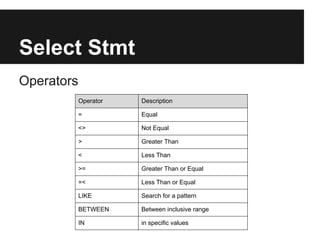
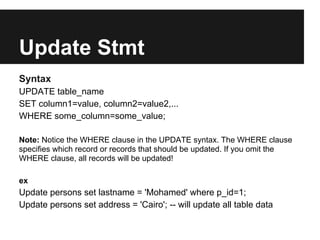
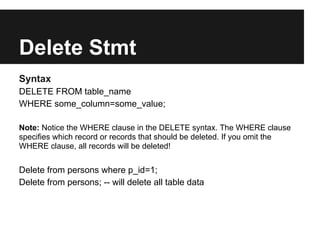
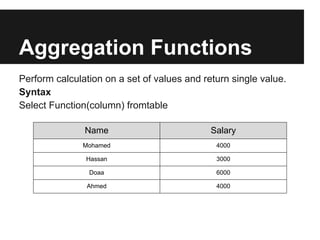
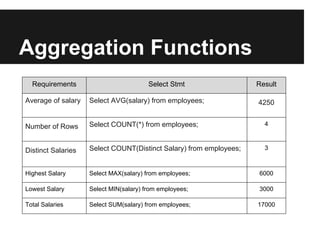
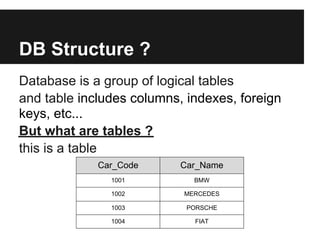
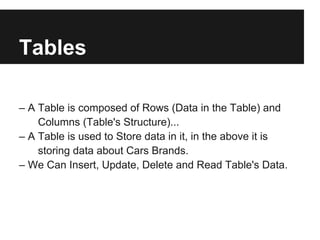
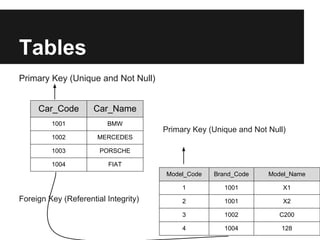
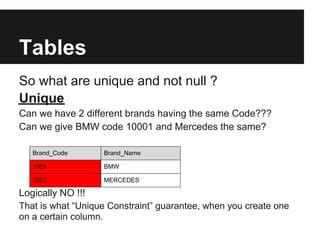
The document discusses dynamic websites using PHP with an Oracle database. It begins by defining what a relational database is and the advantages of using a database over files, including centralization of data, high performance, reduced data redundancy, better security and integrity. It then discusses database structure, explaining that a database consists of logical tables that contain columns, indexes, foreign keys etc. and that a table stores data in rows and columns. It provides an example table to demonstrate this. It further explains concepts like primary keys, unique constraints, not null constraints and foreign keys and how they maintain data integrity. The document concludes by discussing how to design the database using concepts learned and provides SQL examples to demonstrate creating, reading, updating and deleting data from














![Select Stmt
Syntax
SELECT [all|distinct] column_name(s) FROM table_name
WHERE search_condition
ex
- Select * from persons;
- Select firstname, lastname from persons;
- Select Distinct address from persons;
- Select * from persons WHERE address='Egypt';
- Select * from persons where weight > 50;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicwebsiteslec1-130315084140-phpapp02/85/Dynamic-websites-lec1-22-320.jpg)