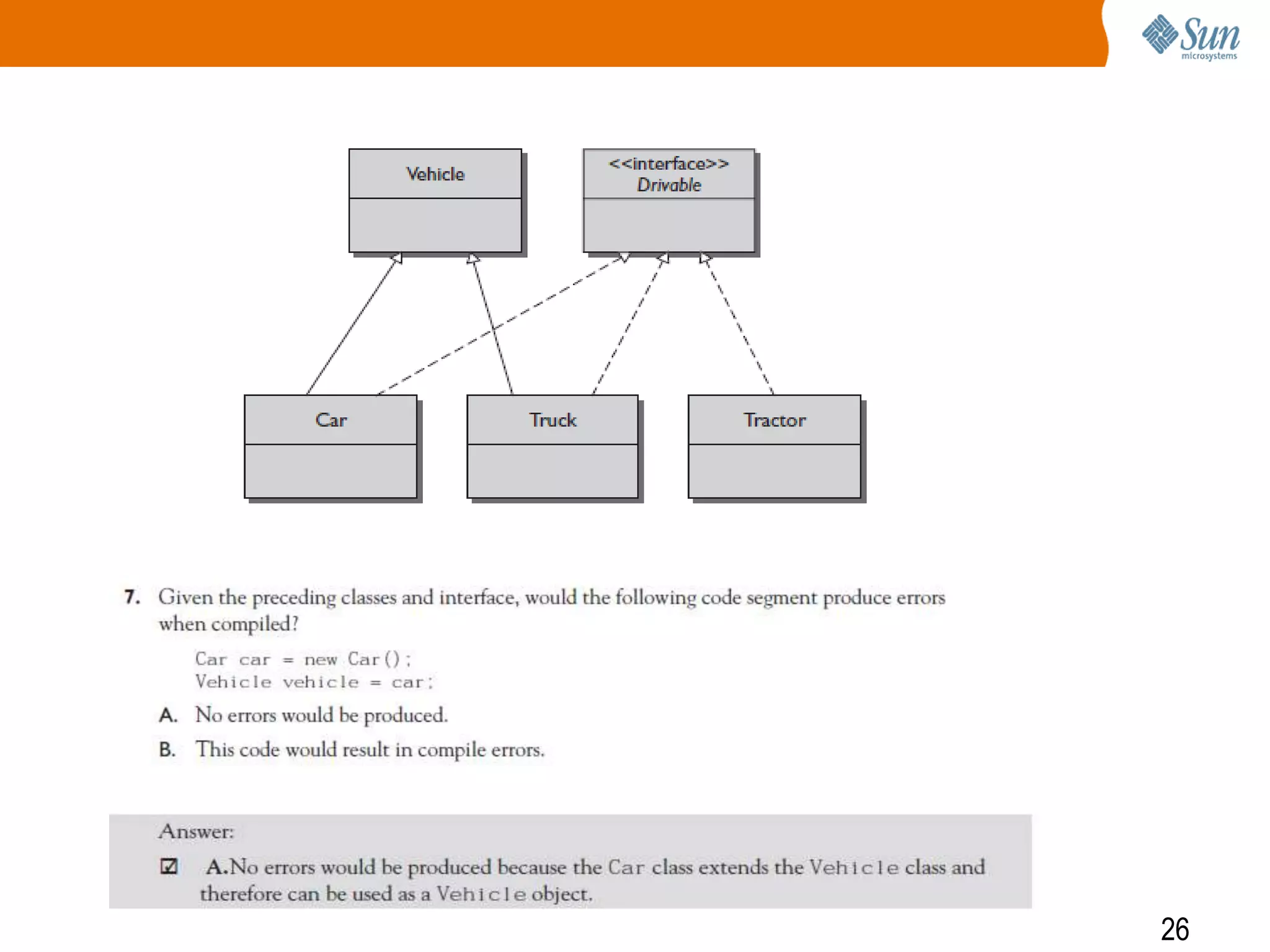
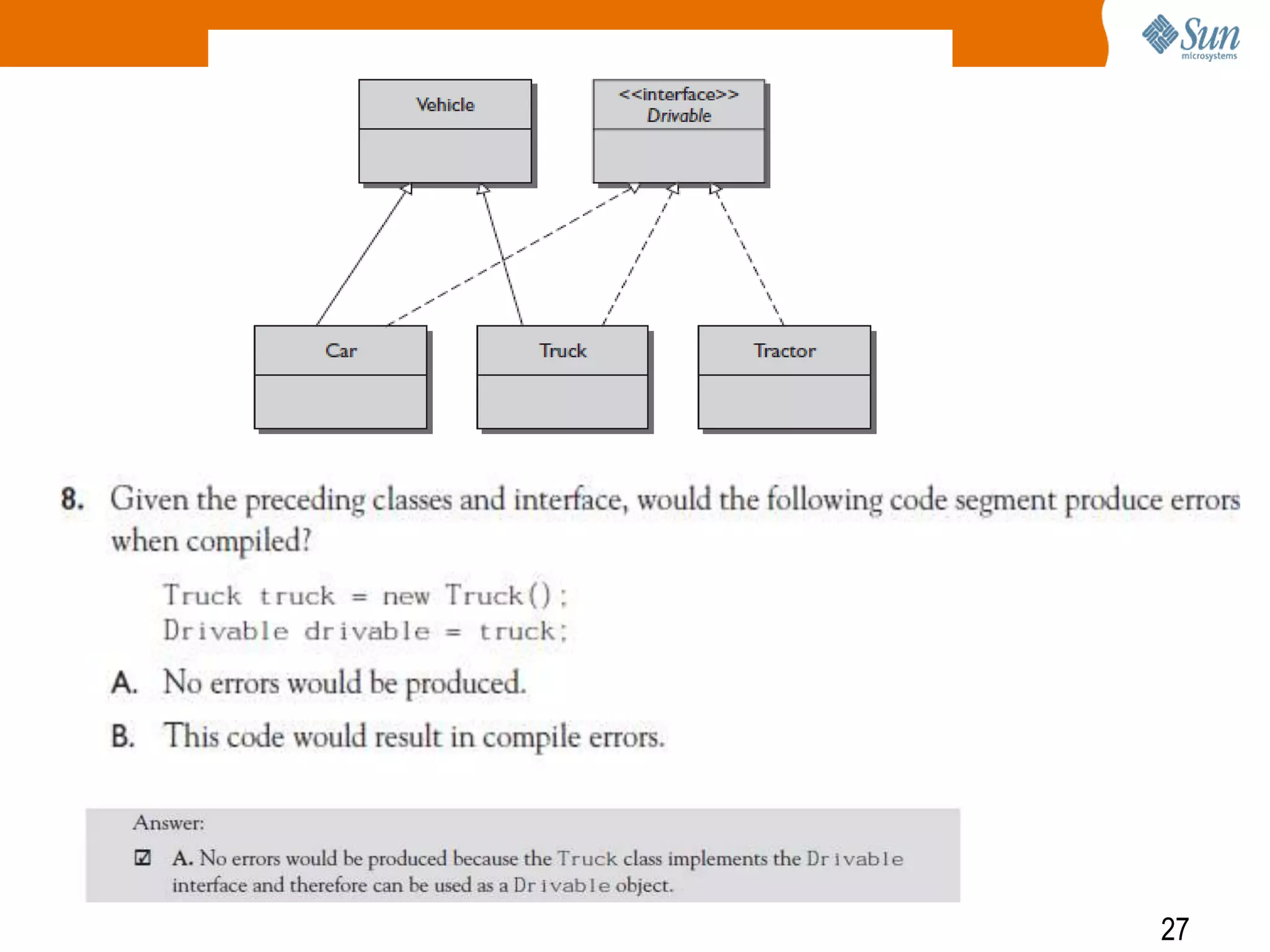
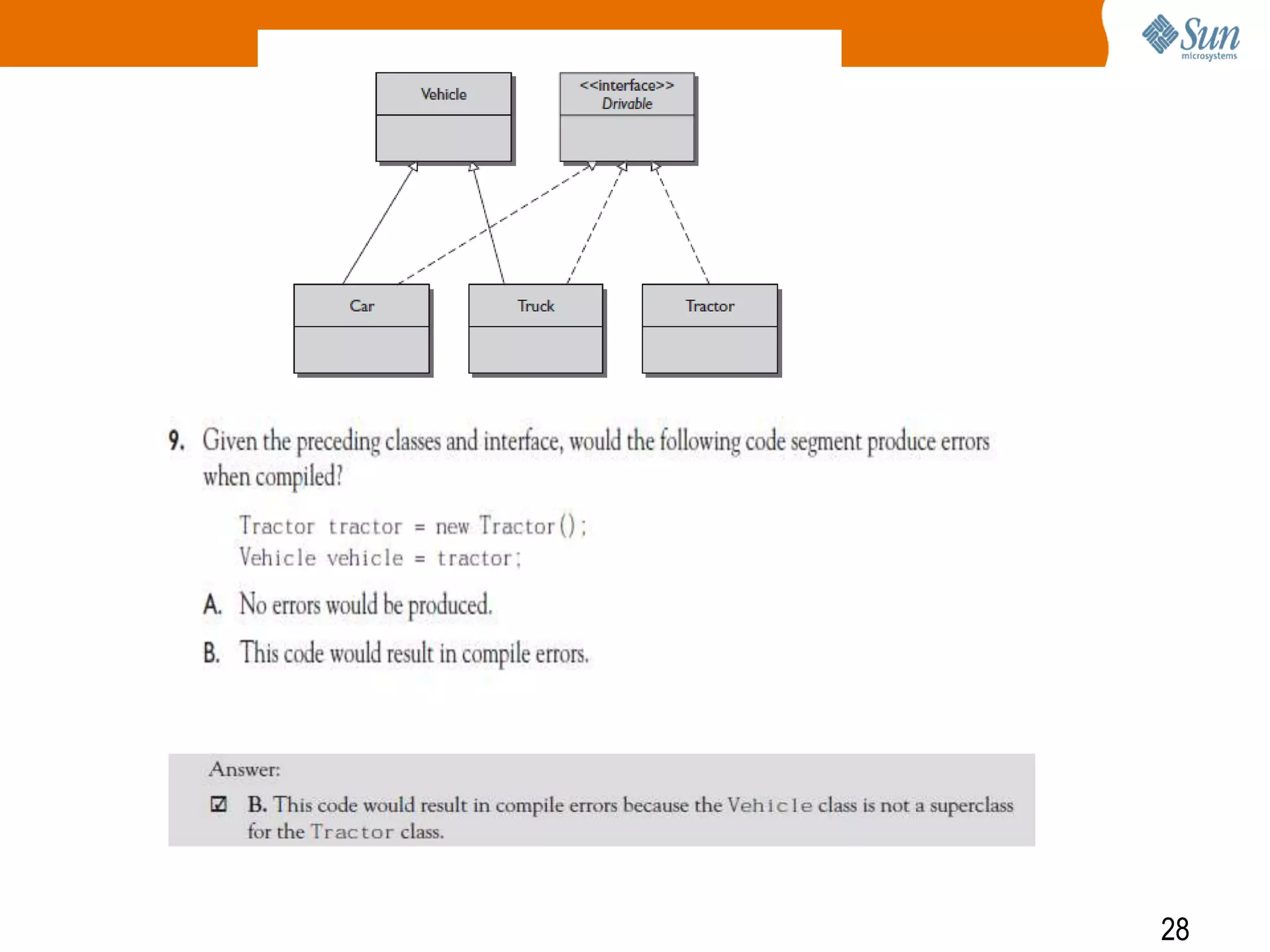
