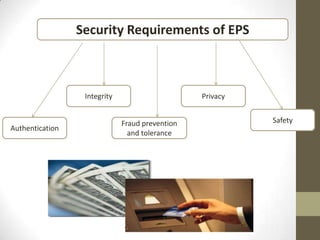
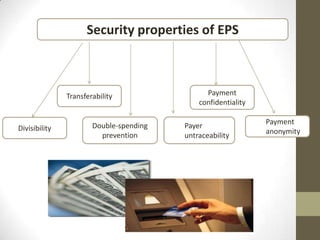
This document discusses security and trust in e-payments. It begins with an introduction on how communication technologies have led to new terms like e-commerce and e-payments. However, these new payment systems require high security to address risks from a lack of trust in online transactions.
The document then defines key terms related to e-payment security like cryptography, public key infrastructure (PKI), and digital signatures. It describes how encryption, digital signatures, and hash algorithms can establish concepts of trust and security through identification, authentication, access control and more.
Finally, the document examines specific e-payment systems and how cryptography and PKI using public/private key pairs and digital certificates can help build trust in online financial exchanges