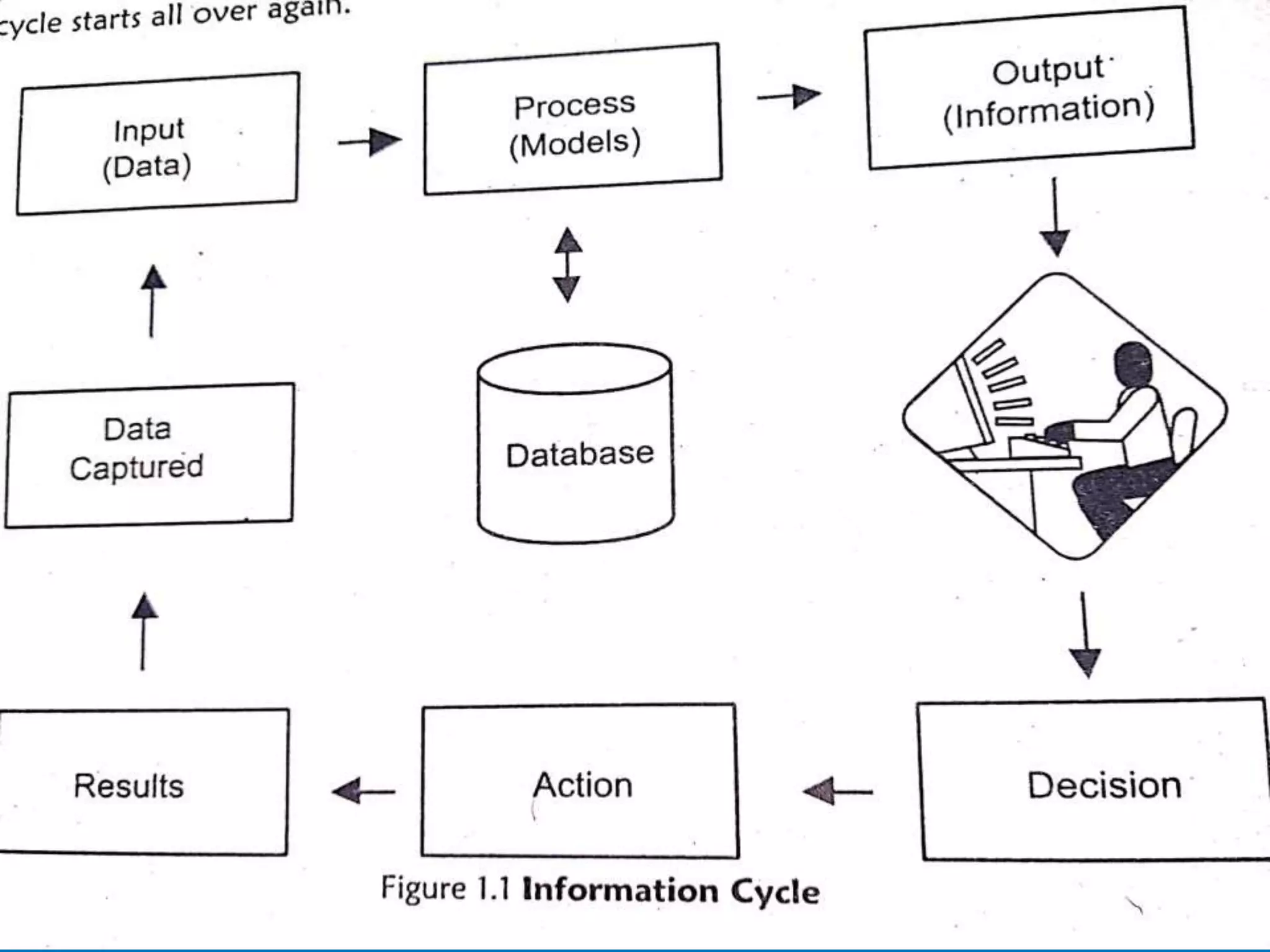
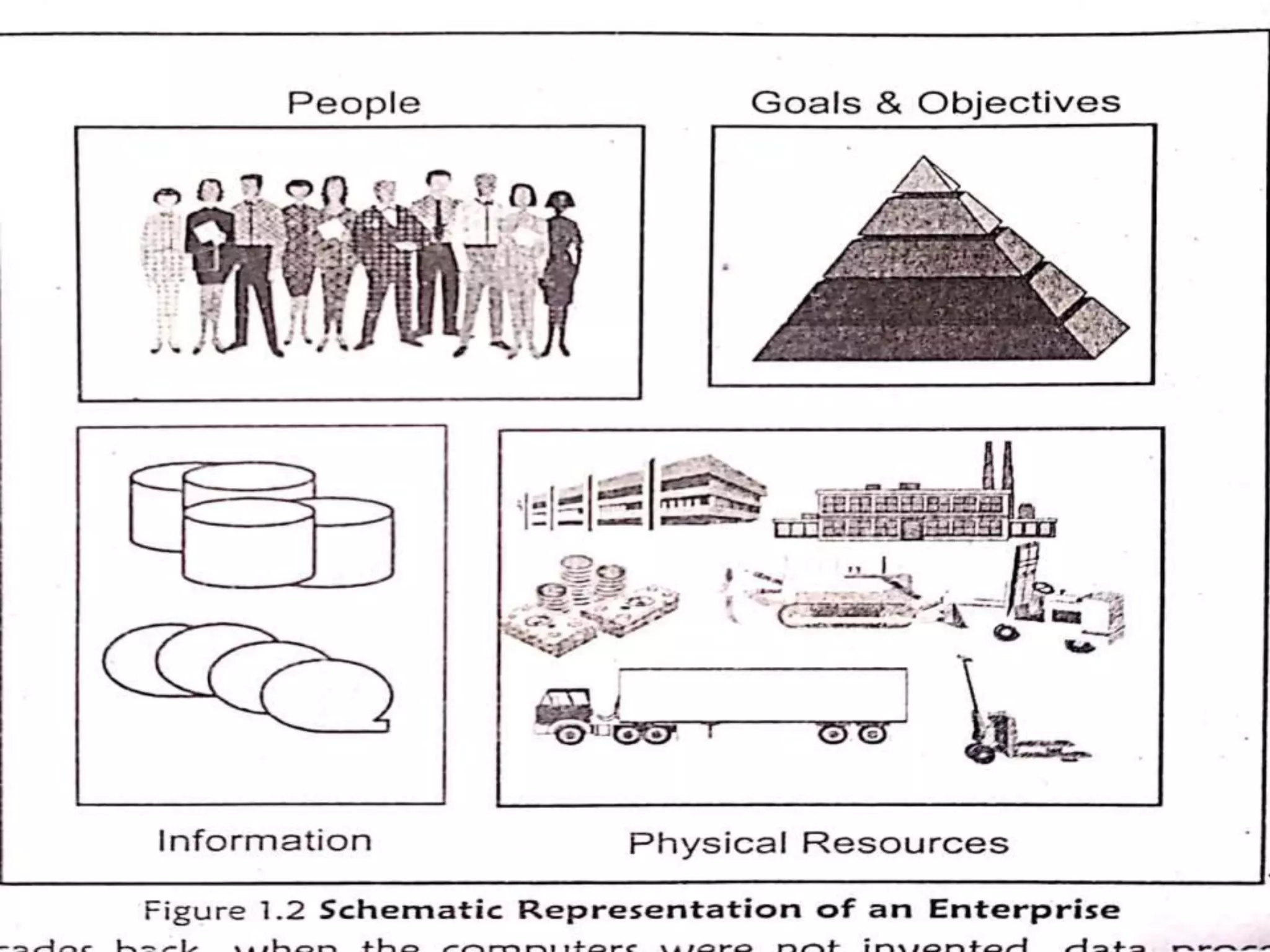
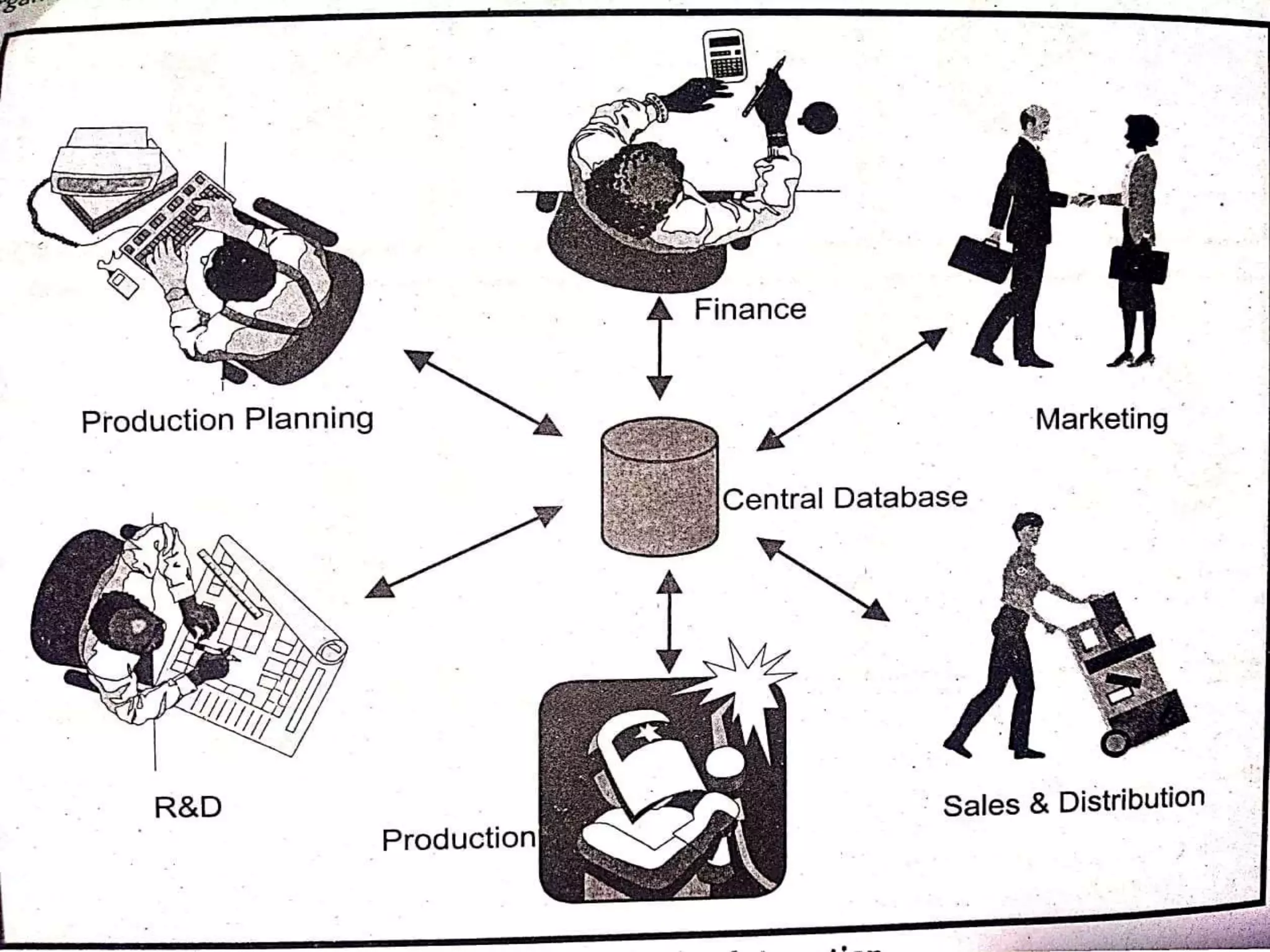
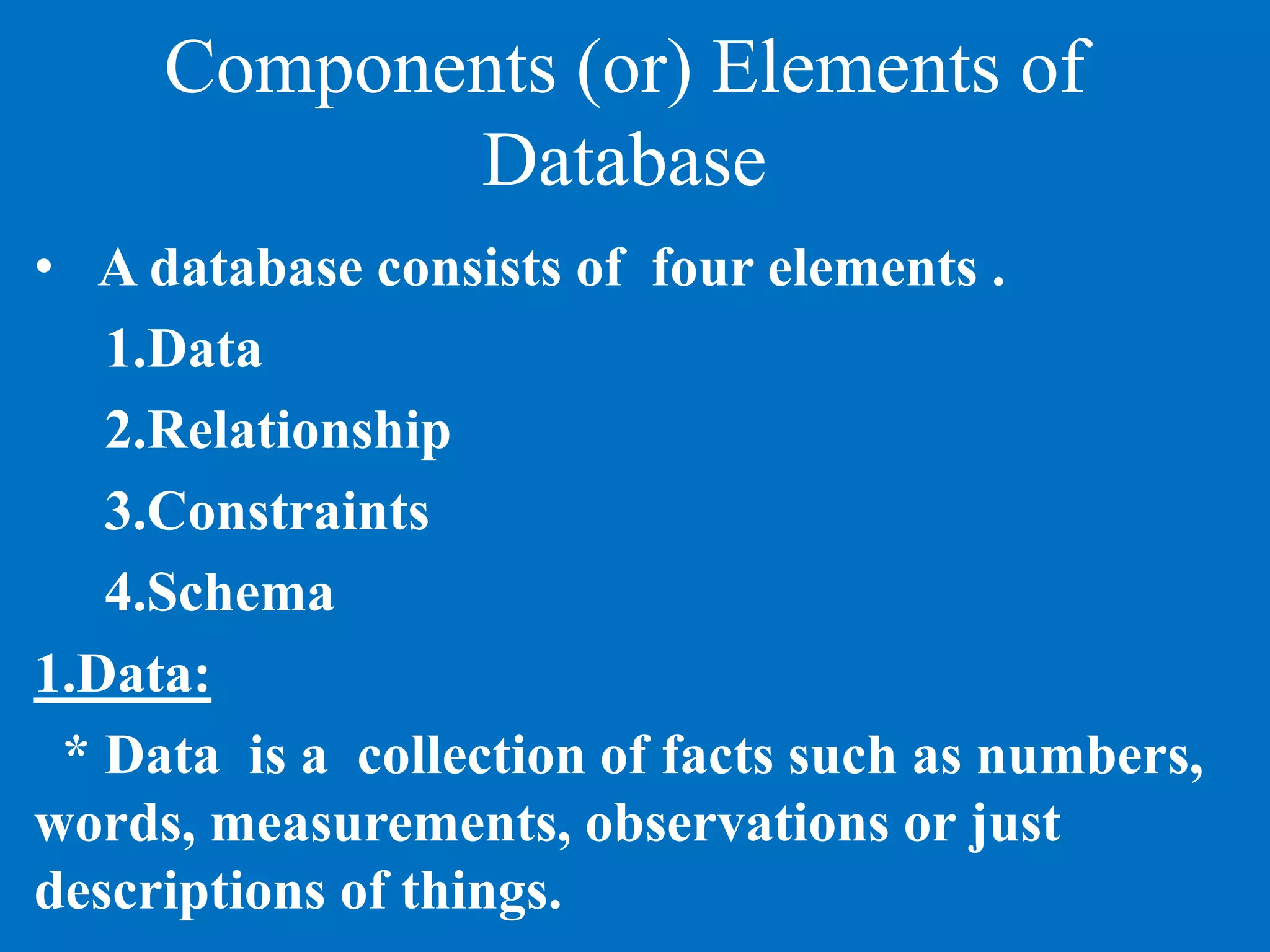