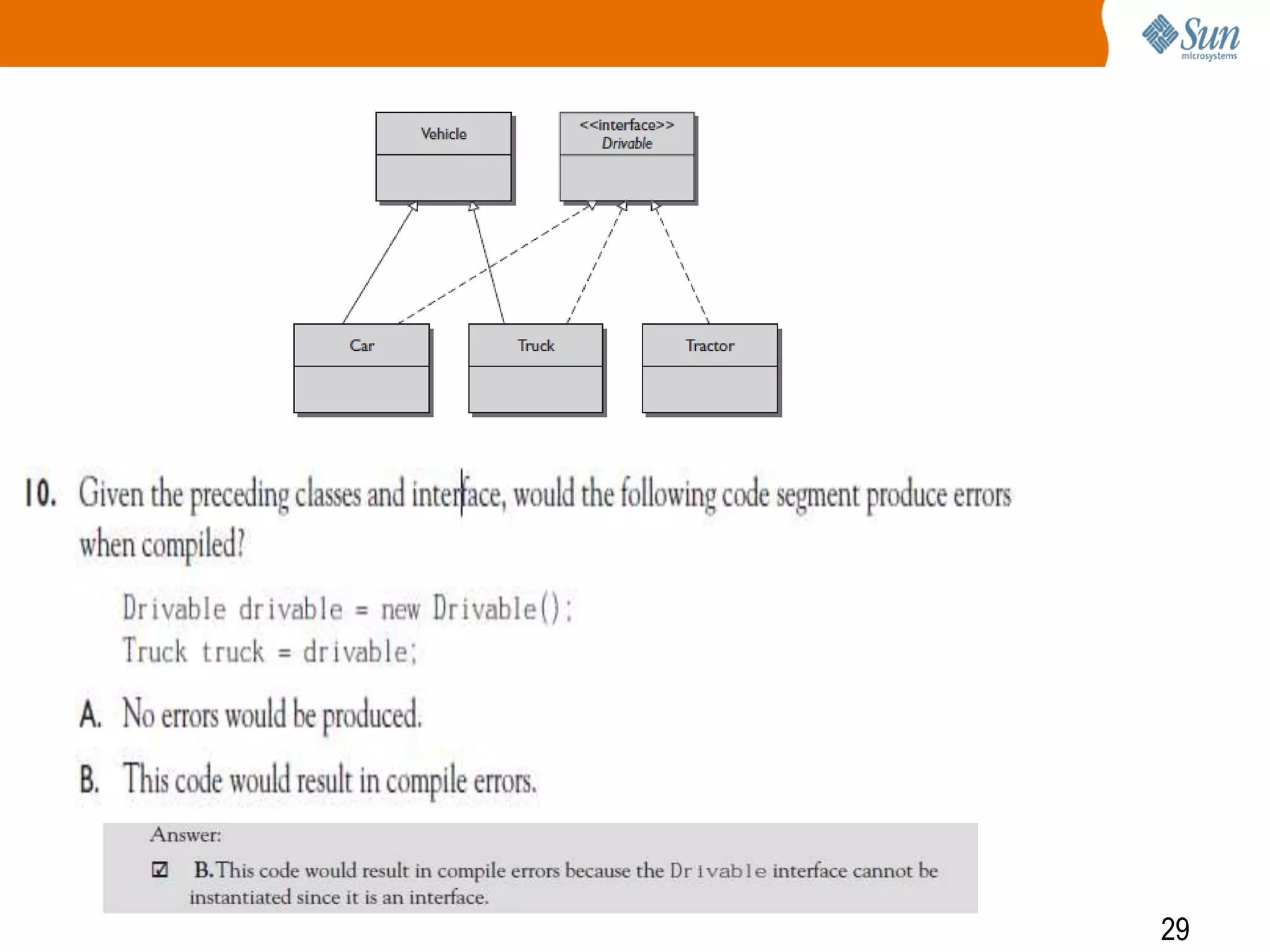
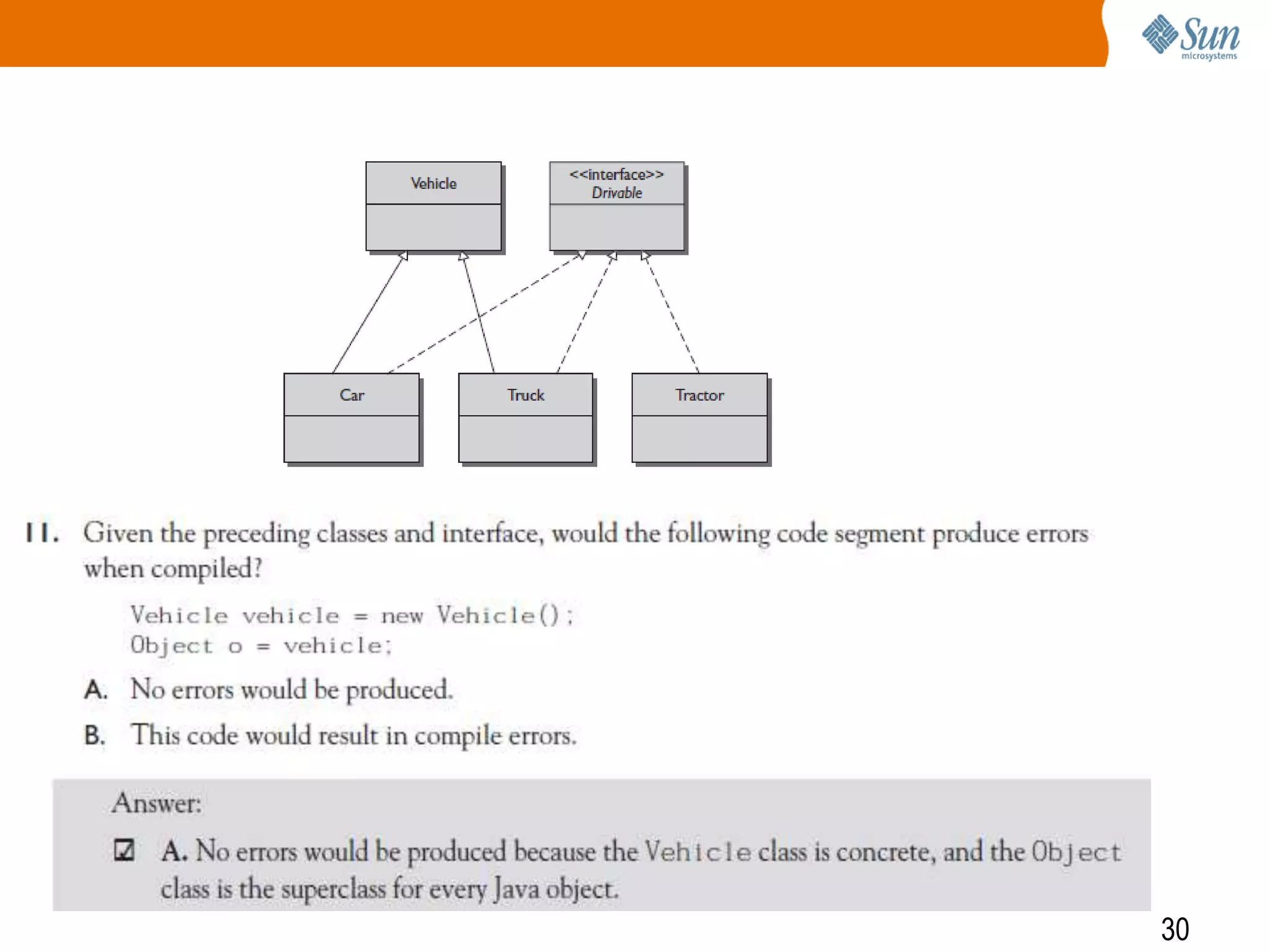
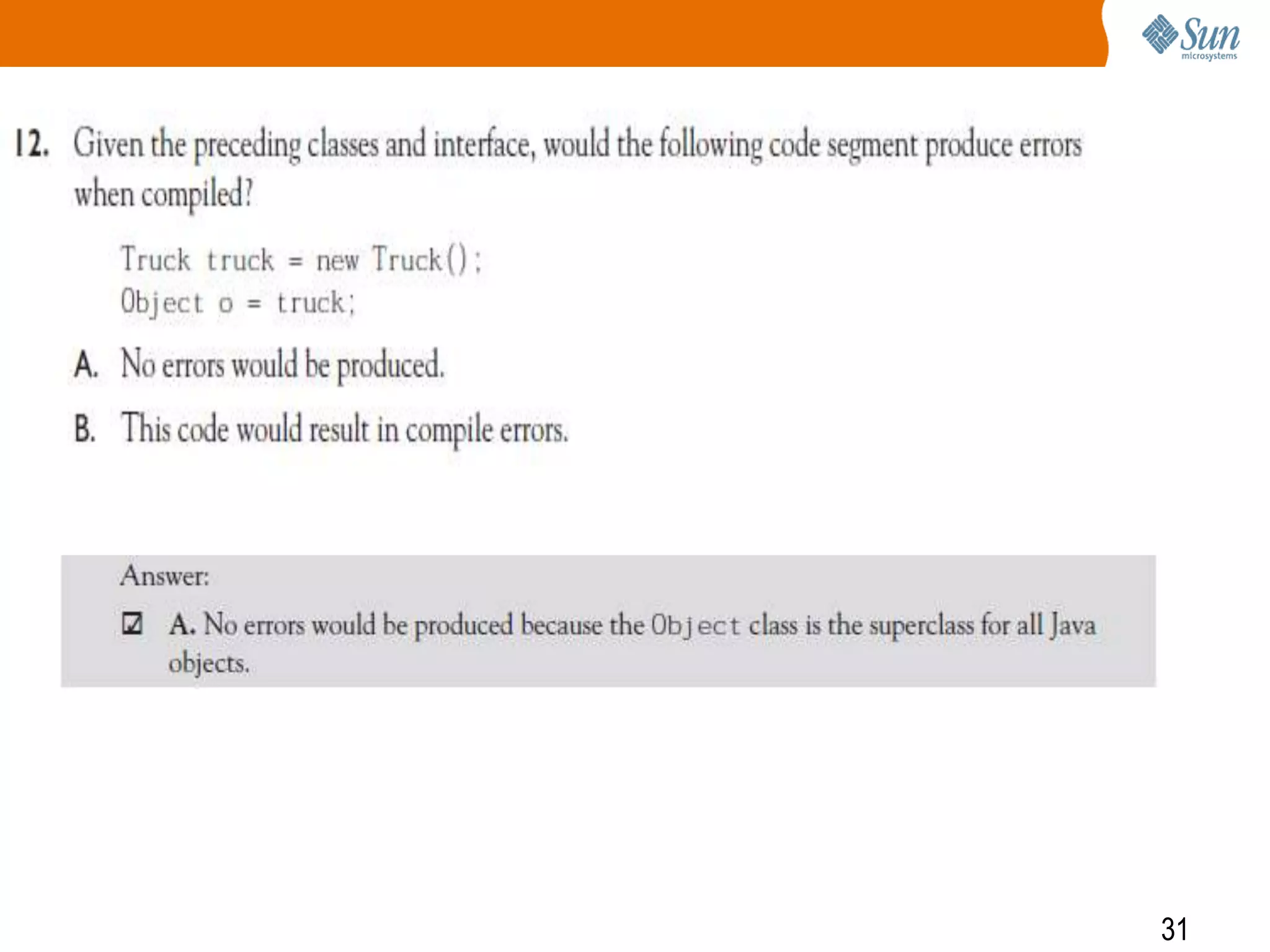
The document explains polymorphism in Java, emphasizing its ability to enable subclasses to be treated as instances of a superclass while allowing method behavior to be tailored for each subclass. It provides examples demonstrating how polymorphic behavior is achieved through method overriding and the principle of 'program to an interface.' The document also discusses the benefits of polymorphism, including code simplicity and extensibility.






