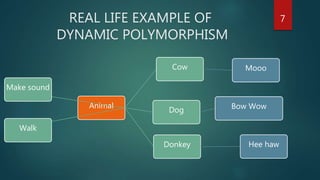
The document discusses dynamic polymorphism, highlighting how it allows objects to take on multiple forms in different contexts. It explains types of polymorphism, including compile time and run time, with a focus on virtual functions that enable function overriding. The text also covers key concepts such as abstract classes and virtual destructors, which are crucial for proper object-oriented programming in C++.