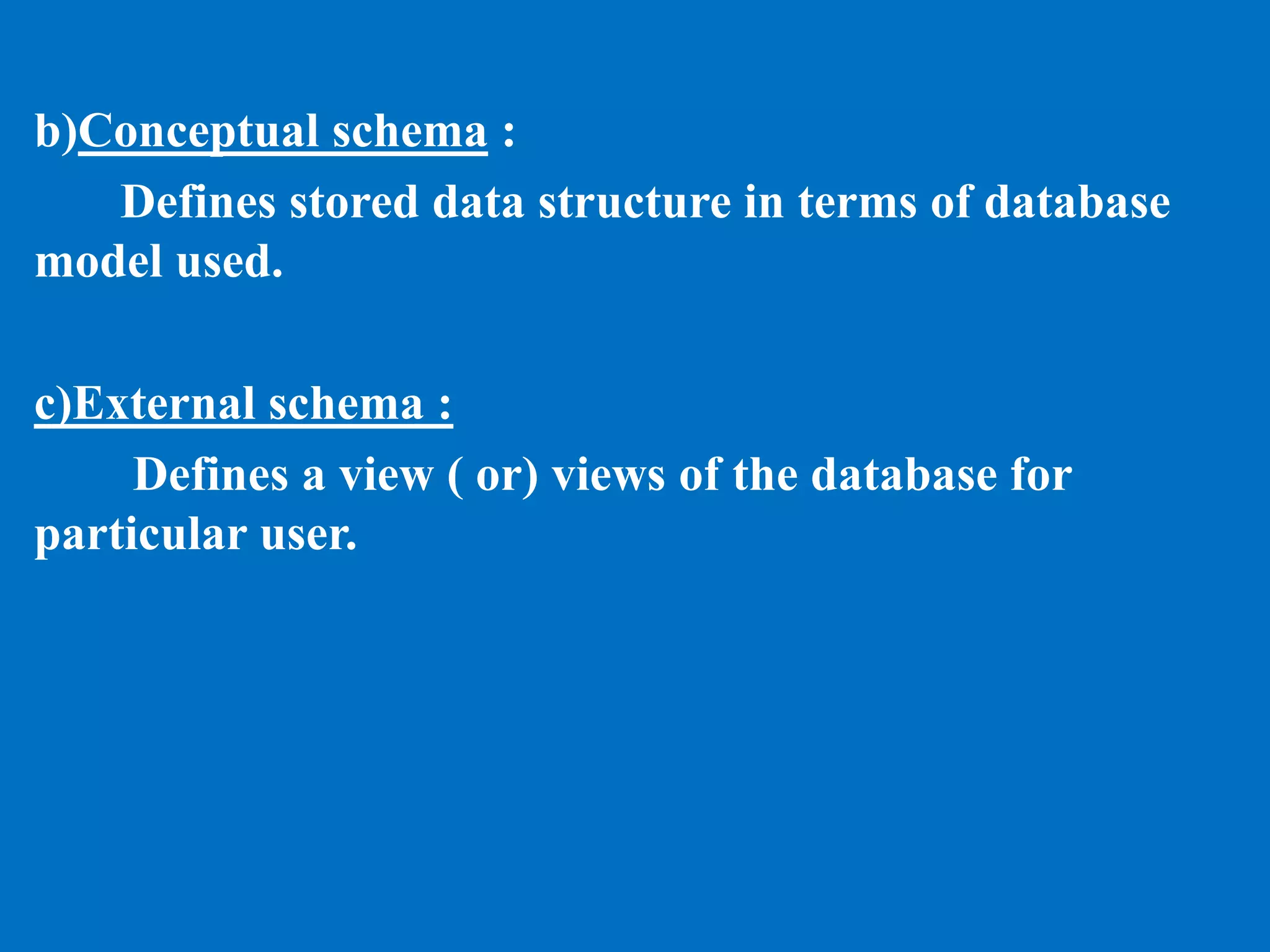
This document provides an introduction to database management systems. It discusses what data and information are, and how data is processed into meaningful information through models. Databases organize related data and provide controlled data redundancy. Historically, clay tablets, quipus, and punched cards were used to store and process data. A database manages data through its key elements - data, relationships between data, constraints on the data, and a schema that defines the organization. The database serves the information needs of an entire enterprise by centrally storing and sharing information across departments.