![Example #1: Polymorphism
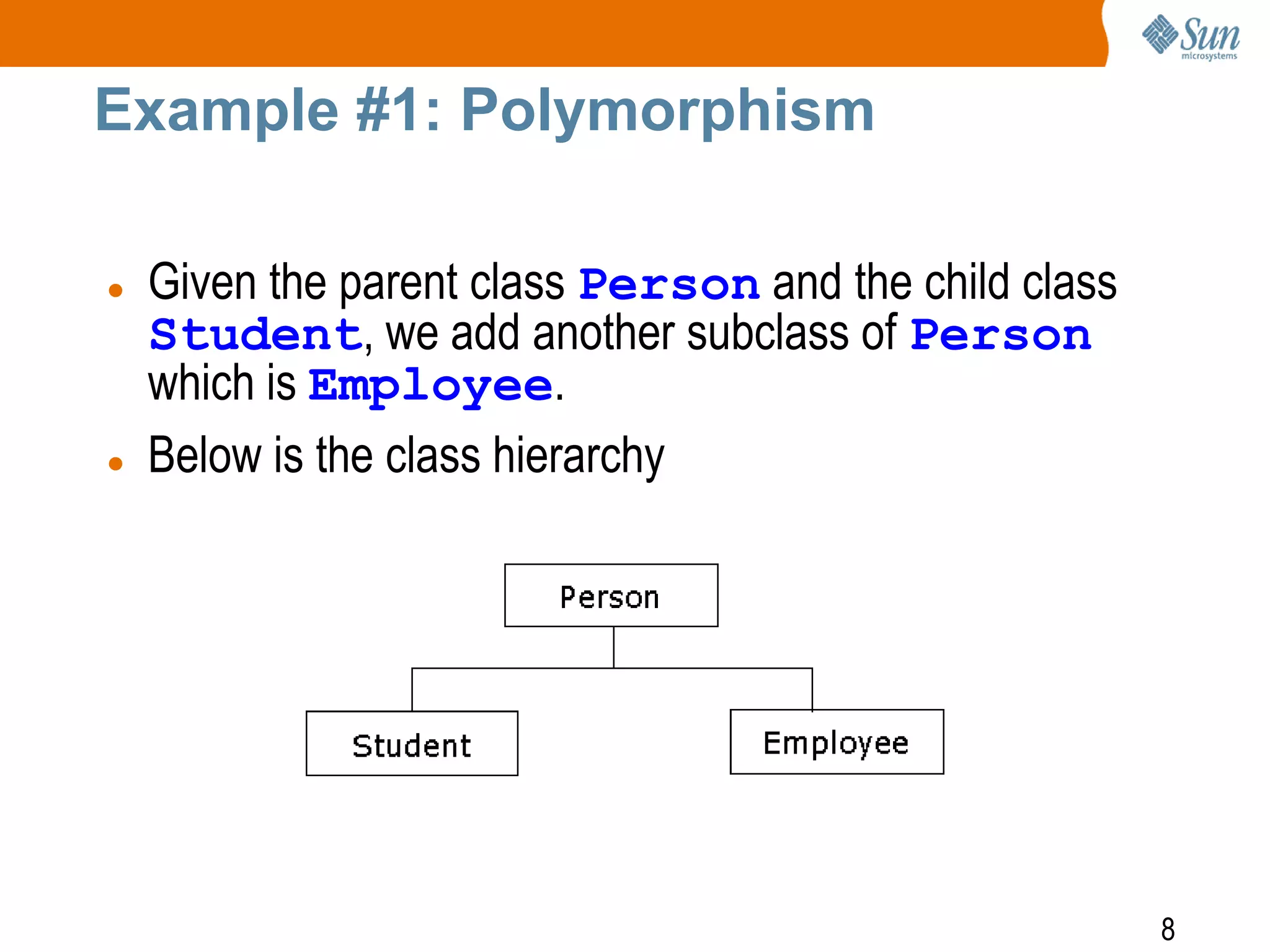
In Java, we can create a reference that is of type super
class, Person, to an object of its subclass, Student.
public static main( String[] args ) {
Student studentObject = new Student();
Employee employeeObject = new Employee();
Person ref = studentObject; // Person reference points
// to a Student object
// Calling getName() of the Student object instance
String name = ref.getName();
}
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-131111205643-phpapp02/75/Chapter8-Understanding-Polymorphism-9-2048.jpg)


![Example #1: Polymorphism
1
public static main( String[] args ) {
2
3
Student studentObject = new Student();
Employee employeeObject = new Employee();
4
5
Person ref = studentObject; //Person ref. points to a
6
7
8
// getName() method of Student class is called
String temp= ref.getName();
System.out.println( temp );
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
ref = employeeObject; //Person ref. points to an
// Student object
// Employee object
//getName() method of Employee class is called
String temp = ref.getName();
System.out.println( temp );
}
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-131111205643-phpapp02/75/Chapter8-Understanding-Polymorphism-12-2048.jpg)

![Example #2: Polymorphism
We can actually pass a reference of type Employee
and type Student to the printInformation method as
long as it is a subclass of the Person class.
public static main( String[] args ){
Student studentObject = new Student();
Employee
employeeObject = new Employee();
printInformation( studentObject );
printInformation( employeeObject );
}
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-131111205643-phpapp02/75/Chapter8-Understanding-Polymorphism-14-2048.jpg)