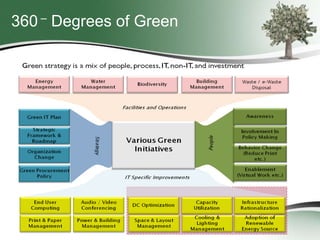
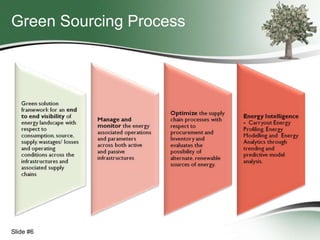
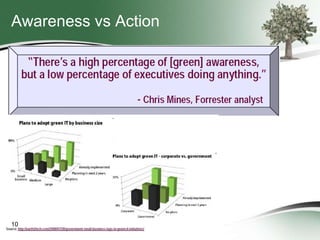
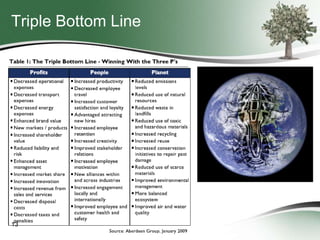
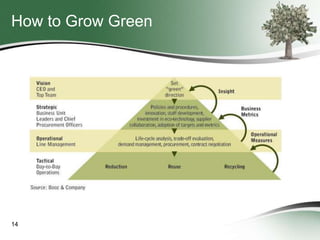
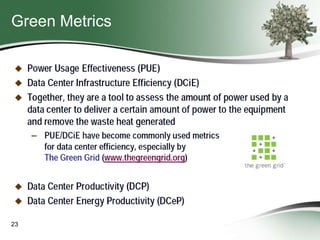
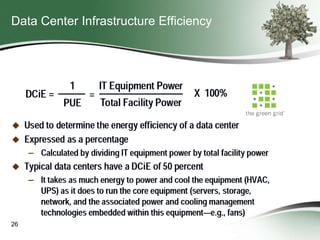
This document discusses how green sourcing can benefit businesses financially and environmentally. It defines green sourcing as purchasing goods and services that minimize environmental impacts and outlines why green outsourcing reduces costs through energy savings, lowers risks from regulations, and provides tax benefits. The document provides tips for both buyers and providers on developing green sourcing programs, asking environmental questions in requests for proposals, and marketing green strengths without greenwashing. It introduces TechNexxus as an outsourcing consulting firm that helps clients with green sourcing strategies.