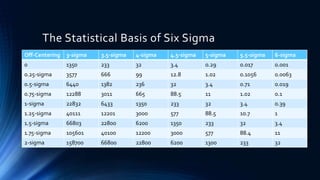
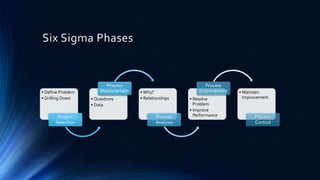
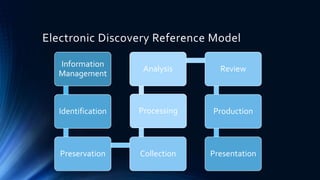
The document outlines the Six Sigma methodology and its application in improving e-discovery processes within legal contexts. It covers the relationship between e-discovery and technology, relevant legal rules, and the benefits of predictive coding to enhance efficiency and reduce errors. The document emphasizes Six Sigma's role in eliminating variations to optimize quality, flexibility, and cycle time in the e-discovery lifecycle.