Embed presentation
Downloaded 88 times


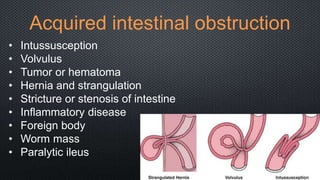




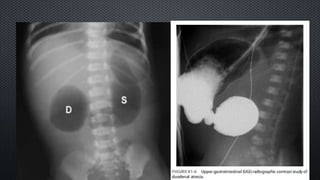


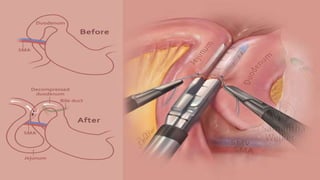


This document discusses intestinal obstruction, its causes, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. Intestinal obstruction is an interruption in the flow of intestinal contents and can be caused by congenital defects, acquired conditions like hernias or tumors, or inflammatory diseases. Patients experience abdominal distension, vomiting, absence of gas or stool, and respiratory distress. Diagnosis involves history, exam, imaging like ultrasound or X-ray, and tests. Treatment consists of IV fluids, gastric decompression, antibiotics, and surgery to remove obstructions or strictures.












