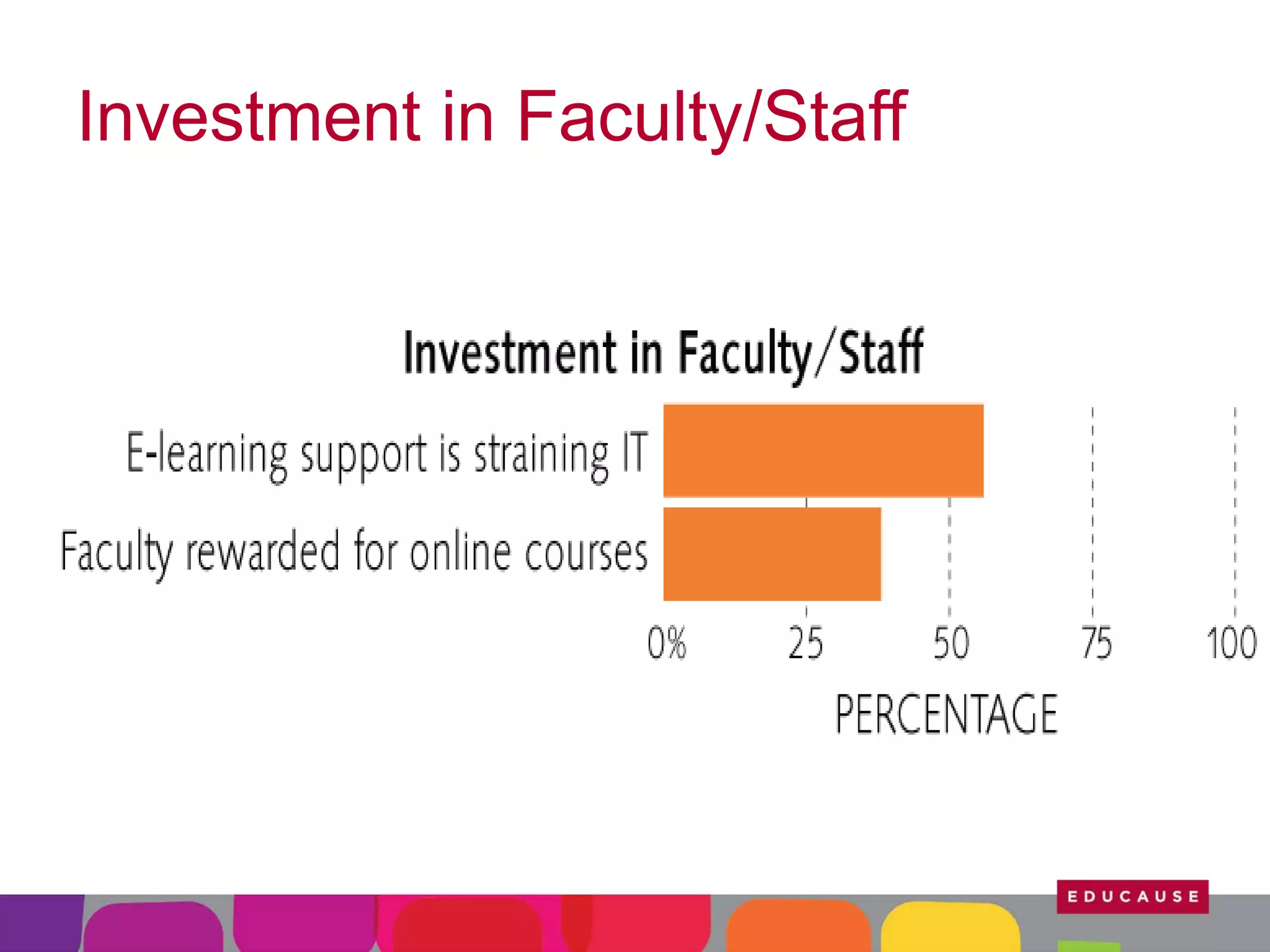
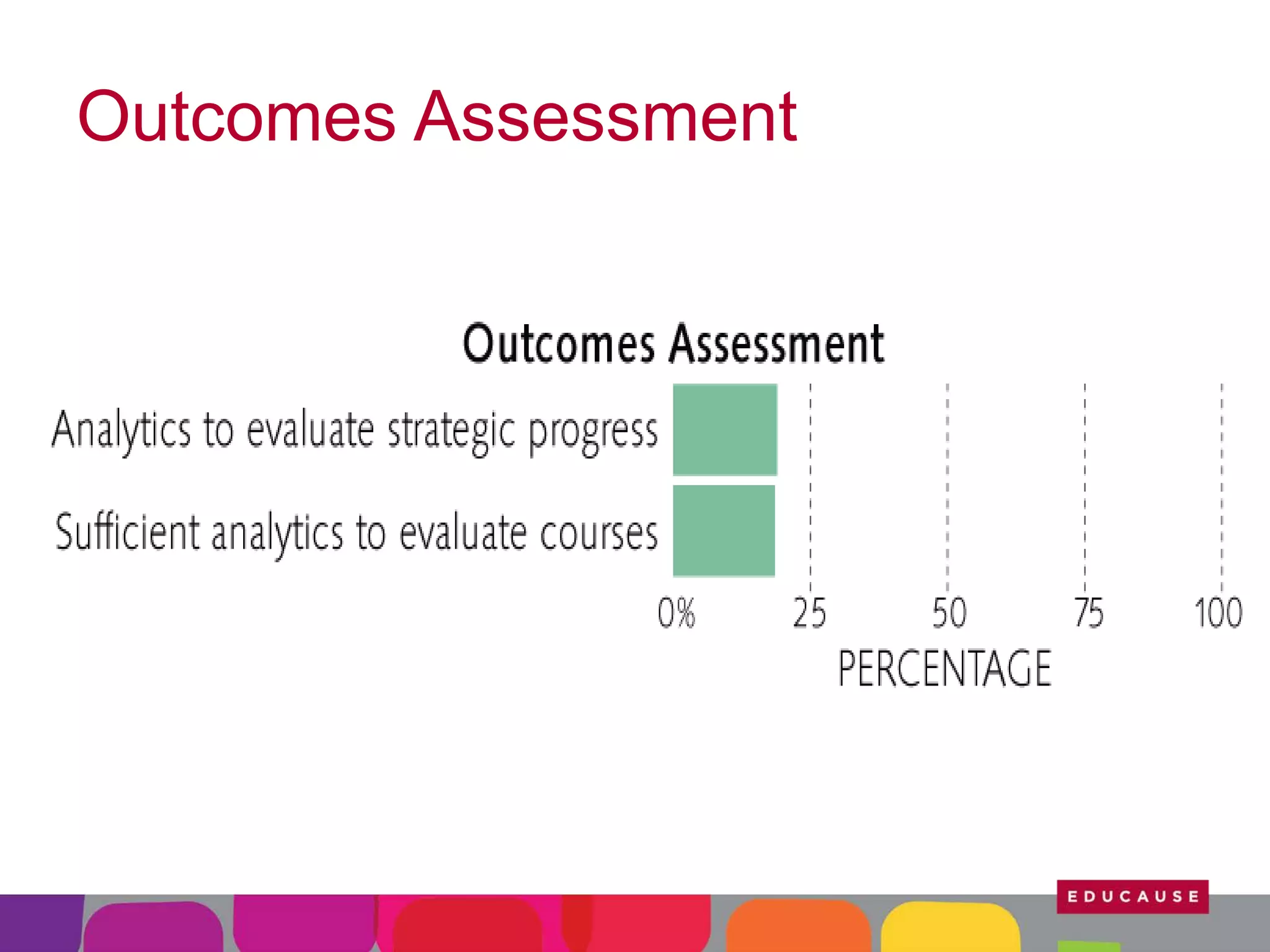
This document summarizes the state of e-learning in higher education. It finds that while most institutions are interested in e-learning, not all are prepared to develop or expand their online offerings. It also discusses the benefits of e-learning for flexibility, teaching, and learning. While online course offerings are growing, some institutions still lack resources or see online learning as not fitting their mission. The document concludes that e-learning initiatives face challenges regarding faculty skepticism, financial models, and ensuring academic quality, but that these challenges can be addressed through strategic planning and investment.